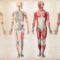
- Position Of Organs In The Human Body
- Antique Images: Vintage Medical Clip Art: Human Body Graphic Of 4 Human Internal Organs
- Boy Body Internal Organs. Medical Human Anatomy For Children, Cartoon Child Organ Set, Cute Kid Viscera Systems Diagram Isolated On White Background, Vector Illustration Stock Vector
- Human Internal Organs Diagram Medical Science Vector Image
Position Of Organs In The Human Body – All humans have internal organs that are vital to survival. Let’s look at what the main internal organs do:
1. Brain – The brain is the control center of the body. It responds to information from the senses and sends signals to other parts of the body telling it what to do.
Position Of Organs In The Human Body

2. Digestive System – Food enters the digestive system through the mouth, throat, stomach, liver and intestines. The way food and drink travel after you chew and swallow. The digestive system extracts nutrients from food to be used by your body.
Human Organs, The Placement Of Human Organs In The Body. Human Anatomy Stock Illustration
3. Genital organs – The genitals are the parts that produce sperm (male) and eggs (female) and are used by humans for reproduction.
4. Heart – The heart is a powerful muscle that pumps blood throughout your body in a steady rhythm.
5. Kidneys – Your kidneys filter your blood. They are used to make sure you have the right amount of salts and sugars in your blood.
6. Liver – The liver helps clear toxins from the blood and produces many of the chemicals needed to digest food.
Amazon.com: Internal Organs Of The Human Body Anatomical Chart
7. Lungs – Your lungs expand and contract, taking in oxygen-rich air from your surroundings and breathing in used air, which is high in carbon dioxide. They are responsible for getting oxygen and carbon dioxide into your blood.
8. Stomach – The stomach is the main digestive system in your body. It contains strong acids that help break down your food.
9. Thyroid Gland – The thyroid is an important gland located in the throat that controls how your body uses energy and makes proteins. It is important that you continue to grow and develop.

Did you know you can become our member and get access to all our great science posters, infographics and more? Anatomical position or standard anatomical position refers to a specific body orientation used when describing human anatomy. The normal anatomical position of the human body consists of the body standing upright and facing forward with the legs parallel to each other. The upper limbs or arms hang to either side and the hands face forward.
Antique Images: Vintage Medical Clip Art: Human Body Graphic Of 4 Human Internal Organs
When the body is lying flat with the arms and legs in the same position, instead of standing upright, it is called a supine position.
Normal anatomical positioning provides a clear and consistent way of describing human anatomy and physiology. When assessing an individual’s anatomy, many anatomical terms are used to describe how various appendages compare to a standardized position. Such terms include posterior or dorsal, meaning proximal and distal, which refer to the back of the body or how close or far something is, respectively. Normal anatomical position creates clear points that help avoid confusion when using anatomical terms.
The five regions of the body include the head, neck, torso, upper and lower extremities. The main area has a head and a face. The chest, known as the trunk, consists of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. Upper parts include the arms, armpits, and shoulders. Finally, the lower extremities consist of the feet, hands, thighs, knees, ankles, and feet. Dividing the body into these regions makes it easier to locate and describe a specific body part. For example, when describing the relative location of the heart, it is referred to as the torso region of the body.
The three planes of the body are the sagittal plane, the coronal plane, and the transverse plane. These planes are imaginary reference points that divide the body into different parts to help depict relative anatomy.
Boy Body Internal Organs. Medical Human Anatomy For Children, Cartoon Child Organ Set, Cute Kid Viscera Systems Diagram Isolated On White Background, Vector Illustration Stock Vector
The sagittal plane is the vertical plane that runs through the middle of the human body and divides the body into right and left halves. The coronal plane runs vertically from the edge of the body and divides it into the front (anterior) and back (posterior) sides of the body. The transverse (or axial) plane runs horizontally, dividing the upper half of the body from the lower half.
Anatomical position, or standard anatomical position, refers to the position of the body when the body is standing upright and facing forward, with the arms hanging by the sides and facing forward. Feet parallel, feet flat on the floor and facing forward. Anatomical position is a standard reference point commonly used in human anatomy and physiology when describing certain anatomical terms and positions. The five regions of the body are the head, neck, torso, upper and lower extremities. The body is divided by three imaginary planes called the sagittal plane, the coronal plane, and the transverse plane. The sagittal plane runs vertically and divides the body into right and left halves. The coronal plane runs vertically, dividing the body into anterior and posterior halves. Finally, the transverse plane moves horizontally and divides the body into upper and lower halves. In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined together into a structural unit to serve a common function.
In the hierarchy of life is an organ tissue and an organ system. Tissues are made up of similar cells that work together to perform a function. Different types of tissues combine to form an organ with a specific function. The intestinal wall is formed by, for example, epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue.
Two or more organs that work together to perform a specific body function form an organ system called a biological system or body system.
Internal Organs List For The Human Body
The tissues of an organ can be broadly divided into parchyma, functional tissue, and stroma, structural tissue with supporting, connective, or accessory functions. For example, the parchyma is the glandular tissue that produces hormones, and the stroma contains nerves that move the parchyma, blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients, and transport metabolic waste, and connective tissue that provides a comfortable environment. should be located and anchored. The primary tissues that make up an organ have a common embryological origin, arising from the same germ layer. Organelles are present in most multicellular organisms. In unicellular organisms such as bacteria, the functional analogue of an organelle is called an organelle. Plants have three main organs.
Abdominal organs can be divided into solid organs or hollow organs. The solid organs are the liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and adrenal glands. The abdominal cavity consists of the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, gallbladder, and rectum.
The number of organs in any organism depends on the definition used. According to the widely accepted definition, 79 organs have been dissected in the human body.
Multicellular animals other than plazozoans, including humans, have different organ systems. These distinct systems are widely studied in human anatomy. The functions of these organ systems often overlap. For example, the nervous and doctrinal systems both work through a common organ, the hypothalamus. For this reason, the two systems are combined and studied as the neuroendocrine system. The same is true for the musculoskeletal system because of the relationship between the musculoskeletal system.
Human Body Cavities
In anatomical terms, viscera (single viscus) refers to the internal organs of the abdominal, thoracic, and pelvic cavities.
Abdominal organs can be divided into solid organs or hollow organs. Solid organs include the liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and adrenal glands. The abdominal organs include the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, gallbladder, and rectum.
The term “visceral” is contrasted with the term “parietal,” which refers to “the wall of a body part, organ, or cavity.”

The two terms refer to opposite sides when describing a membrane or part of connective tissue.
Internal Organs Of Human Body
The relationship of major animal lineages by showing how long these animals shared a common ancestor. On the left, the vital organs are shown, which allows us to determine how long it has evolved.
In animals, the organ level of organization can be detected first in flatworms and in the more developed phyla, the bilaterians. Advanced taxa (ie Placozoa, Porifera, Ctophora, and Cnidaria) do not show tissue fusion into organs.
More complex animals are made up of different organs that have evolved over time. For example, the liver and heart evolved in chordates about 550-500 million years ago, while the intestine and brain appeared in the ancestor of vertebrates, insects, molluscs, and worms about 700-650 million years ago.
The researchers looked for model systems in which organs evolved more directly and ideally evolved multiple times, given the way most vertebrates evolved. An excellent model for this type of study is the plaque, which has evolved more than 100 times in vertebrates, evolved somewhat more directly in some lineages, and is present in intermediate forms in modern taxa.
Human Internal Organs Diagram Medical Science Vector Image
Studies of plate evolution have identified a variety of genetic and physiological processes that contribute to the formation and evolution of organs, including the reprogramming of existing animal tissues and the development of new functional traits.
Diagram of human organs in the body, human internal organs position, position of internal organs in human body, position of liver in the human body, position of organs in the body, pictures of organs in the human body, position of human organs, position of human organs in body, list of organs in the human body, organs of the human body, position of major organs in the human body, model of organs in the human body