What Is The Function Of Guard Cells – A wide flat surface increases the surface area for light absorption Have systems to prevent water loss Have bubbles open during the day but close at night or when it is hot to preserve a waxy cuticle of water on the surface Allow gas exchange system CO2 in and O2 out of an Elephant Ear Plant leaf
3 Leaf structure Waxy phyllodes – waterproof layer (reduces water loss from the surface) Veins (xylem and phloem clumps from the central zone) Make up xylem vascular tissue Stomata – pores on the underside of the leaf through which carbon dioxide and water vapor are exchanged phloem Midrib (vascular tissue i.e. phloem and xylem) Leaf stem (petiole) Stem (supporting plant)
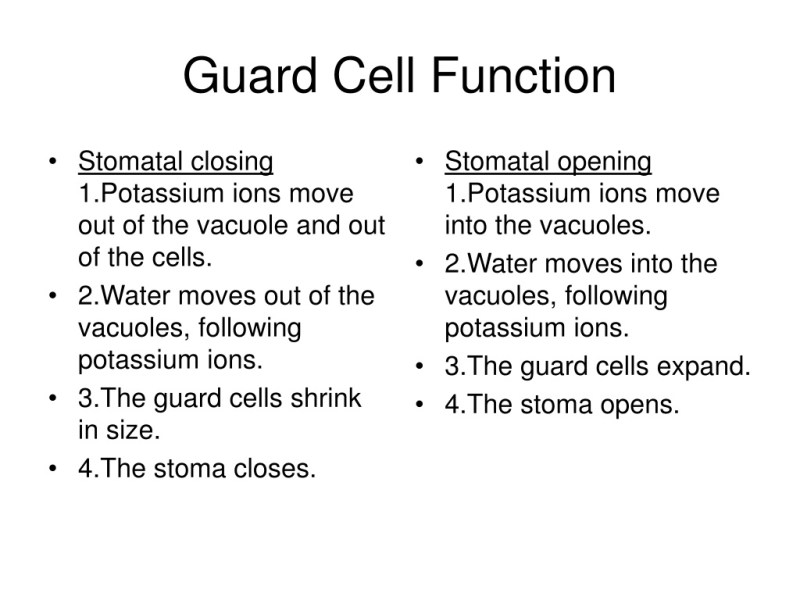
What Is The Function Of Guard Cells

Waxy cutin to prevent water loss Upper side of leaf Underside of leaf Upper epidermis – transparent, no chloroplast nucleus Palisades cell – many chloroplasts vacuolated cytoplasm Chloroplast – membranes covered with chlorophyll Sponge cells Mesophyll – fewer chloroplasts Xylem – plant carries water – transports food ( translocation) Airspace lower epidermis Guard Stoma cells
Advanced Biology. Biology; Physiology; Reproduction. Upper Surface Lower Surface Most Leaves Are Covered With A Layer Or Layers Of Thick Walled Cells Lacking Chlorophyll. The Lower Surface Of Most Leaves Bears Certain
1.waxy 2.Transparent epidermis so no chlorophyll 1.The waxy cuticle is a waterproof layer that reduces water loss through evaporation. 2. The upper cells of the leaf make up the epidermis. They are transparent so light passes straight through to the next layer of cells…
Leaf epidermis with stomata scanning electron microscope State that plants take in carbon dioxide from the air through stomata which can open and close Illustration- Stomata are tiny pores on the surface of a leaf. Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through stomata. During the day stomata are open. During the night stomata are closed. Know that water vapor is lost through stomata On the lower surface of the leaf there are tiny pores called stomata (singular stoma) which open and close. Stomata allow CO2 to diffuse in. Water vapor and oxygen (O2) move out.
8 Stomatal Function What process involves using CO2 and H2O to release O2 as a waste product? Photosynthesis If the plant needs water for photosynthesis, why is water coming out of the stomata? Guard Cells Guard Cells What goes out? O2 H2O CO2 What goes in? Open Stoma Stoma Closed Stoma
These stomata (leaf openings) naturally allow water to evaporate. Why would the plant close stomata with guard cells? Prevent excess water loss (conserve water) So what’s the point of stomata? Allow gas exchange for photosynthesis Guard Cells Guard Cells Open Stoma Open Stoma Guard cells close by swelling with additional water. They do this by pumping K+ ions into the cell, causing water to flow in by osmosis to diffuse the high ion concentration.
Plant Nutrition And Transport Worksheet
10 Stomata-opening Stomata have protective cells around them to control their opening and closing. When there is plenty of water (during the day) the water enters the protective cells and becomes turgid and curved. This opens the stomata and water can escape.
11 Stoma- closed When there is little water available, the protective cells release water and become flaccid = so curved. This closes the stomata and keeps water in the leaf. This happens at night. G
In order for this website to work, we log and share user data with processors. To use this website, you must agree to our Privacy Policy, including our cookie policy. Tip: Transpiration is the mechanism by which water passes through a plant and evaporates from aerial components such as leaves, stems and flowers. For plants, water is important, but for growth and digestion, only a limited amount of water taken up by the roots is used.

Guard cells are the cells that cover each stomach. By opening and closing the stomata, they help control the rate of transpiration.
What Are Guard Cells? Explain Their Role In Regulating Transpiration
The role of Guard cells in regulating transpiration: Guard cells are kidney-shaped cells that protect the stomach and are responsible for opening and closing the pore of the stomach. As potassium ions increase in the guard cells, they absorb water and become swollen or turgid. Because of its turbidity, the stomatal pore is fully exposed and transpiration occurs. As they lose water due to external stimuli like sunlight, temperature, etc., they become flaccid and close the stomatal opening thereby preventing transpiration.
As epidermal cells, they play an essential role in the exchange of gases in and out of plant leaves by controlling the opening and closing of pores called the stoma. They are also the pathways through which the water is released from the leaves to the environment.
Therefore, guard cells play a vital role in photosynthesis by controlling the input of materials required for the process. Apart from regulating the gas exchange, it has also been shown to contain chloroplasts, which also allows them a site of photosynthesis.
Note: Some of the variables that affect guard cell behavior are: humidity, temperature, sun, carbon dioxide, potassium ions, hormones. Although stomata are commonly found in the leaves of plants, it can also be found in the stems.
Using The High Power Objective Of A Microscope An Epidermal Leaf Shows :
What do you mean by public facilities Paragraph on Friendship Slogan on Noise Pollution Disadvantages of Advertising Prepare a Pocket First Aid Guide for your School 10 Slogans on Save the Tiger
How do you solve x2 11x + 28 0 using quadratic class 10 math? biology CBSEFill the gaps with the appropriate prepositions 1 Class 9 english CBSEDifference between a Plant Cell and an Animal CellThe dimensions of the potential gradient are A MLT 3A 1 class 11 physics CBSEDDefine electric potential and write down its class dimen class 9 physics CBSEWhy is the electric field perpendicular to CBSE class 12 equipotential physics free,
How do you solve x2 11x + 28 0 using the quadratic class 10 math

Difference between the Prokaryotic and the Eukaryotic cell class 11 biology CBSEF Fill in the blanks with the appropriate prepositions 1 Class 9 english CBSEDifference between a Plant Cell and an Animal Cell
Plant Cells And Tissues
The dimensions of the potential gradient are A MLT 3A 1 class 11 physics CBSEDFine electric potential and write down its dimen class 9 physics CBSEWhy the electric field is perpendicular to the equipotential class 12 physics CBSEOpen Institutional Access Policy Open Access Program Special Issues Processing Editor Research and Ethics Publication of Evidence of Ethics Processing Charge Awards
All published articles are immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse the whole or part of the article published by , including figures and tables. For articles published under the Creative Common CC BY open access license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please see https:///openaccess.
Sex papers are the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article covering a number of techniques or approaches, providing a perspective for future research directions and describing potential research applications.
Main papers are submitted at the invitation or individual recommendation of the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Guard Cell Photosynthesis And Stomatal Function.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations from scientific journal editors around the world. Editors select a small number of recently published articles in the journal that they believe will be of particular interest to readers, or will be important in the respective research field. Its aim is to provide insight into some of the most exciting work published in the journal’s various research areas.
By Hamdy Kashtoh Hamdy Kashtoh Scilit Preprints.org Google Scholar and Kwang-Hyun Baek Kwang-Hyun Baek Scilit Preprints.org Google Scholar *
Received: 24 October 2021 / Revised: 25 November 2021 / Accepted: 7 December 2021 / Published: 15 December 2021

A stomatal pore is formed by a pair of specialized guard cells and serves as the main gateway for the transpiration of water and CO into the atmosphere.
Mention The Most Significant Function/role Of Guard Cells In Plants
Excessive intake and loss of water is destructive to plants. When the plants are exposed to extreme conditions such as high CO
, low air humidity, and drought, the turgor pressure of the guard cells shows an appropriate response against these stresses, resulting in stomatal closure. This phenomenon involves a complex network of ion channels and their regulation. It is well established that the turgor pressure of guard cells is controlled by the transport of ions across the membrane, such as anions and potassium ions. In this review, the guard cell ion channels are discussed, emphasizing the structure and functions of the main ion channels; anion channel SLAC1 and potassium channel KAT1, and their regulatory components, emphasizing their importance in the response of immune cells to various stimuli.
, and pathogen attacks to survive. The guard cell plays a vital role in plants in adapting to such environmental stimuli, which are increasing due to global warming. It consists of two kidney-shaped cells that form a stomatal pore in the plant leaf epidermis and is responsible for gaseous exchange between the plants and the surrounding environment [1, 2, 3,
What is the function of b cells, what is the function of white cells, what is the function of nerve cells, what is the function of basal cells, what is the function of stem cells, what is the function of cells, function of guard cells, what is the function of glial cells, what is the function of mast cells, what is the function of stomata and guard cells, function of the guard cells, what is the function of t cells