Long Term Effects Of Continuous Birth Control – Contraception is defined as an act or technique that prevents pregnancy by interfering with the normal processes of ovulation, fertilization and implantation.
. Contraceptives are physical or medical products that aid in contraception. There are different types of contraception in the broad method categories of barrier, hormonal, spermicidal, intrauterine, and surgical.
Long Term Effects Of Continuous Birth Control

Tubal ligation, hysterectomy and vasectomy are irreversible surgical contraceptive measures while other methods are reversible or temporary.
Intrauterine Devices (iud)
The effectiveness of each reversible method depends on consistent and correct application; Thus, real-world effectiveness is lower than ideal use estimates. Contraceptives that require daily administration such as daily oral contraceptives or the use of spermicides before each intercourse are less effective because of the increased potential for human error. Convenience and the possibility of consistent adherence to a particular regimen are important considerations when choosing a contraceptive. This presentation will focus on oral hormonal contraceptives.
It is important to note that apart from condoms, any other contraceptive method reduces the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Condoms should be used with other contraceptive methods to prevent STIs.
There are 2 general types of hormonal contraceptives: 1) combined – which contain both synthetic estrogen and progestin, and 2) progestin only.
Combined hormonal contraceptives are available in Canada as a daily oral pill, transdermal patch, and vaginal ring. Progestin-only contraceptives are available as a daily oral pill and intramuscular injection. Intrauterine devices (IUDs) can be either progesterone-medicated or non-medicated copper.
Side Effects Of The Combined Pill
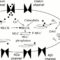
Hormonal contraceptives work by stabilizing hormone levels that suppress the spike release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Ovulation requires a sharp increase in LH and FSH and thus hormonal contraceptives prevent ovulation. Figure 1 shows the average menstrual cycle hormone levels. Hormonal contraceptives are described in Table 2 below to make sperm penetration of the cervix and endometrial lining less favorable and implantation of a fertilized egg.
* Oral contraceptives do not contain androgens (ie: testosterone) as ingredients. However, progesterone can be metabolized in the body to mediate testosterone and androgenic effects. Different progestins have different rates of metabolism of testosterone, so different oral hormonal contraceptives have different androgenic activity depending on the amount and type of progestin.
Oral contraceptives, especially combined oral contraceptives (COCs), are the most common hormonal contraceptives used by women in North America. They are commonly referred to as birth control.
Before starting COCs, each woman must be evaluated for contraindications and additional risk factors, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of using COCs.
Missed Birth Control Pills: What You Should Do When You Miss A Birth Control Pill
Advantages: non-invasive, easy to start and stop; Several strengths and product types are available (Table 3); Other potential health benefits
: cycle regulation; Decreased menstrual flow, iron deficiency anemia; Alleviation of dysmenorrhea, premenstrual or perimenopausal symptoms; reduce acne, hirsutism (but depending on the hormonal composition and individual compatibility it may increase); Reduce pelvic inflammatory disease; Reduce endometrial and ovarian cancer; reduce fibroids (but depending on the hormonal composition and individual compatibility it may increase); Increase bone mineral density – effect of estrogen.
Disadvantages4: highly dependent on simultaneous daily use for effect – vulnerable to human administration errors (progestin-only pills need not be taken 3 hours later than scheduled daily); Does not protect against STIs; Interactions with other drugs, contraindications and side effects must be considered.
Risk factors4, 7: breast cancer or hormone-dependent cancer -> use non-hormonal methods; cerebrovascular disease, history of cerebrovascular accident; Complicated valvular heart disease; Current or past history of venous thromboembolism or pulmonary embolism, known thrombogenic or prothrombin mutations, and antithrombin deficiency; diabetes with microvascular complications; history or current MI or ischemic heart disease, vascular disease; If breastfeeding use progestin-only or barrier method; Migraine with aura at any age; hypertension (SBP ≥160 mm Hg or DBP ≥100 mm Hg); Severe cirrhosis or liver tumors; Smokers > 35 years of age (≥15 cigarettes/day) -> use progesterone-only or non-hormonal; current pregnancy; Abnormal vaginal bleeding – This can be a sign of an STI or cancer; Some drugs [anti-seizure – phenytoin, carbamazepine, primidone, phenylbutazone, felbamate, ozcarbazine and lamotrigine (progestin decreased lamotrigine levels); Antibiotics – rifampin/rifampicin; Antiviral – Ritonavir]
Post Birth Control Syndrome: Definition And Controversy
The World Health Organization also recommends that women under 35 and who smoke use oral contraceptives containing 35 mcg or less of estrogen.
The only antibiotic so far consistently proven to reduce the effectiveness of oral hormonal contraceptives is rifampin, also known as rifampicin.
. When using this drug with birth control, a back-up method must also be used. Other antibiotics are generally considered safe to use without backup with oral hormonal contraceptives

. The theory behind the potential interference of antibiotics with COCs is how estrogen is metabolized. Estrogen is metabolized by the liver and excreted in the bile. Bile is then used in the intestines to help digest food. Bacteria in the normal gut flora can digest modified estrogen back into a form that can be reabsorbed by the body and thus contribute to blood levels of estrogen. Antibiotics kill part of the normal flora when in use and there was concern that this would decrease estrogen levels in the body. For antibiotics other than rifampicin, this has not been shown to significantly reduce the effectiveness of COCs, however pharmacists and doctors may still advise using a back-up method with caution.
Best Contraceptive Pill
If antibiotics cause vomiting or severe diarrhea within 2 hours of taking oral contraceptives, this may reduce the absorption of the tablet and reduce its effectiveness. If this happens, back-up contraception is recommended
Monophasic COCs are products that contain the same level of hormones in each active pill. Multiphasic COCs contain active pills that contain different amounts of hormones on different days of the cycle. For example, tri-cycline contains the same amount of estrogen per 21 tablets, but varying amounts of progestin (7 days of 0.18mg, then 7 days of 0.215mg, then 7 days of 0.25mg). Multiphasic COCs are designed to more closely mimic natural rising and falling hormone levels while suppressing ovulation.
. The total monthly dose of hormones may be lower with multiphasic COCs than with some monophasic ones, which may be helpful for those who experience persistent side effects of monophasic COCs (Table 2).
Most COCs can come in 21-pill or 28-pill versions. In the 21-pill version, there are 21 pills containing all the hormones that last for 3 weeks. During the last 7 days of the cycle, there are no pills and menstruation occurs. In the 28-pill version, there are 21 pills with hormones and 7 pills of placebo, which start the menstrual cycle. The advantage of the 28-pill version is that it helps maintain the habit of taking a daily tablet while allowing menstruation. There are some multiphasic and extended use products that have a different pill.
Blood Clot Risk & The Pill
Oral contraceptives may be used by women who wish to reduce the number of periods for medical or convenience purposes. There is no scientific evidence that menstruation is necessary for optimal health
. Therapeutic amenorrhea (menstrual suppression by medical intervention) can be beneficial in reducing many conditions including premenopausal syndrome (PMS), iron deficiency anemia, menstrual-related headaches, and chronic pelvic pain.
Seasonale and Seasonique are products designed for extended use, 12 weeks of hormone pills per pack. Ceznik is formulated with 3 placebo tablets that allow menstruation to occur every 12 weeks. Regular COCs can be used continuously to achieve the same results. Women will use 21 hormonal pills from each pack and then immediately start a new pack without a 7-day break or placebo pills.

Bleeding often occurs at the initial stage of therapy, at an unpredictable time. For example, non-menstrual bleeding for 8-16 weeks or continuous use may cause bleeding. When heavy bleeding or spotting occurs for several days after at least 3 months of treatment, physicians recommend stopping COCs for a maximum of 3 days to allow menstruation to begin. Do not take a break before 3 months. According to research, women generally become amenorrhoeic after 1 year of treatment
Possible Side Effects Of Stopping Birth Control, According To Ob Gyns
. Extended and continuous use of COCs reduces the number of menstrual cycles per year, however, bleeding occurs at unpredictable times.
Hormone levels affect mood. Women may experience mood swings when starting, changing, and stopping oral contraceptives
. Changes are very personal and can either improve or worsen mood. A potential benefit of hormonal contraceptives is the reduction of mood problems and mood swings associated with PMS
. There has been conflicting research regarding the association between hormonal contraceptives (especially the progestin component for adolescents) and depression.
The Effects Of Continuous Contraceptive Pill Taking
. More research is needed in this area. Women who have an underlying mood disorder or high risk factors for a mood disorder
Long term effects of iud birth control, long term birth control effects, effects of long term birth control use, side effects of continuous birth control pills, long term effects of hormonal birth control, long term side effects of birth control, long term effects of birth control implant, negative long term effects of birth control, long term effects of birth control patch, long term health effects of birth control, long term effects of depo birth control, long term effects of birth control pills