Difference Between Data Analysis And Data Analytics – Pasture puts students first. Our blog articles are independently written by our editorial team. They are not paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines.
Data analyst vs. data scientist are two popular data-related careers in the technology industry. Although many occupations and related occupations are related, they are not the same.
Difference Between Data Analysis And Data Analytics
So, what is the difference between a data analyst and a data scientist? Do roles and skill sets differ? What are the salaries and job prospects like for these two career paths? In this guide, we will cover the following:
Data Analysis Process Steps: A Guide To The Key Stages Of Analyzing Data
How do data analyst and data scientist roles compare? Data scientists typically have the skill set of a data analyst plus additional skills, explains Jenna Bellassai, senior data writer at Forage and former senior data scientist.
“Most people who become data scientists start out as data analysts — but not all,” Bellassai says. “A data analyst specializes in manipulating data to create reports or dashboards, while a data scientist performs a combination of data analysis, software engineering and machine learning to create statistical models.”
Another important difference is that the role of data analytics has become ubiquitous. As a result, the skills of analysts are in high demand across industries, domains, and companies of all sizes, says Aswini Thota, senior data scientist at Bose Corporation with over 12 years of experience in data analytics.
On the other hand, data scientists have a deep understanding of mathematics and computer science. Data scientists are increasingly valued for their ability to create accurate models to inform strategic decision-making.
How Are Data Science, Data Literacy, And Ai Different?
When considering data analyst and data scientist careers, it’s important to remember a few things that differentiate each of these data-focused jobs. “Data analysts use their deep domain knowledge and analytical skills to explain the reasons that led to the results,” Thota says. “In contrast, data scientists develop predictive models that can ‘learn’ hidden relationships and rules within historical data to predict future outcomes.”
Although some of the functions these data professionals work in overlap, significant differences emerge when comparing roles, skills and salaries.
The roles of data analysts focus on understanding business problems, identifying relevant databases, cleaning and combining data and analyzing it to help businesses make informed decisions. It begins by gathering data from various sources, such as databases, spreadsheets, and other business systems.

On the other hand, the responsibilities of data scientists primarily involve developing and implementing predictive models and algorithms to solve strategic business problems. They start by understanding the problem they are trying to solve and identifying the data needed to solve it.
What’s The Difference Between Data, Analytics, Insights And Why Should I Care?
However, the roles are similar as well. “The main goal of data analysts and data scientists is to use data to inform strategy and make business decisions,” Thota explains. “They aim to leverage historical data resources to gain insights that drive business growth.” Data collection, data cleaning and data analysis are roles that data analysts and data scientists share.
Although data analysts and data scientists need the same skills to perform data cleansing, transformation and analysis, each career path requires specific hard and soft skills.
“Data scientists need to have a broader understanding of statistical models and machine learning algorithms, as well as programming and cloud computing skills,” Thota says. “On the other hand, data analysts need to be proficient in using data analysis tools, data visualization, and reporting methods and have excellent communication and collaboration skills to work effectively with stakeholders.”
Soft skills that can help data analysts in their work include strong communication and collaboration skills to work effectively with team members.
How To Get Started With Industrial Data Analytics
Soft skills that can benefit data scientists include problem-solving skills and the ability to identify and solve complex data problems, and the ability to work in a team environment.
In the following chart, Thota highlights the key skill sets required for data analytics versus data scientist roles, as well as some common skills that are important for both positions:
Although data analysts and data scientists have some overlap in their skills and roles, data scientists can command higher salaries. “Data scientists, on average, earn a higher salary than data analysts due to their specialized skills and strong understanding of computer science and machine learning,” Thota explains.
According to Glassdoor, the average salary for data analysts in the United States is around $70,000, with top-level positions reaching $114,000. In contrast, the average annual salary for data scientists is more than $126,000, while lead data scientists and those with more experience are likely to earn more than $162,000 in gross pay.
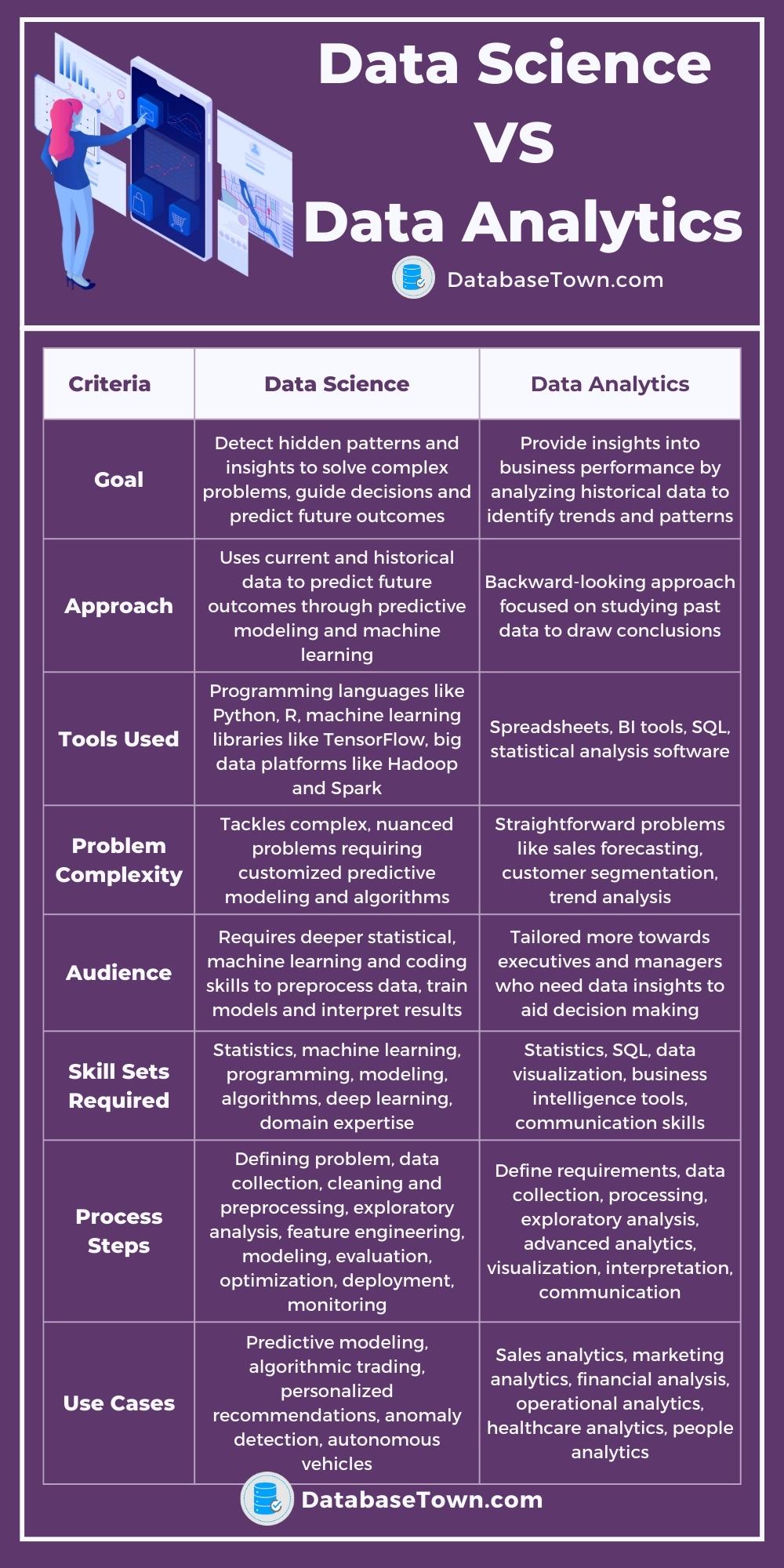
Data Science Vs. Data Analytics: The Differences Explained
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) notes that job outlook is above average for operations research analysts, the job category that includes data analysts. From 2021 to 2031, data analyst jobs are projected to grow 23%, faster than the average for all jobs.
For data scientists, the job outlook is even better, according to the BLS. This region is expected to see employment growth of 36% between 2021 and 2031, and 40,500 new jobs are expected to be added during that time.
Data analysts and data scientists both use data to inform strategy and make business decisions by deriving insights from data that drive business growth. These two in-demand career paths give professionals the opportunity to use data-driven decisions to shape the future of the organization.
However, each role has its own unique focus, so the path you choose should reflect your career interests. If you want to use data to leverage your domain knowledge and analytical skills and help explain the things that drive results, then you might enjoy being a data analyst. But if you want to build models and algorithms that can dig into historical data to predict future outcomes, you’d rather be a data scientist.
What Does A Business Data Analyst Do? 2024 Career Guide
When determining which career path might be the best fit, Thota emphasizes that it’s important to understand the complexity of the problems you prefer to work on. “Data analysts typically work with structured and well-defined databases to solve specific business problems, while data scientists can work with unstructured databases to predict and quantify the unknown,” he says.
It’s also important to think about your programming ability and your desire for strategic versus strategic solutions.
“While data analysts and data scientists use software tools like SQL, Python, R, and Tableau, the methods they use and the goals they intend to achieve can be different,” Thota says. “Do you prefer communicating knowledge or building large-scale systems? Data analysts are valued for the insights they bring to the table, while data scientists are expected to build large-scale models that provide predictive power.

He adds that business leaders often rely on data analysts to provide quick insights or strategic recommendations to help them correct or mitigate immediate risks. Data scientists, on the other hand, should be satisfied with long-term results. “Many of the projects that data scientists work on are strategic, and can take months or even years to fully implement predictive models,” Thota concludes.
Data Analytics In Construction
Robin Madell has spent more than two decades as a corporate writer, business journalist, and communications consultant in New York, San Francisco, and Los Angeles. In the world of data, there are several terms that are often used interchangeably but have different meanings. These conditions include:
Understanding the difference between these terms is important for individuals and organizations looking to use data to make informed decisions. In this article, we will explore the definitions, uses, and tools associated with each term, as well as their differences and similarities.
Data analysis is the process of examining data sets to draw conclusions about the information they contain, with the help of specialized software and systems. Data analysis, on the other hand, is the process of reviewing, cleaning, transforming and shaping data to discover useful information, conclusions and support decision making. Data mining is the process of discovering patterns in large data sets and involves the use of algorithms and statistical models. Data science is an interdisciplinary field that involves the use of scientific methods, procedures, algorithms and systems to derive knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data. Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that involves the development of algorithms that enable machines to learn and make decisions based on data. Big data refers to large data sets that are too complex or large for traditional data processing software to handle.
Data Analysis Data analysis is the process of examining data sets to draw conclusions about the information they contain. It involves the use of specialized software and systems to analyze and interpret data, with the aim of making the right decisions. Data analytics is widely used in a variety of industries, including healthcare, finance, retail, and marketing. Tools commonly used in data analysis include Excel, SAS, R, and Python. Data Analysis Data analysis involves the review, cleaning, transformation, and modeling of data to discover important information, conclusions, and support decision making. The process of data analysis can be done manually or with the help of software tools. Data analysis is used in a variety of fields, including business, science, and social science. Tools commonly used in data analysis include Excel, SQL, R,
Unstructured Vs Structured Data: 4 Key Differences [infographic]
Difference between business analytics and business analysis, difference between analysis and analytics, difference between big data and analytics, difference between data analysis and data analytics, difference between data analytics and data science, what is the difference between data analysis and data analytics, what is the difference between data analytics and data science, difference between business analytics and data analytics, what is the difference between analysis and analytics, difference between data science and business analytics, difference between bi and data analytics, data analysis and analytics






