Harmful Effects Of Acid Rain On The Environment – A lock (locked lock) or https:// means you are securely connected to a .gov website. Share sensitive information on official, secure websites only.
Acid rain, or acid deposition, is a broad term that includes any type of precipitation with acidic components, such as sulfuric or nitric acid that falls to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms. This could include rain, snow, fog, hail or even acidic dust.
Harmful Effects Of Acid Rain On The Environment

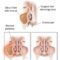
This image shows the pathway for acid rain in our environment: (1) SO2 and NOx emissions are released into the air, where (2) the pollutants transform into acidic particles that can be transported long distances. (3) These acidic particles then fall to the ground due to wet and dry deposition (dust, rain, snow, etc.) and (4) can cause adverse effects on soil, forests, streams and lakes.
The Harmful Effects Of Nitrogen Oxides
Reacts with water, oxygen and other chemicals to form sulfuric and nitric acids. These then mix with water and other materials before falling to the ground.
Acid rain is caused by natural sources such as volcanoes, most of it comes from burning fossil fuels. The major SO sources
Over long distances and across borders making acid rain a problem for everyone and not just those who live close to these sources.
. The sulfuric and nitric acids formed in the atmosphere fall to the ground mixed with rain, snow, fog or hail.
Is Deforestation The Main Cause Of Acid Rain?
Acidic particles and gases can also be deposited from the atmosphere in the absence of moisture as dry precipitation. The particles and acid gases may quickly deposit on surfaces (water bodies, vegetation, buildings) or react during atmospheric transport to form larger particles that may harm human health. When the accumulated acids are washed off a surface by the next rain, this acidic water flows over and through the ground, and can harm plants and wildlife, such as insects and fish.
The amount of acidity in the atmosphere that is deposited to the ground by dry deposition depends on the amount of rain that an area receives. For example, in desert areas the ratio of dry to wet deposition is higher than an area that receives several inches of rain each year.
Acidity and alkalinity are measured using a pH scale with 7.0 being neutral. The lower the pH of the substance (less than 7), the more acidic it is; the higher the pH of a substance (greater than 7), the more alkaline it is. Normal rain has a pH of about 5.6; it is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide (CO

) dissolves into it and forms weak carbonic acid. Acid rain usually has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4.
Explainer: What Is Acid Rain?
Policymakers, research scientists, ecologists, and modelers rely on the National Atmospheric Deposition Program’s (NADP) National Trend Network (NTN) to measure wet deposition. The NADP/NTN collects acid rain at more than 250 monitoring sites across the US, Canada, Alaska, Hawaii and the US Virgin Islands. Unlike wet deposition, dry deposition is difficult and expensive to measure. The Clean Air Status and Trends Network (CASTNET) provides dry deposition estimates for nitrogen and sulfur pollutants. CASTNET measures air concentrations at more than 90 locations.
When acid deposits are washed into lakes and streams, some can turn acidic. The Long Term Monitoring (LTM) Network measures and monitors surface water chemistry at more than 280 sites to provide valuable information on the health of aquatic ecosystems and how water bodies respond to changes in acidifying emissions and deposition acid. We and our partners use cookies to Store and/or access information on a device. We and our partners use data for personalized ads and content, ad and content measurement, audience insights and product development. An example of data being processed could be a unique identifier stored in a cookie. Some of our partners may process your data as part of their legitimate business interest without asking for consent. To view the purposes for which they believe they have a legitimate interest, or to object to this data processing, use the vendor list link below. The submitted consent will only be used for the processing of data coming from this website. If you wish to change your settings or withdraw consent at any time, the link to do so is in our privacy policy available from our home page.
Acid rain occurs when acidic gases rise into the sky and mix with the clouds, this causes the clouds to ‘absorb’ the acidic gases and when the clouds produce rain, it falls with a higher than normal level of acidity.
Rain is naturally acidic, but acid gases make it even more acidic. Acid gases are mainly caused by humans burning fossil fuels such as coal and oil; but nature also creates these gases with volcanoes.
Module 47 Photochemical Smog And Acid Rain
Alkalies are the opposites of acids; for example, toothpaste and baking powder are both alkaline. Strong alkalis can also be dangerous, such as ammonia and bleach.
The ph scale is used to measure the strength of acids and alkalis. A low ph number tells us that a substance is an acid; a high number tells us that a substance is alkaline.
Rain is usually slightly acidic, with a ph of around 5.5, if the ph of the rain is below 5.5, the rain is most likely contaminated with acid gases.

The gases that cause acid rain are sulfur and nitrogen. When these gases mix with the oxygen and water vapor in the air, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide are formed. Most of the sulfur released into the atmosphere comes from power stations; Volcanoes also produce a lot of sulfur when they erupt. Most of the nitrogen oxides come from the vehicles that people around the world travel in every day, from planes, cars and trucks.
Effects Of Air Pollution
Acid rain is a worldwide problem, when acid gases are released, they rise into the sky, and are then carried by strong winds. Acid rain in the Scandinavian countries is caused by air pollution in Britain and other European countries. In the United States, winds blow the air pollution to certain areas in Canada.
When acid rain occurs, it affects trees, lakes, buildings and agricultural land. Sometimes the rain is not very acidic and does not cause many problems, but when it is acidic, it can be very harmful to the environment.
The acid in acid rain drains important minerals from the leaves and soil, and is very bad for plants, trees and agricultural land. If the soil is alkaline; when acid rain falls on it the acid becomes neutral so the plants are not affected much, but if the soil is slightly acidic, it can be disastrous. When enough acid rain falls into lakes and rivers, almost all life can die out in a relatively short period of time depending on the mass of water.
People are affected when we breathe in air pollution, this can cause breathing problems, and even cancer. Drinking water contaminated with acid rain can cause brain damage over time.
Acid Rain Can Damage Your Home And Here’s What You Can Do About It
Acid rain also eats into stone and metal, so buildings can be affected by corrosion over time, especially sandstone and limestone which are examples of soft stones. Acid deposition refers to acid and acidified substances, with include sulfuric and nitric and ammonium acids, which are derived from the atmosphere. emissions of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and ammonia, respectively. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are mainly released by burning fossil fuels, while ammonia emissions are mainly related to agricultural activities. Atmospheric deposition delivers acids and acidifying compounds to the Earth’s surface, and adverse ecological impacts occur mostly in sensitive regions downwind of elevated emissions in eastern North America, northern and central Europe and southern China. Foliage is affected by acid deposition, and forest soils have changed by depleting available calcium and magnesium and increasing concentrations of dissolved inorganic aluminum in soil waters, affecting tree health. Acidic deposition has also harmed water quality in eastern North America and Europe by reducing pH levels (i.e. increasing acidity) and acid neutralizing capacity, and increasing dissolved inorganic aluminum concentrations. Many surface waters in acid-sensitive regions affected by acid deposition show chronic and/or episodic (i.e., short-term) acidification that has reduced the species diversity and abundance of aquatic life. Most of the attention was focused on fish, but an entire food web was negatively affected. In North America and Europe recent reductions in sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions have reduced acid deposition and improved surface water quality somewhat. However, recovery of forest soils and biota has generally declined. In this chapter the effects of acid deposition will be illustrated using examples from research conducted at the Hubbard Stream Ecosystem Study.
For over five decades, HBEF research has provided insight into the effects of air pollution on the structure and function of ecosystems. Note that an acid deposit was first identified in North America at Hubbard Brook, NH (Likens et al., 1972). When it was first recognized in the 1960s and 1970s, acid deposition was viewed as a simple problem that was limited in scope. It is now clear that acids and acidifying compounds enter largely isolated, unmanaged ecosystems from long-range atmospheric transport and deposition. These air pollutants
Harmful effects of styrofoam on the environment, harmful effects of plastic on the environment, harmful effects of pesticides on the environment, harmful effects of acid, harmful effects of methane on the environment, harmful effects of herbicides on the environment, why is acid rain harmful to the environment, how is acid rain harmful to the environment, what are the effects of acid rain on the environment, harmful effects of radiation on the environment, harmful effects of acid rain, effects of acid rain on the environment