Which Organelle Is The Site Of Protein Synthesis – Ever heard of the phrase “form follows function”? It’s a philosophy that applies to many businesses. In architecture, This means that buildings should be constructed to support the activities that will be carried out within them. for example, A skyscraper should be built with several banks of elevators; A hospital should be built so that the emergency room is easily accessible.
Our natural world, especially in cell biology, originated the principle of the following mode of action, and this becomes clear when we look at eukaryotic cells. Unlike prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells have: (1) a membrane-bound nucleus; (2) endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi apparatus; chloroplasts, many membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and others; and (3) multiple rod-shaped chromosomes. Because the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is surrounded by a membrane, it is often said to have a “true nucleus.” The word “organelle” means “small organ” and, as already mentioned, Organelles have specialized functions, just as the organs of your body have specialized functions.
Which Organelle Is The Site Of Protein Synthesis

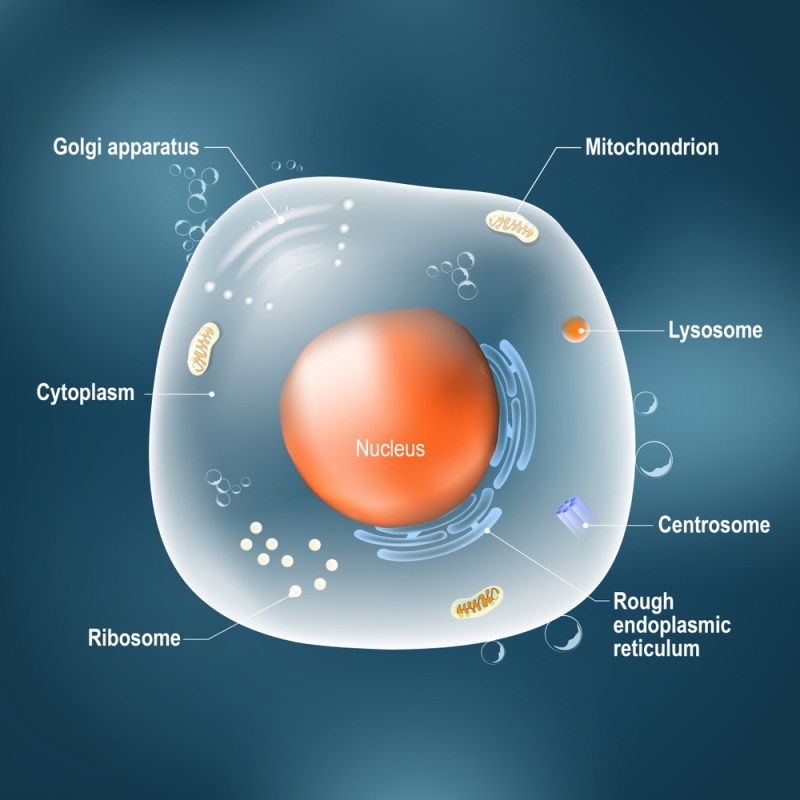
Figure 1. These figures show the major organelles and other cell components of (a) a typical animal cell and (b) a typical eukaryotic plant cell. In plant cells, the cell wall chloroplast, plastids and a central vacuole—structures not found in animal cells. Plant cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes.
Cell Organelles: Ap® Biology Crash Course
Before we start looking at individual organelles, The matrix in which they sit needs to be shortened: the cytoplasm. The part of the cell referred to as the cytoplasm is slightly different in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. In eukaryotic cells that contain a nucleus; The cytoplasm is everything between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope. In prokaryotes, which do not have a nucleus, Cytoplasm means everything inside the plasma membrane.
A major component of the cytoplasm in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the gel-like cytosol; ions, A water-based solution containing small molecules and macromolecules. In eukaryotes, The cytoplasm contains membrane-bound organelles suspended in the cytosol. Cytoskeleton, a fibrous structure that supports and gives shape to cells, is part of the cytoplasm and helps organize cellular components.
Although the cytosol is mostly water, It is a semi-solid like Jello due to the amount of protein suspended in it. glucose and other simple sugars in the cytosol; polysaccharides; Amino acid Broths are rich in macromolecules and small organic molecules, including nucleic acids and fatty acids. sodium, potassium, Ions of calcium and other elements can be found in the cytosol. Many metabolic reactions, including protein synthesis, take place in this part of the cell.
Figure 2. The nucleus stores chromatin (DNA and proteins) in a gel-like substance called the nucleoplasm. The nucleolus is an integrated region of chromatin where ribosome synthesis occurs. The boundary of the nucleus is called the nuclear envelope. It consists of two phospholipid bilayers: an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. Nuclear pores allow materials to enter and leave the nucleus.
Getting In Touch Is An Important Step: Control Of Metabolism At Organelle Contact Sites
) constructs the cell’s DNA and directs ribosomes and protein synthesis. Let’s see the details in picture (2).
The nuclear envelope is a double membrane structure that forms the outermost part of the nucleus (Figure 2). Both the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope are phospholipid bilayers.
Ions between the nucleus and cytoplasm; The nuclear envelope, which controls the passage of molecules and RNA, is punctuated. The nucleoplasm is the semi-solid liquid inside the nucleus. We find chromatin and nucleolus.

To understand chromatin; It helps to think of chromosomes first. Chromosomes are structures inside the nucleus made up of the genetic material, DNA. In prokaryotes, DNA is organized into a circular chromosome. In eukaryotes, Chromosomes are linear structures. Every eukaryotic species has a specific number of chromosomes in the nucleus of its body cells. for example, Humans have 46 chromosomes, fruit flies have eight. When the cell is ready to divide, the chromosomes can differentiate from each other. When the cell is in the growth and maintenance phases of its life cycle. Proteins are attached to chromosomes, which resemble unwound strands of thread. These intact protein-chromosome complexes are called chromatin (Figure 3); Chromatin describes the material that makes up chromosomes when condensed and decondensed. We will focus on chromatin and chromosomes in more detail later.
Eukaryotic Cell: What Is It, Difference From Prokaryotic Cells, And More
Figure 3. (a) This diagram shows the various levels of chromatin (DNA and protein) organization. (b) This image shows paired chromosomes. (Credit: Modification by NIH; scale-bar data by Matt Russell)
We already know that the nucleus directs the synthesis of ribosomes, but how does it do this? Some chromosomes have segments of DNA that encode ribosomal RNA. A darkly stained area within the nucleus called the nucleolus (plural = nucleoli) binds ribosomal RNA to associated proteins, assembles the ribosomal subunits, and transports them to the cytoplasm through pores in the nuclear envelope.
Figure 4. Ribosomes are composed of a large subunit (top) and a small subunit (bottom). During protein synthesis, ribosomes combine amino acids into proteins.
Ribosomes are cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. When viewed under an electron microscope, ribosomes appear as clusters (polyribosomes) or as small dots floating freely in the cytoplasm. They may be attached to the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane or to the cytoplasmic side of the endoplasmic reticulum and the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. Electron microscopy has shown us that ribosomes, which are large complexes of protein and RNA, consist of two subunits, called large and small (Figure 4). Ribosomes receive their “orders” for protein synthesis from the nucleus, where they transcribe DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA travels to ribosomes, which translate the code given the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids in a protein. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
Rna Translation: Major Steps Of Protein Synthesis • Microbe Online
Because protein synthesis is an essential function of all cells, ribosomes are found in practically every cell. Ribosomes are especially abundant in cells that synthesize large amounts of proteins. for example, The pancreas is responsible for making many digestive enzymes, and the cells that produce these enzymes contain many ribosomes. Therefore, We see another example of the function below.
) are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule. ATP represents the cell’s short-term stored energy. Cellular respiration is the process by which ATP is made using the chemical energy contained in glucose and other nutrients. In the mitochondria, this process uses up oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. In fact, carbon dioxide, which is released as a byproduct, comes from a cellular reaction.
In accordance with our content of the following mode of operation; It is important to point out that muscle cells have a very high concentration of mitochondria, which produce ATP. Your muscle cells need a lot of energy to keep your body moving. When your cells don’t get enough oxygen; They cannot produce much ATP. Instead, The small amount of ATP they make in the absence of oxygen is coupled with lactic acid production.

Figure 5. This electron micrograph shows a mitochondrion as viewed with a transmission electron microscope. This organelle has an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The inner membrane has folds called cristae that increase its surface area. The space between the two membranes is called the intermembrane space, and the inner membrane is called the mitochondrial matrix. ATP synthesis is located on the inner membrane. (Credit: Modification by Matthew Britton, scale bar data by Matt Russell)
The Cell: Organelles
Mitochondria are oval in shape; Double-membrane organelles (Figure 5) contain their own DNA and ribosomes (we’ll talk about these later.) Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins. The inner layer has folds called cristae. The area surrounding the folds is called the mitochondrial matrix. cristae and matrix have different roles in cellular respiration.
Peroxisomes are small organelles surrounded by a thin membrane. They carry out oxidation reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids. They also eliminate many toxins that may enter the body. Many of these oxidation reactions produce hydrogen peroxide H
Which will damage the cells; However, When these reactions are confined to peroxisomes; Enzymes safely break down H.
Into oxygen and water. for example, Alcohol removes toxins by peroxisomes in liver cells. Glyoxysomes, specialized peroxisomes in plants, are responsible for converting stored fats into sugars.
Ribosome Definition And Examples
Figure 6. Membrane and secretory proteins are integrated into the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The membrane of the RER also sometimes fixes proteins. (Credit: Modification by Magnus Manske)
= “within”) to repair lipids and proteins; A group of membranes and organelles in a eukaryotic cell that work together for packaging and transport (Figure 6). It has a nuclear envelope; lysosomes; vesicles and contains the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus;
Which is the site of protein synthesis, which organelle is responsible for protein synthesis, what is the protein synthesis, which structure is the site of protein synthesis, which type of rna is involved in protein synthesis, site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm, what organelle is the site of protein synthesis, site of protein synthesis, the site of protein synthesis is the, organelle for protein synthesis, protein synthesis is the process of, what is the process of protein synthesis