What Body System Is The Gallbladder In – In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before being released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies below the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary widely among animal species. Via the common hepatic duct, it receives and stores the bile produced by the liver and passes it through the common bile duct to the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats.
The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, which are formed by a substance that cannot be dissolved—usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a breakdown product of hemoglobin. These can cause severe pain, especially in the upper right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated by removing the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, an inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including gallstones, infection, and autoimmune disease.
What Body System Is The Gallbladder In

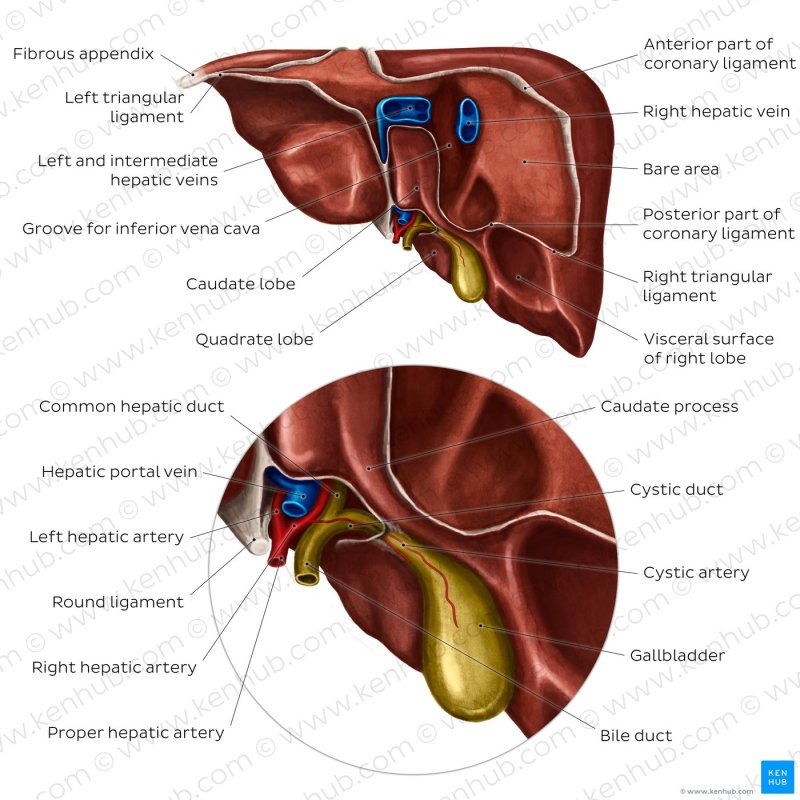
The gallbladder is a hollow gray-blue organ that lies in a shallow depression below the right lobe of the liver.
Claire Nielsen: Gallbladder Plays Huge Role In Our Digestive Health
In adults, the gallbladder measures approximately 7 to 10 cm (2.8 to 3.9 in) in length and 4 cm (1.6 in) in diameter when fully expanded.
The gallbladder is divided into three parts: the base, the body and the neck. The fundus is a rounded base, angled to face the abdominal wall. The body lies in a depression on the surface of the lower liver. The neck narrows and continues with the cystic duct, which is part of the biliary tree.
The gallbladder fossa, against which the fundus and body of the gallbladder lie, is located below the junction of the hepatic segments IVB and V.
The cystic duct joins with the common hepatic duct to become the common bile duct. At the junction of the neck of the gallbladder and the cystic duct, there is a protrusion of the wall of the gallbladder that forms a mucosal fold known as “Hartmann’s pouch”.
Gallbladder Cancer Treatment
The lymphatic drainage of the gallbladder follows the cystic node located between the cystic duct and the common hepatic duct. Lymph from the lower part of the organ drains into the lower liver lymph nodes. All the lymph finally drains into the celiac lymph nodes.
The wall of the gallbladder consists of several layers. The innermost surface of the gallbladder wall is lined with a single layer of columnar cells with a brushlike border of microvilli that closely resemble intestinal absorptive cells.
Beneath the epithelium is the lower lamina propria, the muscular layer, the outer perimuscular layer and the serosa. Unlike other parts of the intestinal tract, the gallbladder does not have a muscularis mucosae and the muscle fibers are not arranged in different layers.

The mucosa, the inner part of the gallbladder wall, consists of a lining of a single layer of columnar cells, with the cells having small hairy appendages called microvilli.
Anatomy Of The Digestive System
The muscle layer lies under the mucous membrane. It is formed by smooth muscles, with fibers lying in longitudinal, oblique and transverse directions and not arranged in separate layers. Muscle fibers here contract to expel bile from the gallbladder.
A peculiarity of the gallbladder is the presence of Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses, deep protrusions of the mucous membrane that can extend through the muscle layer and indicate adomyomatosis.
The outer layer of the fundus of the gallbladder and the surfaces not in contact with the liver are covered by a thick serosa that is exposed to the peritoneum.
Rarely, two or three gallbladders may coexist, either as separate bladders draining into the cystic duct or sharing a common branch draining into the cystic duct. In addition, the gallbladder may not form at all. There may also be gallbladders with two slits separated by a septum. These abnormalities are unlikely to affect performance and are generally asymptomatic.
The Amazing Gallbladder| Dr. Berg
The location of the gallbladder relative to the liver can also vary, with documented variations including gallbladders found within,
Above, on the left side, behind and separate or hanging on the liver. Such variants are very rare: from 1886 to 1998, only 110 cases of left-sided liver were reported in the scientific literature, or less than one per year.
An anatomical change known as a Phrygian cap may occur, which is a harmless fold at the base, named for its resemblance to a Phrygian cap.

Early in development, the human embryo has three germ layers and rests on the embryonic yolk sac. During the second week of embryogenesis, as the embryo grows, it begins to surround and develop parts of this sac. The developed parts form the basis of the gastrointestinal tract of the adult. Sections of this foregut begin to differentiate into organs of the gastrointestinal tract, such as the esophagus, stomach, and intestines.
What Is Gallbladder Cancer?
During the fourth week of embryological development, the stomach rotates. The stomach, which originally lay in the middle of the embryo, turns so that its body is on the left side. This rotation also affects the part of the gastrointestinal tract just below the stomach, which will then become the duodenum. By the fourth week, the developing duodenum begins to give off a small bump on its right side, the hepatic diverticulum, which will then become the biliary tree. Just below this is another outlet known as a cystic diverticulum, which will eventually develop into a gallbladder.
1. Bile ducts: 2. Intrahepatic bile ducts, 3. Left and right hepatic ducts, 4. Common hepatic duct, 5. Cystic duct, 6. Common bile duct, 7. Ampulla of Vater, 8. Large duodenal papilla
The main functions of the gallbladder are to store and concentrate bile, also called bile, which is needed to digest fats in food. Bile produced by the liver flows through small vessels into the larger hepatic ducts and finally through the cystic duct (parts of the biliary tree) into the gallbladder where it is stored. The gallbladder stores 30 to 60 milliliters (1.0 to 2.0 US fl oz) of bile at a time.
When food containing fat stimulates the digestive tract, it stimulates the secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK) from the I cells of the duodenum and jejunum. In response to cholecystokinin, the gallbladder contracts rhythmically and releases its contents into the common bile duct, which eventually drains into the duodenum. Bile emulsifies fats in partially digested food and thus helps in their absorption. Bile is mainly composed of water and bile salts, but it also acts as a means of removing bilirubin, a product of hemoglobin metabolism, from the body.
Liver And Gallbladder: Anatomy, Location And Functions
Bile secreted by the liver and stored in the gallbladder is not the same as bile secreted by the gallbladder. During the storage of bile in the gallbladder, it is concentrated 3-10 times
By removing some water and electrolytes. This is due to the active transport of sodium and chloride ions
Through the gallbladder epithelium, which creates an osmotic pressure that also causes reabsorption of water and other electrolytes.

Gallbladder function appears to be protective against carcinogenesis, as indicated by observations that removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) increases the subsequent risk of cancer. For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis of eighty studies found that cholecystectomy adversely affects the risk of right colon cancer.
Human Internal Digestive Organ Gallbladder Anatomy Stock Photo By ©magicmine 323016058
Another rectal study reported a significantly increased overall cancer risk, including an increased risk of several different types of cancer, after cholecystectomy.
Most gallstones do not cause symptoms, as the stones remain in the gallbladder or are passed through the biliary system.
If a stone blocks the gallbladder, inflammation known as cholecystitis can occur. If the stone is retained in the biliary system, jaundice may occur; if a stone blocks the pancreatic duct, pancreatitis can occur.
Certain medications may be used, such as ursodeoxycholic acid; lithotripsy, a non-invasive mechanical procedure to break up stones, may also be used.
Anatomy For Radiology: Abdomen
Known as cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder is usually caused by obstruction of the duct with gallstones, which is known as cholelithiasis. Blocked bile builds up and pressure on the gallbladder wall can cause the release of substances that cause inflammation, such as phospholipase. There is also a risk of bacterial infection. An inflamed gallbladder is likely to cause sharp and localized pain, heat, and swelling in the upper right corner of the abdomen and may have a positive Murphy’s sign. Cholecystitis is often treated with rest and antibiotics, especially cephalosporins and, in severe cases, metronidazole. In addition, it may be necessary to surgically remove the gallbladder if the inflammation has progressed significantly.
A cholecystectomy is a procedure in which the gallbladder is removed. It can be removed for recurrent gallstones and is considered an elective procedure. Cholecystectomy can be surgical or laparoscopic. During surgery, the gallbladder is removed from the neck to the fundus,
And thus the bile will drain directly from the liver into the biliary tree. About 30 percent of patients may experience some degree of indigestion after the procedure, although severe complications are much rarer.

Bile duct injury (bile duct injury) is a traumatic injury to the bile ducts. It is most often an iatrogenic complication of cholecystectomy – surgical removal of the gallbladder, but it can also be caused by other operations or major trauma. Risk
Gallbladder Removal Is Common. But Is It Necessary?
What is a polyp in the gallbladder, what system is the gallbladder in, what is sludge in the gallbladder, what is polyps in gallbladder, what is the gallbladder for, where is the gallbladder located in the human body pictures, what is the gallbladder, what is bile in the gallbladder, gallbladder located in the body, what does the gallbladder do in the digestive system, what organ system is the gallbladder in, what body cavity is the gallbladder in