What Is The Function Of Animal Cells – The functions of an animal cell depend solely on the organelles and structures associated with the cell. The parts of an animal cell have distinct functions. Read on to find out more…
The functions of an animal cell depend solely on the organelles and structures associated with the cell. The parts of an animal cell have distinct functions. Read on to find out more…
What Is The Function Of Animal Cells

The animal cell is the smallest unit that makes up the diverse tissues of animal species. There are hundreds of cell types in a developing organism, which differ according to their location and function. Red blood cells make up the blood, while nerve cells make up the tissues of the nervous system. Likewise, there are more than 200 cell types in an adult human. The general functions of an animal cell are attributed to the specific role of the different parts. So, before we delve deeper into the topic of our discussion, let us first try to understand the structure of the animal cell.
Plant Cells Vs. Animal Cells (with Diagrams)
The structure of an animal cell differs slightly from a plant cell in terms of shape, protective covering, and organelles. In the eponymous animal cell plan, it is roughly circular in shape and lacks an outer cell wall; While the plant cell is rectangular in shape and has a solid cell wall. In short, the outer layer of an animal cell is the elastic membrane. Other features that distinguish an animal cell from a plant cell are the presence of smaller vacuoles and the absence of plastids.
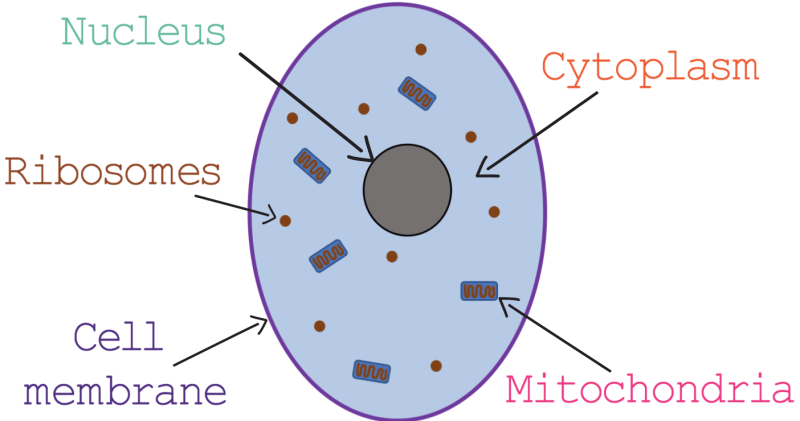
The functions of animal cells and organelles are related to each other. In fact, the collective action of the parts of an animal cell is responsible for the overall functioning of the cell. Let us take the example of the ribosome organelle, which performs the main function of protein production. Likewise, mitochondria are centers for energy release. Because of the lack of a cell wall, the animal cell is a more diverse type. Some of the functions of the cell in relation to its specific parts are explained below.
When you point to the animal cell model, you will notice that this cell is lined with a double-layered cell membrane. This membrane not only separates the inner cell content from the outer, but also allows the transfer of substances between the cell and its surroundings.
An animal cell is basically divided into two parts, the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The latter is the space that occupies the bulk of the cell and where the cell’s organelles are located. The cytoplasm is filled with a jelly-like substance, and the function of the cytoplasm in the cell is to support the internal parts.
Question Video: Identifying Organelles In An Animal Cell
The cell nucleus is the control center for all types of animal cells. It contains genetic material, or more precisely chromosomes. The nucleolus is located in the proximal center of the nucleus and is essential for protein synthesis in animals.
As the name suggests, ribosomes are composed of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and protein. It is found freely in the cytoplasm, or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. As far as the importance of ribosomes in cell functions is concerned, they are essential for making proteins.
The endoplasmic reticulum (abbreviated as ER) is essential for the synthesis, metabolism, and transport of compounds. They resemble a closed network with sac-like structures. There is the rough ER (RER) and the smooth ER (SER), with ribosomes preceding and assisting in protein synthesis.

Mitochondria (singular form, mitochondrion) are found in the cytoplasm. They are the powerhouse of the animal cell, performing the main function of converting nutrients and oxygen directly into energy sources.
Plant And Animal Cells Plant And Animal Cells Can Be Studies In Greater Detail Using A Light Microscope. Light Passes Through A Thin Slice Of The Specimen.
Known by different names (Golgi bodies and Golgi complex), it is an organelle with a sac-like structure. The function of the Golgi apparatus is to mobilize cellular materials, which are then transported out of the cell with the help of vacuoles.
Lysosomes, sometimes called vesicles, are roughly circular in shape. They contain digestive enzymes, and you can predict the function of lysosomes. Lysosomes help digest waste and remove it from the cell.
Centrioles are only found in animal cells. Composed of bundles of microtubules (nine in number), there are two centromeres located near the nucleus. They are cylindrical organelles that play a role in guiding cells during mitotic cell division.
These are found in unicellular animals and plants. In single-celled eukaryotes, the functions of cilia and flagella are responsible for the movement of the organism from one place to another. Structurally, they resemble hairs and are located in the cell membrane.
Animal And Plant Cells
With this brief information about animal cell functions and structure, we hope that you have accurately understood the concept of cell function and how organelles play their role in the cell. If there is any defect in the parts of the cell, the cell will not function normally. To gain a comprehensive understanding, you can make a comparison between the functions of a plant cell and the functions of an animal cell and point out their basic differences.
Sign up to receive the latest and greatest articles from our site automatically every week (give or take)… straight to your inbox.
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We’ll assume you’re ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Cookie Settings Accept

This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may have an impact on your browsing experience.
Animal Cells And The Membrane Bound Nucleus
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is necessary to obtain user consent before running these cookies on your website. The animal cell is the basic functional unit of animal life. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal cells were first observed in the 17th century when the microscope was invented. Robert Hooke, the English natural philosopher, was the first to describe microscopic pores, which he later called pores
, albeit from samples of the cork plant. The Dutch scientist Anton van Leeuwenhoek was also able to observe the cells under a microscope. Aside from single-celled organisms, such as prokaryotic cells and protozoa, he was the first to describe red blood cells and sperm cells in animals and humans.
Animal cells are the basic structural and functional units of animal tissues and organs. They are eukaryotic cells. This means that, unlike prokaryotic cells, animal cells contain membrane-bound organelles suspended in the cytoplasm and encased in a plasma membrane. This basic advantage is not limited to animal cells though. Both animal cells and plant cells are eukaryotic organisms, so the plant cell also has this feature. However, plant cells can be easily distinguished from animal cells by the presence of a cell wall. Apart from this, animal cell also lacks plastids, especially chloroplasts, which are involved in plant photosynthesis.
Parts Of An Animal Cell Book
Diagram of an animal cell. The cell (plasma) membrane surrounds the cytoplasmic contents, such as the nucleus, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, lysosomes, ribosomes, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, centrosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum.
The typical structure of an animal cell includes organelles, cytoplasmic structures, the cytosol, and the cell membrane. Organelles are membrane-bound structures within a cell and each has a distinct role. Cytoplasmic structures are structures in the cytoplasm that are not surrounded by membranes yet have a crucial role in some cellular activities. Cytosol is the liquid component of cytoplasm. It is where a wide range of cellular processes take place, e.g. Cell division.
The cell membrane of an animal cell is a lipid bilayer containing embedded proteins. The structural organization of the cell membrane allows selective permeability. Not all substances will be able to enter the cell. Small, nonpolar molecules may pass through with relative ease. However, polar molecules cannot, and therefore require transporters such as membrane proteins. The cell membrane is the only structure that surrounds the animal cell. Although it does not have a cell wall, the cell membrane of an animal cell contains cholesterol which provides structural integrity and support. Furthermore, the presence of cholesterol and the lack of cell walls in animal cells makes them fluid rather than rigid, thus making them capable of movement.

The nucleus is the most prominent organelle in the animal cell. It contains chromosomes, the nucleus, nuclear bodies, and nucleosomes. It is surrounded by a nuclear envelope (also called
Explain The Main Function Of Cell Wall In Plant And Animal Cells
) perforated by nuclear pores. Since it contains most of the animal’s genetic material, it is considered one of the
Of the cell, as it regulates most cell activities such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. It does this by regulating gene expression.
Network ER
What is the function of glial cells, what is the function of goblet cells, what is the function of b cells, what is the function of stem cells, what is the function of skin cells, the function of animal cells, what is the function of cork cells, what is the function of muscle cells, what is the function of blood cells, what is the function of nerve cells, what is the function of centrioles in animal cells, what is the function of t cells