High Levels Of Potassium In The Body – A 63-year-old man presented to the emergency department because of severe weakness and nausea. He suffered a heart attack a month ago and was recently given aspirin, Carvedilol, and atorvastatin. An EKG was obtained and the readings are shown below:
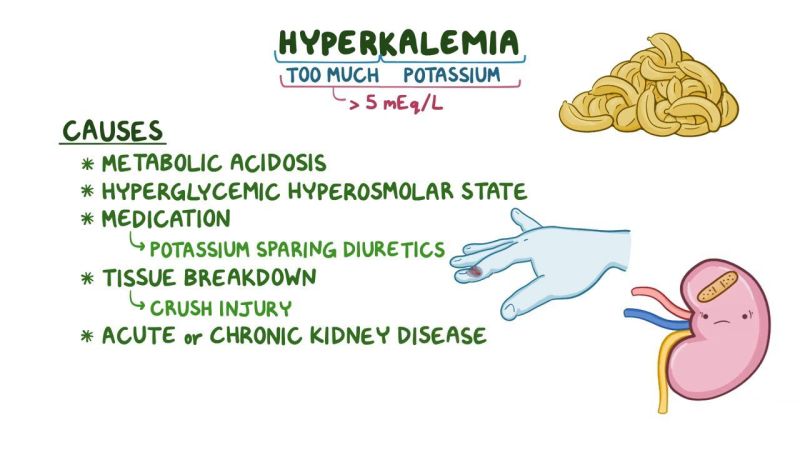
Common causes include metabolic acidosis; hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state; use of medications, such as potassium-sparing diuretics; and tissue damage, such as injuries from being hit.
High Levels Of Potassium In The Body

In addition, individuals with acute or chronic kidney disease can experience hyperkalemia if their potassium intake is high.
Solved] Chapter 29 Fluids, Electrolytes, And Introduction To Acid Base…
Ultimately, if hyperkalemia is severe enough, it can lead to flaccid paralysis that starts in the lower extremities and works its way up.
Additionally, severe hyperkalemia can affect kidney function – causing a person to become oliguric – meaning their daily urine output can fall below 400 milliliters.
If the ECG is normal and the person shows no symptoms of hyperkalemia, and there is no obvious cause for the hyperkalemia, it may be caused by pseudohyperkalemia. This occurs when potassium leaves the cells during or after a blood draw.
For example, potassium is released from muscle cells during muscle contraction, so if a person repeatedly clenches their hand during a blood draw, then potassium levels can increase – in fact, levels can rise up to 2 mEq/L in that forearm!
Healthy Foods That Are High In Potassium
For example, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the lymphocytes are weak so they break easily and release potassium. The key is to repeat the serum potassium level and obtain a CBC.
Often, potassium levels between 6 and 7 mEq/L, will cause a T wave peak with a narrow base in precordial leads V1 to V6.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier, its licensors and contributors. All rights reserved, including rights to text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.

USMLE® is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB) and the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME). COMLEX-USA® is a registered trademark of The National Board of Osteopathic Medical Examiners, Inc. NCLEX-RN® is a registered trademark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc. Test names and other trademarks are the property of their respective trademark holders. No trademark holders are endorsed or affiliated with this website.? We don’t think so. Chances are, you, like many others, tragically underestimate the importance of potassium. When dissolved in water, this mineral becomes very reactive and produces positively charged ions. Due to its special ability to conduct electricity, making it necessary for a number of bodily functions, potassium is classified as one of the five essential electrolytes.
Hyperkalemia: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Cost, And Side Effects
Research has linked increasing intake of foods high in potassium to a variety of impressive health benefits. We will discuss what potassium is, why we need potassium, how potassium functions in the body, and common signs of potassium deficiency. Plus we will share a list of 15 foods rich in potassium.
Potassium is the third most abundant mineral in the human body. Testing shows that most of the potassium in your body—about 98%—can be found in your cells. Your muscle cells take up 80% of these potassium stores, while the remaining 20% is divided between bones, liver and red blood cells.
Potassium functions as an electrolyte in your body. Once dissolved in water or another liquid, it breaks down into positive ions that send electrical signals. Your body uses these signals to control a number of important processes.
Potassium is responsible for three main functions: balancing fluid levels, sending nerve signals, and regulating muscle contractions. When potassium levels fall too low, or spike too high, the consequences can be very serious.
Low Potassium Diet: Benefits And How It Works
Water accounts for about 60% of our body weight as adults. Water is inside and outside our cells: the 40% that is inside our cells is called intracellular fluid (ICF) and the 60% that is outside our cells in places like blood, spinal fluid, and the spaces between cells is called fluid. extracellular (ECF). ).
Electrolytes—especially sodium and potassium—significantly influence the amount of water in your ICF and ECF. Potassium is the main electrolyte found in your ICF and determines how much water is in your cells at any given time. Sodium plays a similar role when it comes to your ECF.
When everything is going well, there is the same concentration of electrolytes and a stable amount of water both inside and outside your cells. The technical term for the ratio between electrolytes and fluids is osmolality. The goal is to maintain a balanced osmolality between your ICF and ECF.

When osmolality becomes unbalanced, water from the side with less electrolytes shifts to the side with more to balance electrolyte levels. When water enters or leaves your cells, it can cause them to swell or shrink. In some cases, your cells can even burst.
Electrolyte Imbalances: What Is It, Causes, Presentation And More
Regulating fluid balance is a major health issue. Changes in cell volume as we discussed above can have very damaging effects on brain cells. When ECF volume drops, this can have a negative impact on blood flow to organs, including your heart.
Eating potassium-rich foods, in addition to ensuring you drink enough water to stay well hydrated, is an important part of maintaining balanced fluid levels.
Your nervous system handles communication between your brain and body. This communication is transmitted in the form of nerve signals that regulate muscle contractions, heart rhythm, reflexes, and various other functions.
Potassium plays a major role in the process of transmitting nerve signals. When potassium enters a nerve cell, a sodium-potassium exchange is initiated which produces the electrical charge necessary to transmit signals. And when it exits the nerve cell, it repolarizes it, so the nerve signal can be processed.
Potassium Bicarbonate: Benefits, Side Effects, Dosage
The range for healthy blood potassium levels is between 3.6 and 5.0 mmol/L. If your blood potassium levels drop by as little as 1%, this can trigger a serious imbalance. This in turn can interfere with the transmission of nerve signals throughout your body.
To maintain healthy nervous system function, it is important to meet your body’s minimum recommended intake of potassium.
As we discussed above, muscle contraction is one of the control functions of nerve signals. Changes in potassium levels negatively impact nerve signals, which interfere with muscle contractions, including your heartbeat.

Potassium is so important for muscle health, we include 12 milligrams of potassium in our athletic performance blend to help increase endurance and reduce post-workout soreness.
Noninvasive Quantification Of Blood Potassium Concentration From Ecg In Hemodialysis Patients
Hypokalemia occurs when potassium levels fall too low. Hyperkalemia occurs when the rise is too high. Both can be dangerous.
The main danger associated with changes in potassium levels is changes in your heart rhythm. Low potassium levels can cause arrhythmia, an irregular heartbeat that requires medical treatment and even surgery. High potassium levels can cause the heart to weaken and enlarge excessively, which can also cause arrhythmias. When your heart fails to beat properly, it also fails to circulate blood to the brain, muscles and other organs.
According to an article published in Experimental and Clinical Cardiology, “Hypokalemia is associated with an increased risk of arrhythmias in patients with cardiovascular disease, as well as a 10-fold increase in all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and heart failure mortality.” In other words, if you have a heart problem, low potassium levels make it 10 times more likely that the problem will be fatal.
Hyperkalemia is also strongly associated with a higher risk of death for patients with heart disease as well as kidney disease, according to a 2017 study.
How To Lower Potassium Levels
Hopefully now you understand how important it is to maintain potassium levels in your body.
However, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) conducted by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) shows that less than 2% of adults living in the United States meet dietary guidelines for potassium intake. While this is not ideal, it is unlikely to cause a potassium deficiency.
In most causes, potassium deficiency occurs when the body rapidly loses large amounts of potassium. Common causes include prolonged vomiting, prolonged diarrhea, or other health conditions or situations that result in large fluid losses.

As the NHANES data may tell you, it’s very rare for someone to get too much potassium. There is no strong evidence to suggest that we can get too much potassium from food sources alone, although we can do so by taking excessive amounts of potassium supplements. There are examples of people consuming potassium in larger doses than their kidneys can process, with sometimes fatal consequences.
Cushing Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Research shows that in many cases, blood levels of potassium that are too high occur when the body has difficulty removing the mineral from the body through urine. Therefore, very high potassium levels are more likely to affect individuals with impaired kidney function. Certain populations have an increased risk of developing hyperkalemia (regarding high potassium levels), including:
Luckily, when it comes to finding potassium in food, you have many options besides the most well-known: bananas. In fact, bananas aren’t the most potassium-packed food on our list! Many nuts, beans, vegetables, fruit, and types of fish contain high levels
Normal levels of potassium in the body, effects of high potassium levels in the body, high levels of potassium in the blood, potassium levels in the body, effects of high potassium levels in the human body, low levels of potassium in the body, results of high potassium levels, high levels of potassium, treatment of high potassium levels, risk of high potassium levels, signs of high potassium levels in the body, symptoms of high potassium levels in body