What Is The Function Of Protein Synthesis – If you came directly to this page, you can see the previous tutorial on DNA, which provides background information on protein synthesis.
As mentioned, a series of nucleotides represent the genetic information that makes us unique and the blueprint for who and what we are and how we act. Part of this genetic information is devoted to the synthesis of proteins that are important to our body and are used in various ways. Proteins are made from the information templates in our DNA, as illustrated below:
What Is The Function Of Protein Synthesis

The nucleotides of the X symbol are a pattern of DNA sequences used to code for a specific protein. Each DNA molecule consists of two strands, only one of which is the coding strand that contains the protein sequence information. The complementary strand is the template strand, and it is this strand that binds RNA nucleotides together to make a copy of the DNA coding strand.
Protein Synthesis Internet Activities Digital And Printable
The sequence of these nucleotides is used to create amino acids, which are linked together to make proteins.
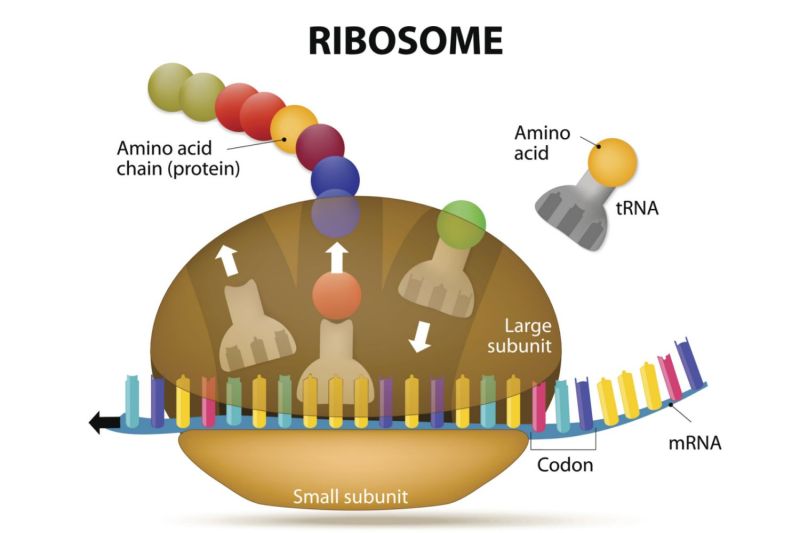
In eukaryotes, most of the genetic information is contained in the nucleus, although protein synthesis actually occurs in the ribosomes contained in the ribosomes.
At the beginning of protein synthesis, such as DNA replication, the double helix structure of DNA unwinds to replicate the genetic sequence of mRNA responsible for coding for a specific protein.
Initially, the DNA is folded, allowing the enzyme RNA polymerase to transfer (copy) the genetic information to mRNA. If the DNA coding strand is: G-G-C-A-T-T, then the template strand will be: C C G T T A and the mRNA will look like this G G C A U-U (note that uracil replaces thymine).
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
With the genetic information responsible for the creation of the material now contained in the mRNA strand, the mRNA moves out of the nucleus and away from the DNA toward the ribosomes.
This guide focuses on the relationship between organisms. It also studies how energy is transferred in the food chain and ..
This lesson looks at some of the communities in freshwater habitats. For example, symbiosis occurs in society.

There are many environmental factors that result from the use of water in one way or another and for each of its activities.
Question Video: Identifying Which Organelle Is The Site Of Translation
Darwin’s finches are an example of natural selection in action. They are an excellent example of the gene pathway of a species.
The nervous system is essentially a biological information pathway. This guide provides an overview of the nervous system.
Plants produce hormones to regulate their growth. For example, auxins affect plant growth. Know the role of auxin i..Protein biosynthesis begins with transcription and post-transcriptional modifications in the nucleus. The mature mRNA is exported to the cytoplasm where it is translated. The polypeptide chain is folded and modified after translation.
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a basic biological process that occurs inside cells and balances the loss of cellular proteins (through degradation or export) by the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of important functions as zymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for prokaryotes and eukaryotes, but there are some distinct differences.
Mechanical Support, Enzyme Circulation, Protein Synthesis And Detoxifi
Protein synthesis can be broadly divided into two steps – transcription and translation. During transcription, a piece of protein DNA, known as ge, is converted into a template molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This conversion is carried out in the cell nucleus by enzymes known as RNA polymerases.
In eukaryotes, this mRNA is initially produced in a premature form (pre-mRNA), which undergoes post-transcriptional modification to produce the mature mRNA. The mature mRNA is exported from the cell nucleus through nuclear pores to the cell cytoplasm for translation. During translation, mRNA is read by ribosomes, which use the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA to determine the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes catalyze the formation of covalent peptide bonds between amino acids to form a polypeptide chain.
After translation, the polypeptide chain must be folded to produce a functional protein; for example, the polypeptide chain must function as a zym to produce a functional active site. To adopt a three-dimensional (3D) functional form, a polypeptide chain must first form a series of smaller substructures called secondary structures. The polypeptide chain folds over these secondary structures to form the overall 3D tertiary structure. Once properly folded, the protein can undergo various post-translational modifications to mature. Post-translational modifications can alter the ability of a protein to function within a cell (eg, cytoplasm or nucleus) and the protein’s ability to interact with other proteins.

Protein biosynthesis plays a key role in disease, as changes and errors in this process through basic DNA mutations or misfolding of proteins are often the main causes of disease. DNA mutations change the subsequent sequence of mRNA, which changes the amino acid sequence of the mRNA. Mutations can cause a shortening of the polypeptide chain by creating a stop sequence that results in early termination of translation. Alternatively, a mutation in the mRNA sequence changes the specific amino acid encoded at that position in the polypeptide chain. This amino acid change can affect the protein’s ability to function or fold properly.
Protein Synthesis Overview
Misfolded proteins often contribute to disease because misfolded proteins have the ability to bind to dse protein complexes. These clusters are associated with a number of diseases, often neurological, including Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Transcription occurs in the nucleus using DNA as a template to produce mRNA. In eukaryotes, this mRNA molecule is known as pre-mRNA because it undergoes post-transcriptional modifications in the nucleus to produce the mature mRNA molecule. However, in prokaryotes, post-transcriptional modifications are not required, so the mature mRNA molecule is produced immediately by transcription.
It shows the structure of the nucleotide with 5 carbons indicating the 5′ nature of the phosphate group and the 3′ nature of the hydroxyl group, which are necessary for the formation of phosphodiester bonds.
Indicates the internal direction of the DNA molecule with the coding strand 5′ to 3′ and the free template strand 3′ to 5′.
Large Scale Cell Type Specific Imaging Of Protein Synthesis In A Vertebrate Brain
First, a enzyme known as a helicase acts on the DNA molecule. DNA has an antiparallel, double helix structure consisting of two complete polynucleotide strands held together by hydrogen bonds between base pairs. Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds, causing a region of the DNA to be cleaved, separating the two DNA strands and exposing a series of bases. Although DNA is a double-stranded molecule, only one of the strands acts as a template for pre-mRNA synthesis – this strand is known as the template strand. The other strand of DNA (which is complementary to the template strand) is known as the coding strand.
Both DNA and RNA are intrinsically oriented, meaning there are two DSs per molecule. This property of directionality is due to the asymmetric subunits of nucleotides, with a phosphate group on one side of the ptosis sugar and a base on the other. The five carbons in ptosis sugars are numbered from 1′ (where ‘in the primary sense) to 5′. Therefore, phosphodiester bonds that connect nucleotides are formed by joining the hydroxyl group on the 3′ carbon of one nucleotide to the phosphate group on the 5′ carbon of another nucleotide. Thus, the coding strand of DNA runs in the 5′ to 3′ direction and the complementary strand of the template DNA runs in the opposite direction from 3′ to 5’.
Zim RNA polymerase binds to the exposed template strand and reads from the ge in the 3′ to 5′ direction. At the same time, RNA polymerase cleaves a single strand of pre-mRNA in the 5′-to-3′ direction by catalyzing the formation of phosphodiester bonds between active nucleotides (free in the nucleus) that are capable of complete base pairing with the template strand. , synthesizes. . Behind the moving RNA polymerase, the two DNA strands are rejoined, so only 12 DNA base pairs are exposed at a time.

RNA polymerase makes pre-mRNA molecules at a rate of 20 nucleotides per second, which allows it to produce thousands of pre-mRNA molecules from the same gene per hour. Despite the fast speed of synthesis, RNA polymerase zyme has its own reading mechanism. Editing mechanisms allow RNA polymerase to remove incorrect nucleotides (that are not complementary to the DNA template strand) from the growing pre-mRNA molecule through the excision reaction.
The Ultimate Guide To Muscle Protein Synthesis
When RNA polymerase reaches a specific DNA sequence that terminates transcription, RNA polymerase cleaves and pre-mRNA synthesis is completed.
The pre-synthesized mRNA molecule is complementary to the template DNA strand and shares the same nucleotide sequence as the coding DNA strand. However, there is an important difference in the composition of DNA nucleotides and mRNA molecules. DNA consists of bases – guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine (G, C, A and T) – RNA also consists of four bases – guanine, cytosine, adenine and uracil. In RNA molecules, the thymine of the DNA base is replaced by uracil, which can pair with adine. Therefore, in
Function of rrna in protein synthesis, dna function during protein synthesis, function of mrna in protein synthesis, function of protein synthesis, what is the protein synthesis, function of ribosomes in protein synthesis, what is the sight of protein synthesis, the process of protein synthesis, what is the function of trna in protein synthesis, what is the process of protein synthesis, protein synthesis is the primary function of, what is the path of protein synthesis