Number Of Cells In The Human Body – The researchers found that the average adult male has approximately 36 trillion cells in his body, while the average adult female has 28 trillion. Unexpectedly, the mass of small cells in our body, such as blood cells, is about the same as large ones, such as muscle cells, a finding that has puzzled researchers.
To count the number of cells in the human body, Ian Hatton of the Max Planck Institute for Mathematics in the Sciences in Leipzig, Germany, and his colleagues analyzed more than 1,500 scientific papers, looking at factors such as the number of cell types in the body, how many specimens of each type are present in each tissue and the average size and mass of each cell type. They found over 400 known cell types in 60 different tissues.
Number Of Cells In The Human Body

Using data from the International Commission on Radiological Protection, which collected the mass of each tissue in a 70-kilogram adult male, a 60-kilogram adult female, and a 32-kilogram child, the team then estimated how many cells were present in each body. guy.
Scientists Have Basically No Idea How Many Cells Are In The Human Body
“The key was to look for papers that described the number of cells in different tissues,” says team member Eric Galbraith of McGill University in Canada. “And then knowing that those tissue types were made up of particular cells and knowing what the size range of those cells was.”
The team estimates that an adult female has 28 trillion cells and a child 17 trillion cells, while adult males have 36 trillion. The first two estimates are based on records that largely described adult males, so there’s a little more uncertainty in these numbers, Galbraith says. “Unfortunately there is still more information on reference men than on women or children,” he says.
Even for adult males there is still a lot of uncertainty. “The distinction between male, female and child is probably quite slight compared to other sources of error in the data,” Hatton says. “Even the variation between different 70-kilogram male subjects can be comparable to the differences between male and female, so I don’t think it’s fair to emphasize this difference.”
Beyond the number of cells, the team also found that the total mass of each cell size in the body appears to be roughly equal. “You could imagine that there is an average cell size, and that we would be made up mostly of this average cell size,” Galbraith says. “But in reality this is not true.”
Structural Organization Of The Human Body
“In our bodies we have about the same amount, in terms of mass, of very small and very large cells and every cell size in between,” he says. “We all start from a single cell, so why does cellular development expand to occupy the entire size range of cells?”
“It’s just fascinating from a pure scientific point of view to have some sort of quantification of cellular diversity in the human body,” says John Runions of Oxford Brookes University in the UK. “When I teach students about cell biology and development, I say something like, ‘we all begin as a single fertilized cell, the zygote, which undergoes successive rounds of cell division accompanied by differentiation to produce an adult organism with X cells.’”
“The X has always been the hard part,” he says. “I am pleased that my mobile number statement can now be at least in the correct order of magnitude.”

Health We Know Almost Nothing About the Thousands of Proteins in the Human Body Free Health News The Amazing Ways Electricity in Your Body Shapes You and Your Health Features Subscribers Only Last Word How Much of My Body from 40 Years Ago remains part of me today? Health for Regular Subscribers Only Even healthy snacks could be causing hidden harm to your body Leader Subscribers Only
Blood: Function, What It Is & Why We Need It
1 Sperm caught breaking Newton’s third law of motion 2 What time is the full moon partial lunar eclipse this weekend? 3 Physicist tries to create space-time from scratch 4 Is space-time quantum? Six ways to unravel the fabric of the universe 5 Can we get unlimited green hydrogen by splitting seawater? 6 The fastest semiconductor ever could dramatically speed up computer chips 7 Why free will doesn’t exist, according to Robert Sapolsky 8 ChatGPT wrote code that can leak sensitive information from databases 9 Record-breaking quantum computer has more than 1,000 qubits 10 What are solid state batteries and why do we need them? Unfortunately, your cells can’t fill out census forms, so they can’t tell you this themselves. And while it’s easy enough to look under a microscope and count some types of cells, this method is also not practical. Some cell types are easy to spot, while others, like tangled neurons, tangle in the dark. Even if you could count ten cells per second, it would take you tens of thousands of years to finish counting. Additionally, there would be some logistical problems you might encounter along the way to counting all the cells in your body, such as dividing your body into small portions for observation under a microscope.
For now, the best we can hope for is a study recently published in the Annals of Human Biology, titled, with admirable clarity, “An Estimation of the Number of Cells in the Human Body.”
The authors, a team of scientists from Italy, Greece and Spain, admit that they are certainly not the first to address this question. They looked at scientific journals and books from the last two centuries and found many estimates. But those estimates spanned a huge range, from 5 billion to 200 million trillion cells. And virtually none of the scientists who offered these numbers provided an explanation for how they obtained them. Clearly, this is a topic ripe for research.
If scientists can’t count all the cells in the human body, how can they estimate them? The average weight of a cell is 1 nanogram. For an adult man weighing 70 kilograms, simple arithmetic would lead us to conclude that that man has 70 trillion cells.
Cells Of The Human Body Royalty Free Vector Image
On the other hand, it is also possible to make this calculation based on the volume of the cells. The average volume of a mammalian cell is estimated to be 4 billionths of a cubic centimeter. (To get an idea of that size, check out The Scale of the Universe.) Based on the typical volume of an adult human, you might conclude that the human body contains 15 trillion cells.
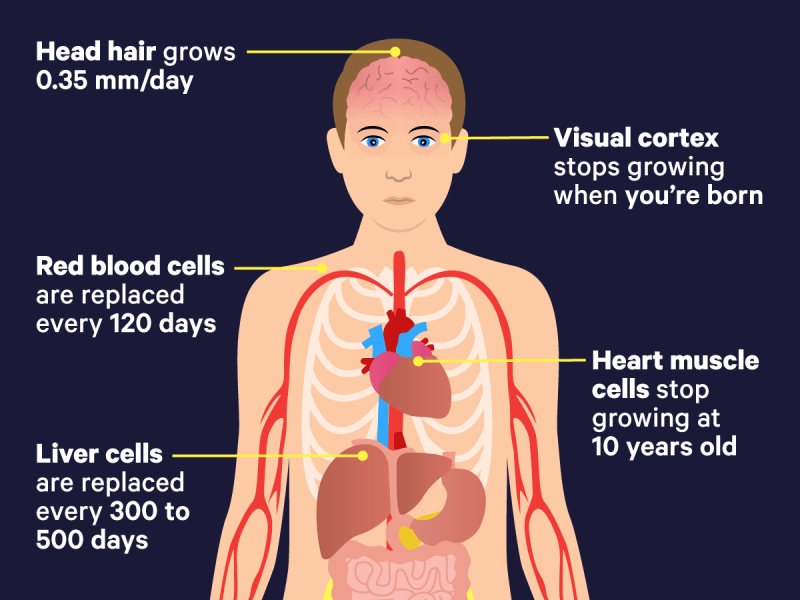
So if you choose volume or weight, you’ll get drastically different numbers. To make matters worse, our bodies are not filled with cells evenly, like a jar full of gummies. Cells come in different sizes and grow at different densities. Look at a container full of blood, for example, and you will find that the red blood cells are packed tightly together. If you used their density to estimate the cells in a human body, you would arrive at a staggering 724 trillion cells. Skin cells, on the other hand, are so sparse that it would give a paltry estimate of 35 billion cells.
So the author of the new paper started estimating the number of cells in the body the hard way, breaking it down by organs and cell types. (They didn’t try to count all the microbes that call our bodies home, attaching only to human cells.) They scoured the scientific literature for details on the volume and density of cells in the gallbladder, knee joints, intestines, bone. marrow and many other tissues. They then came up with estimates for the total number of each cell type. It is estimated, for example, that we have 50 billion fat cells and 2 billion heart muscle cells.

This isn’t a definitive number, but it’s a great start. While it’s true that people can vary in size – and therefore vary in the number of cells – adult humans do not vary by orders of magnitude except in movies. Scientists declare with great confidence that the common estimate of a trillion cells in the human body is wrong. But they see their estimate as an opportunity for collaboration – perhaps through an online database assembled by many experts on many different body parts – to focus on a better estimate.
Importance Of Stem Cells
Curiosity is justification enough to think about how many cells the human body contains, but there can also be scientific benefits to establishing the number. Scientists are learning about the human body by building sophisticated computer models of the lungs, heart and other organs. If these models had ten times as many cells as real organs, their results could be completely off the mark.
The number of cells in an organ also affects some medical conditions. The authors of the new study find that a healthy liver contains 240 billion cells, for example, but some cirrhosis studies have found that the diseased organ has only 172 billion.
Perhaps most importantly, the very fact that some 34 trillion cells can cooperate over decades, giving rise to a single human body rather than a chaotic war of selfish microbes, is astonishing. The evolution of even a basic level
Pictures of cells in the human body, list of cells in the human body, average number of cells in the human body, examples of cells in the human body, number of brain cells in human body, how many cells in the human body, type of cells in the human body, functions of cells in the human body, cells of the human body, diagram of cells in the human body, name of cells in the human body, lifespan of cells in the human body