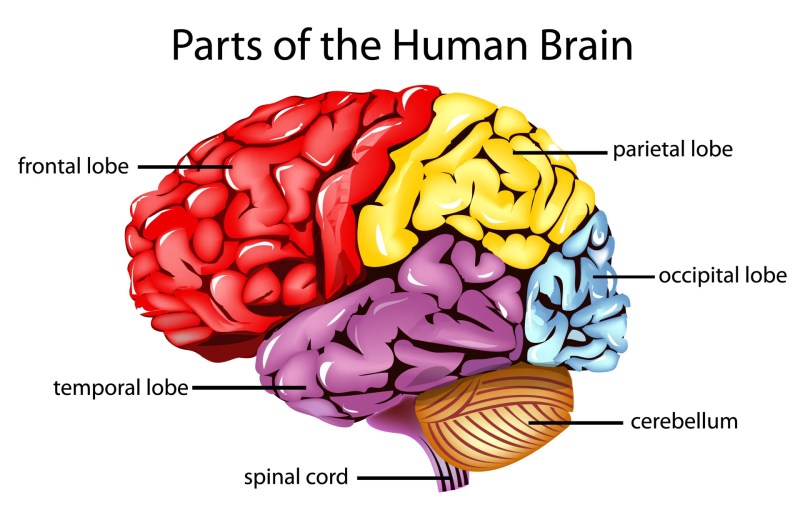
Parts Of Human Brain And Their Functions – It is of paramount importance to know the role of brain region function in the organization of neurofeedback training therapy in order to have highly effective results for optimal performance in various spheres of life and treatment of various pathological conditions and disorders. The brain is divided into regions, areas and lobes, each of which is responsible for a specific function.
The human brain is not only one of the most important organs in the human body; it is also the most complex. The brain is the central part of the nervous system that controls the functions of various organs in the body.
Parts Of Human Brain And Their Functions

, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. The brain performs higher functions such as interpreting touch, sight and hearing, as well as speech, reasoning, emotions, learning and fine control of movements.
Ventricles Of The Brain: Anatomy, Function, Associated Conditions
Which passes messages from one side to the other. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body.
(LH) is usually the dominant hemisphere. Responsible for the activities on the right side of the body. LH is good at logic and analytical reasoning. Two main language centers are in the LH: Broca’s area, which deals with verbal expression and speech production, and Wernicke’s area, which deals with verbal comprehension. Verbal memories are stored in the left hippocampus. Only about 20% of people who are left-handed are actually right-hemisphere dominant.
(RH) is the non-dominant hemisphere. Responsible for activities on the left side of the body. RH is involved in creativity, perception, and visuospatial processing. It is also involved in face recognition.
), covering the surface of the brain. The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain that functions to make human beings unique. Distinctly human traits, including higher thought, language, and human consciousness, as well as the ability to think, reason, and imagine, originate in the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is what we see when we look at the brain. This is the outermost part that can be
Human Brain Left And Right Functions Stock Illustration
: frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe and temporal lobe. These lobes are associated with various functions ranging from reasoning to auditory perception.
For each of the primary senses, there is an area called the primary sensory cortex. These include somatosensory, visual, auditory, vestibular, gustatory, olfactory and visceral sensations. The vestibular cortex is located in the insula, just below the temporal and frontal lobes.
Association areas give meaning to sensations. Each primary sensory area has an associative area to which it projects. Association areas make associations between different types of sensory information and connect new sensory data with memories of past experiences.

These are large areas of the cerebral cortex that receive sensory input from many different sensory modalities and different association areas and help make associations between different types of sensory information. We have
How Does The Human Brain Work?. What Is The Brain?
Is where the visual, auditory, and somatosensory association areas meet. This is what gives us our spatial awareness of our body. It is the kinesthetic sense that is very strong in professional dancers or athletes for example. On the left side – Wernicke’s area, which deals with reading, naming things. On the right side, this area helps us understand the emotional nuances/undertones of speech (the many ways to say “I’m fine”).
Includes the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain receives information from the posterior association area and helps integrate this information with past experience using the limbic association area. It has a lot to do with thinking and making judgments, and that’s where you figure out what’s socially acceptable, how to behave; just anything related to harsh human conditions.
Is located on the medial side of the frontal lobe. It is what helps form memories and turns them into motor responses and processes emotions and directs emotional responses. This is very important for social interactions and personality expression.
Located at the front of the brain. It is responsible for immediate and sustained attention, time management, working memory, executive planning, and initiative, and is associated with reasoning, motor skills, higher-level cognitive abilities, and expressive language.
Lobes Of The Brain: Cerebral Cortex Anatomy, Function, Labeled Diagram — Ezmed
. This area of the brain receives information from different lobes of the brain and uses this information to make body movements. It works in conjunction with the premotor areas to plan and execute movements. The frontal lobes are very strongly connected to the amygdala, which deals with emotions.
Is located anterior to the primary motor cortex and receives processed sensory information. This helps plan complex movements and sends the plan to the primary motor cortex. It is responsible for the sensory guidance of movement and control of the proximal and trunk muscles of the body.
Is located in front of the premotor cortex and helps control voluntary eye movements. Stimulation of the frontal eye field on one side results in a conjugate eye movement to the contralateral side.

Stimulation of the supplementary motor area elicits positional responses such as turning the head and eyes toward the moving arm and programming complex movements involving multiple body parts.
Human Brain Anatomy, Function Area, Mind System, 3d Render Stock Illustration
Located only in the left cerebral hemisphere. It is at the front of the premotor cortex, near the areas of auditory sensation. This is what helps control motor movements to produce speech. The corresponding area on the right side controls the emotional nuances of spoken words. In other words, it’s what helps you dictate how you say/form the words of your speech. It is responsible for language production and language comprehension (It has direct connections with the muscles responsible for the movements of the tongue, lips, vocal cords and pharynx).
Is located in the front part of the frontal lobe, occupies nearly 1/4 of the cortex and performs cognitive functions. It regulates sensory information flow in the posterior sensory systems. It leads to the planning, initiation and inhibition of actions through the basal ganglia and motor cortical/subcortical areas. It modulates the brain’s affective system through the amygdala and brainstem connections. Prefrontal cortex associated with intelligence, cognition, planning, judgment, problem solving, conceptualization, recall, and personality. It is necessary for judgment, reasoning, perseverance and conscience. It’s also related to mood. Closely related to the limbic system (the emotional part of the brain).
Neurofeedback to Fz and Fpz can influence social behavior. Weaknesses in this area are associated with oppositional defiant disorder and antisocial behavior. Slowing may be evident in these frontal areas. Neurofeedback training in the right prefrontal cortex can lead to a reduction in fear as well as feelings of calmness and well-being due to connections with the amygdala. Frontal problems typically present as patients who are foggy, struggle to focus, get into trouble, have social problems, are fearful, unmotivated, and detached.
Deals with the more spatial aspects of mathematics. The right parietal lobe also deals with map orientation, right-left recognition, and spatial recognition.
Brain Functions Stock Illustrations
Is located in the postcentral gyrus and is involved with conscious awareness of the general somatic senses. It receives information from the skin and skeletal muscles. It exhibits spatial discrimination and precisely localizes a stimulus. Here
– receives sensory input from the opposite side of the body. Stimulation of the primary somatosensory cortex produces contralateral tingling or numbness, but never pain.
Is located behind the primary somatosensory cortex and integrates sensory information, forms an overall understanding of the stimulus, and determines the size, texture, and relationship of parts. The primary gustatory cortex is responsible for the perception of taste.

Can cause problems related to multiple objects at the same time, as well as problems related to both sides of the visual field.
Human Brain Functions And Cognifit
The application of neurofeedback training in P3 makes it possible to regulate problem solving, increase mathematical and complex grammatical achievements, increase attention.
To solve the problem of dyscalculia, it is good to train both the left and right parietal lobes P3 and P4.
Located in the lateral lower part of the brain. This lobe is also the location of
Is located in the upper part of the temporal lobe and is responsible for processing auditory (sound) information. It receives information related to pitch, rhythm and volume.
Our Brains Control Our Thoughts, Feelings, And Behavior
Is located behind the primary auditory cortex and stores memories of sounds and allows the perception of sounds. It is responsible for understanding, recognizing and formulating language. It is located in the center of the Wernicke area.
On the medial surface of the temporal lobe are three structures critical to normal human functioning. From rostral to caudal, they are the olfactory cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus. They are responsible for visceral function, emotions, behavior and memory. Stimulating the limbic temporal cortex can trigger past events. The left posterior region is memory for verbal information. The right posterior area is memory for visual information.
At the tip of the cribriform are the nasal openings and they impinge on the olfactory bulb, which then travels to the primary olfactory cortex via the olfactory tract. This cortex is where you get your sense of smell before you know what the smell is. The olfactory cortex is located in the medial aspect of the temporal lobe, in the uncus (also known as the piriform lobe). The olfactory cortex is also called the Rhinencephalon or “brain of the nose”. It is the most primitive part of the brain and connects directly to the limbic system (emotional system), which is why smells often directly evoke emotions as well as our deepest memories.

It is responsible for the reaction and memory of emotions, especially fear. The amygdala is also involved in mood and conscious emotional response
Parts Of The Human Brain And Their Functions
Human brain and functions, human brain and their functions, human brain parts and their functions, chart of the brain parts and their functions, brain parts and their functions chart, brain and their functions, the human brain parts and their functions, human body parts and their functions, different parts of brain and their functions, brain parts and their functions, major parts of brain and their functions, structures of the brain and their functions