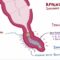
Where Is The Nervous System Located In The Body – The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. The brain and spinal cord are protected by bony structures, membranes and fluid. The brain is located in the cranial cavity of the skull and consists of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The nerves involved are the cranial nerves and the spinal nerves.
The nervous system has three main functions: sensory input, information integration, and motor output. Sensory input is when the body gathers information or information through neurons, glia, and synapses. The nervous system consists of excitable nerve cells (neurons) and synapses that form between neurons and connect them to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons act on excitation or inhibition, and although nerve cells may vary in size and location, their relationship to each other determines their function. These nerves transmit impulses from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. The data is then processed through the integration of information that occurs only in the brain. After the brain processes the information, impulses are transmitted from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands, which is called the motor output. Glia cells reside in tissues and are non-excitatory, assisting with myelination, ion regulation, and extracellular fluid.
Where Is The Nervous System Located In The Body

The nervous system consists of two main parts or subdivisions, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. The brain is the “control center” of the body. The CNS contains various centers that carry out sensory, motor and integration of information. These centers can be divided into Lower Centers (including the spinal cord and brainstem) and Higher Centers that communicate with the brain through effectors.
Senses, Nervous & Respiratory Systems
The PNS is an extensive network of spinal and cranial nerves connected to the brain and spinal cord. It contains sensory receptors that help process changes in the internal and external environment. This information is sent to the CNS via afferent sensory nerves. The PNS is then divided into the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. Autonomic control of internal organs, blood vessels, smooth and cardiac muscles. Somatic is voluntary control of the skin, bones, joints and skeletal muscles. The two systems work together, with nerves from the PNS entering and becoming part of the CNS, and vice versa.
The central nervous system (CNS) represents the largest part of the nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. Together with the peripheral nervous system (PNS), it plays a key role in controlling behavior.
A variety of effects are possible when the central nervous system is damaged or peripheral nerves are involved. It can increase or decrease the functionality of your internal organs, it can even affect your facial expressions, i.e. you may frown a lot, your smile may be crooked, your lungs may overwork or underwork, your lung capacity may increase or decrease, you may have a full bladder , but you can’t urinate, your bowels become empty and you can’t clean them completely with each stool, the muscles in your arms, legs and trunk can be weaker and fatter, not from disuse, but when the nerves that go to them from your spine are restricted from working properly, headaches, earaches, sore throats , may have blocked sinuses. Even your ability to orgasm can be affected.
The central nervous system is thought of as a system dedicated to information processing, where a corresponding motor output is calculated in response to sensory input. Many research topics show that motor activity is present long before the maturation of sensory systems, and that feelings alone influence behavior without dictating it. This brought about the concept of the CNS as an autonomous system.
Peripheral Nervous System: What It Is And How It Works
Neurons are highly specialized for processing and transmitting cellular signals. Given the diversity of functions performed by neurons in different parts of the nervous system, there is, as might be expected, great diversity in the shape, size, and electrochemical properties of neurons. For example, the soma of a neuron can vary from 4 to 100 micrometers in diameter.
The soma (cell body) is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell and is therefore where most protein synthesis occurs. The diameter of the nucleus varies from 3 to 18 micrometers. A neuron’s dendrites are cellular extensions with many branches, and metaphorically, this overall shape and structure is called a dendritic tree. This is where most of the input to the neuron occurs. However, information flow (ie, from dendrites to other neurons) can also occur—except at the chemical synapse, where impulse feedback is inhibited by the axon’s lack of chemoreceptors and the dendrites’ inability to secrete neurotransmitter chemicals. This explains how the nerve impulse is conducted.
The axon is a thinner, cable-like projection that can be tens, hundreds, or even tens of thousands of times the diameter of the soma in length. The axon carries nerve signals away from the soma (and also returns some types of information to it). Many neurons have only one axon, but this axon can, and usually will, undergo extensive branching, allowing connections with many target cells.

The part where the axon leaves the soma is called the axon hillock. In addition to being an anatomical structure, the axon hillock is also the part of the neuron with the greatest density of voltage-gated sodium channels. This makes it the most easily excitable part of the neuron and the spike initiation zone for the axon: in neurological terms, it has the largest hyperpolarized action potential threshold. Although the axon and axon hillock are generally involved in information flow, this region may also receive input from other neurons.
Unit 9: The Nervous System
An axon terminal is a specialized structure at the end of an axon that is used to release neurotransmitter chemicals and communicate with target neurons. Although the canonical view of the neuron attributes specific functions to its various anatomical components, dendrites and axons often function contrary to what is called their primary function.
Axons and dendrites in the central nervous system are typically only about a micrometer thick, while some in the peripheral nervous system are much thicker. The soma is usually about 10 to 25 micrometers in diameter and is often not much larger than the nucleus of the cell it contains. The longest axon of a human motor neuron can be over a meter long, stretching from the spine to the toes. Sensory neurons have axons that extend over 1.5 meters from the toes to the dorsal columns in adults. Giraffes have single axons several meters long along the entire length of their necks. Much of what is known about axonal function comes from studies of the giant squid, which is an ideal experimental preparation because of its relatively large size (0.5–1 millimeter thick, several centimeters long).
Sensory afferent neurons transmit information from tissues and organs to the central nervous system. Efferent neurons transmit signals from the central nervous system to effector cells and are sometimes called motor neurons. Interneurons connect neurons in certain regions of the central nervous system. Afferent and efferent can also refer to neurons that bring or send information to a brain region in general.
Excitatory neurons excite their target postsynaptic neurons or target cells, causing them to act. Motor neurons and somatic neurons are all excitatory neurons. Excitatory neurons in the brain are often glutamatergic. Spinal motor neurons that synapse on muscle cells use acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter. Inhibitory neurons inhibit target neurons. Inhibitory neurons are also called short axon neurons, interneurons, or microneurons. The output of some brain structures (neostriatum, globus pallidus, cerebellum) is inhibitory. The main inhibitory neurotransmitters are GABA and glycine. Modulating neurons produce more complex effects called neuromodulation. These neurons use neurotransmitters such as dopamine, acetylcholine, serotonin and others. Each synapse can receive both excitatory and inhibitory signals, and the output is determined by the summation of the summation.
What Is The Nervous System?
For another introduction to the nervous system, watch this video. This is the first in a series of nine videos. Although you can enjoy all the videos in this series, you are only required to watch the first video. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the component of the nervous system that connects the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body. It consists of nerves and ganglia that transmit signals between the central nervous system and the organs, limbs, and skin.
The PNS is divided into the CNS and the sensory and motor units that carry information from it. It is important in bodily functions such as movement, sensation, and vegetative processes.
The PNS is all the nerves that branch off from the components of the central nervous system and extend to other parts of the body – sensory organs, muscles, and glands. The PNS connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body.

The primary function of the peripheral nervous system is to connect the brain and spinal cord with the rest of the body and the external environment. The
The Central Nervous System
Where are the ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system located, where is the liver located in body, where is the parasympathetic nervous system located, where is the autonomic nervous system located, where is the central nervous system located, where is the nervous system located, nervous system in the body, where is the somatic nervous system located, where is the nervous tissue located, where is the nervous system, where is the nervous system located in the human body, where is the central nervous system located in the body