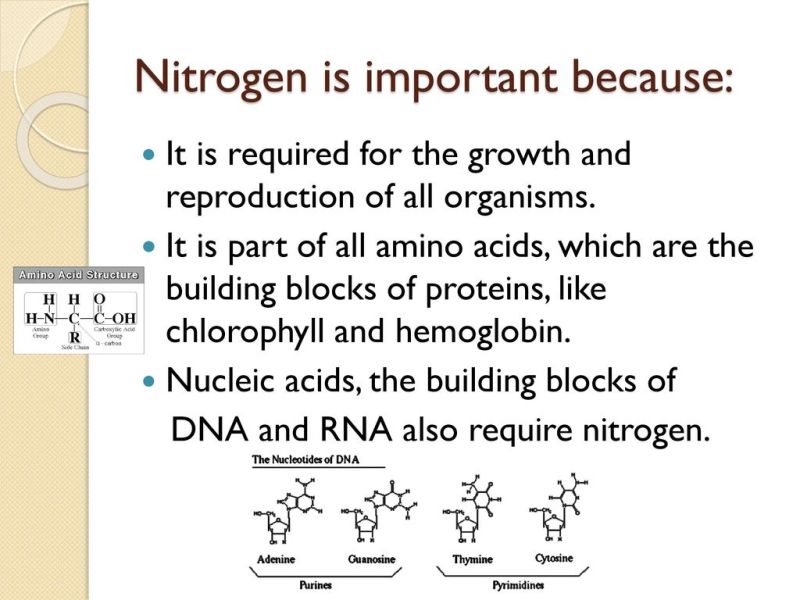
How Are Bacteria Important To The Nitrogen Cycle – The nitrogen cycle refers to the movement of nitrogen within and between the atmosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere. The nitrogen cycle is important because nitrogen is an essential nutrient for sustaining life on Earth. Nitrogen is an essential component of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, and nucleic acids, which are the building blocks of genetic material (RNA and DNA). While other resources such as light and water are abundant, ecosystem productivity and biomass are often limited by the amount of available nitrogen. This is the primary reason why nitrogen is an essential part of fertilizers used to improve soil quality for agricultural activities.
The nitrogen cycle is an essential part of how the Earth system works. Click on the image on the left to open the Understanding Global Change infographic. Locate the nitrogen cycle icon and identify other Earth system processes and phenomena that cause or affect changes in nitrogen cycling.
How Are Bacteria Important To The Nitrogen Cycle

Nitrogen cycles through abiotic and biotic components of the Earth system. The largest reservoir of nitrogen is found in the atmosphere, mostly nitrogen gas (N
Reversing Nitrogen Fixation
) 78% of the air we breathe consists of nitrogen gas. Most nitrogen enters ecosystems through certain types of bacteria in the soil and plant roots that convert nitrogen gas into ammonia (NH).
) This process is called nitrogen fixation. A very small amount of nitrogen is fixed by lightning interacting with air. After fixing nitrogen, other types of bacteria convert ammonia to nitrate (NO
), which can then be used by other bacteria and plants. Consumers (herbivores and carnivores) obtain nitrogen compounds from the plants and animals they eat. Nitrogen returns to the soil when organisms release waste or die and are decomposed by bacteria and fungi. Nitrogen is released back into the atmosphere by bacteria breaking down nitrate and nitrite into nitrogen gas (also known as denitrification).
Nitrogen levels in aquatic and terrestrial habitats can vary significantly, and can be affected by a variety of human activities and environmental phenomena, including:
Why Is Nitrogen Fixation Important To Living Things?
The Earth System model below includes some of the processes and phenomena associated with the nitrogen cycle. These processes operate at different rates and at different spatial and temporal scales. For example, nitrogen fixation by bacteria takes place at small spatial scales, while human use of fertilizers can affect entire ecosystems. Can you think of additional cause and effect relationships between parts of the nitrogen cycle and other processes in the Earth system?
Click on the bold words linked on this page (eg agricultural activities, productivity and biomass, and nutrient levels) to learn more about these processes and phenomena. Alternatively, explore the Understanding Global Change infographic and find new topics that interest you and/or are locally relevant. Are you looking for details about the stages of the nitrogen cycle, i.e. the life cycle? The following article covers all the details of the nitrogen cycle and introduces you to one of the most efficient processes in nature.
The nitrogen cycle is one of the most important nutrient cycles in the natural world. Nitrogen is an important element as the building blocks of life for all organisms; That is, DNA, RNA and other proteins are made of nitrogen. All living things need it to live and grow, and it makes up an important part of the air we breathe. But atmospheric nitrogen is not in a form usable by most organisms. Plants, fungi, animals and humans can use nitrogen in compound form.

Free nitrogen available in the air is converted by certain bacteria into compounds of this element that can be used by other organisms through a process called the nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen fixation is a bacterial activity in soil and water. Certain bacteria living in the roots of legumes like beans, alfalfa, peanuts etc. also help in this process.
Nitrogen Cycling And Microbial Cooperation In The Terrestrial Subsurface
) is the most stable form of this element available in the atmosphere and needs to be converted into nitrate ions (NO
CO] can be readily taken up by plants. Animals get their share of nitrogen by eating plants and their products. Humans get their share by eating plants, animal meat and products (ie fruits and vegetables). Let’s take a look at the stages of the nitrogen cycle in the following paragraph.
And cannot be used by most organisms. Thus, atmospheric nitrogen is ‘fixed’ by a biological process called the nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen accumulates in soil and surface water due to precipitation process. After it settles in the soil, it undergoes changes, resulting in two separate nitrogen atoms combining with hydrangea (H) and ammonium (NH).
It is carried out with the help of microorganisms. These microorganisms are divided into three groups, i.e., bacteria in symbiotic relationship with plants, i.e. leguminous plants, free aerobic bacteria and algae. Thus, alfalfa and beans are planted alongside crops to take care of nitrogen depletion in the soil. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and cyanobacteria use the enzyme nitrogenase to break the bonds of the atmospheric form of this element into two molecules that combine with hydrogen and other compounds. Many times, a small amount of nitrogen fixation with the help of light hits atmospheric nitrogen and converts the nitrogen into ammonia and nitrates.
The Nitrogen Cycle Game
The enzyme nitrogenase is active only in the absence of oxygen. Therefore, most of these microorganisms live below the layers of oxygen – except in the slime on the roots of plants. Bacteria, called rhizobium, grow in swellings or oxygen-deprived nodules in the roots of leguminous plants. Aquatic cyanobacteria use heterocysts, cells other than oxygen, for nitrogen fixation.
. After this is done, Nitrobacter, another soil bacteria, proceeds with the second step of nitrification by oxidizing NO.
. In both of these steps, bacteria gain energy and need oxygen to carry out reactions. Bacteria responsible for nitrification are called nitrifying bacteria.

Assimilation is the process by which plants and animals take nitrate and ammonia formed after the steps of the nitrogen cycle into their biological cells, i.e. nitrogen fixation and assimilation. Plants take up NO
Why Is The Nitrogen Cycle Important In Your Soil?
Through their roots and synthesizes them into various plant proteins and nucleic acids. Animals take up this form of nitrogen by consuming plant tissues.
The death of plants or animals or waste excretion by animals is the initial form of organic nitrogen. Many bacteria and fungi convert this organic nitrogen into ammonium (NH
) This process is called ammonification or mineralization. The converted ammonia becomes available to participate in other biological processes.
Called denitrification by anaerobic bacteria. The denitrification process takes place deep in the soil or near the water table under strictly anaerobic conditions. Thus, wetlands are excellent areas for reducing excess nitrogen levels with the help of denitrification. This step is carried out with the help of Pseudomonas and Clostridium under anaerobic conditions. These bacteria are facultative organisms and can survive in the presence of oxygen.
From Here Make A Note Of Nitrogen Cycle And All Important Point Should Be Mentionwhose Answer Will Be Best I
These are some interesting facts about nitrogen cycle and its stages in brief. It is one of the most important cycles that occur on Earth and helps sustain life on our planet.
Sign up (give or take) to automatically receive the latest and greatest articles from our site each week…direct to your inbox.
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We assume you agree to this, but you can opt out if you wish. Accept cookie settings

This website uses cookies to improve your experience as you navigate through the website. Among these cookies, cookies classified as necessary are stored on your browser because they are necessary for the functioning of basic functions of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies are stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.
How Are Nitrogen And Carbon Cycles? How Are These Two Cycles Similar And Different?
Essential cookies are absolutely necessary for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensure basic functions and security features of the website. These cookies do not collect any personal information.
Non-essential cookies are any cookies that are not specifically required for the website to function and are specifically used to collect user personal data through analytics, advertisements, other embedded content. It is mandatory to obtain user consent before running these cookies on your website. Quick access to A Level Biology revision Sign up now to get access to the entire library of A Level Biology resources for all exam boards
If you’re ready to pass your A-Level Biology exams, become a member now to get full access to our entire library of revision materials.
Not ready to buy a revision kit yet? No problem. If you want what we want to see
Nitrogen Cycle Explained
Why are bacteria important in the nitrogen cycle, how do nitrogen fixing bacteria contribute to the nitrogen cycle, nitrogen fixing bacteria cycle, why are nitrogen fixing bacteria important, nitrifying bacteria nitrogen cycle, nitrogen cycle bacteria role, denitrifying bacteria nitrogen cycle, important of nitrogen cycle, why are nitrogen fixing bacteria important to plants, bacteria in the nitrogen cycle, why are nitrogen fixing bacteria so important, the nitrogen cycle