Where Is The Cytoplasm In A Cell – Home Games & Quizzes History & Social Science & Tech Biographies Animals & Nature Geography & Travel Art & Culture Money Videos
Although every effort has been made to follow the rules of citation style, some differences may occur. Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other resources if you have any questions.
Where Is The Cytoplasm In A Cell

Encyclopedias Encyclopedia editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that material or studying for an advanced degree. They write new content and verify and edit content received from contributors.
Important Points Of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm, a semifluid substance of a cell that is external to the nuclear membrane and internal to the cellular membrane, sometimes referred to as the nonnuclear material of protoplasm. In eukaryotes (ie, cells with a nucleus), the cytoplasm contains all organelles. Among such organelles are the mitochondria, which are the sites of energy production through ATP (adenosine triphosphate) synthesis; endoplasmic reticulum, site of lipid and protein synthesis; the Golgi apparatus, the site where proteins are modified, packaged, and sorted in preparation for delivery to their cellular destinations; lysosomes and peroxisomes, sacs of digestive enzymes that carry out intracellular digestion of macromolecules such as lipids and proteins; cytoskeleton, a network of protein fibers that give shape and support to the cell; and the cytosol, the fluid mass that surrounds various organelles. If you are looking for information about the cells of living organisms and how they work, you should start reading about cytoplasm.
A cell is the smallest unit of life. If you look at a living cell under a microscope, the first thing you will see is the nucleus. Located in the center of the cell, the nucleus contains the genetic material or DNA and is called the ‘brain’ of the cell. If you look around, you will see that the nucleus is surrounded by a colorless gel-like substance. This cellular substance is known as the cytoplasm, which performs many functions and is the location of the various phases of the cell cycle.
It is composed of water and other solute ions. About 80% of the cytoplasm is water. It also contains dissolved carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
The space between the cell membrane and the nucleus is filled by the cytoplasm, also known as the cell substance.
Cell Structure* — The Science Sauce
It is a jelly-like substance that performs many functions. It helps transport cellular molecules to various sites within the cell, and houses various cell organelles.
The cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus is called endoplasm, while that near the cell membrane is called ectoplasm.
Depending on the level of cellular activity, the cytoplasm can be found in either a watery state known as cytosol or a gel-like state known as cytogel.

Primary cell organelles found suspended in the cytoplasm include the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria (only in animal cells), ribosomes, Golgi apparatus (only in animal cells), centrosomes, lysosomes, vacuoles (only in plant cells) and chloroplasts. (only in. plant cells).
Basic Cell Structures.
Different cell organelles perform different functions. Ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins, while the Golgi apparatus receives proteins synthesized by ribosomes and transports them to different parts of the cell. Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell and produce the energy molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from the food we eat. Centrosomes aid in cell division, vacuoles help maintain turgor pressure in plant cells, and chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis.
Cytoplasm is more prominent in animal cells than in plant cells. In plant cells, large parts of the cellular space are occupied by vacuoles.
In the absence of a cell wall in animal cells, it is the cytoplasm that gives the cells shape and structure.
The cytoplasm also contains complex membrane networks called microfilaments and microtubules. They are composed of F-actin chains.
What Is An Animal Cell?
The cytoplasm serves as a platform for cell organelles to carry out their respective functions. Not only this, all the major events of the cell cycle including cell division take place in it.
An organism born with a non-functional cytoplasm or one that does not function properly is unable to survive.
Cytoplasm is one of the main components of the cell, essential for its proper functioning. When the cell dies, the cytoplasm begins to shrink and shrink away from the cell membrane.

Sign up (give or take) to automatically receive the latest and greatest articles from our site every week…directly to your inbox.
Creative Plant Cell Project Ideas To Try This Year
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We’ll assume you’re OK with this, but you can opt-out if you want. Accept cookie settings
This website uses cookies to improve your experience as you navigate through the website. Among these cookies, cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored in your browser because they are necessary for the basic functionalities of the website to work. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will only be stored in your browser with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.
Essential cookies are absolutely necessary for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensure basic functionality and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be specifically necessary for the website to function and are specifically used to collect user personal data through analytics, advertisements, other embedded content, are called non-essential cookies. goes User consent must be obtained before running these cookies on your website. Definition: The contents of a cell surrounded by a cell membrane but not including the nucleus if present.
Cell Organelles Biological Anatomy Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Illustration
The cell is known as the building block of all life. Blocks are made up of many particles and parts before forming a complete block. Like a block, the cell of a living organism is made up of many parts.
, the study of cells tells us that inside a cell, there may essentially be a nucleus, other organelles, and cytoplasm.
Is a rich, semi-fluid substance contained in the cells of organisms that is enclosed by the cell membrane. It contains various cytoplasmic components, such as cytosol, cytoplasmic structures, mitochondria, and other organelles. In some contexts, the nucleus, which is a major organelle suspended in the cellular fluid, is considered part of the cytoplasm. And so in this case, it would be the largest organelle in the cytoplasm. However, this view takes cytoplasm as synonymous with protoplasm. Protoplasm is the liquid living material of the cell that is originally formed

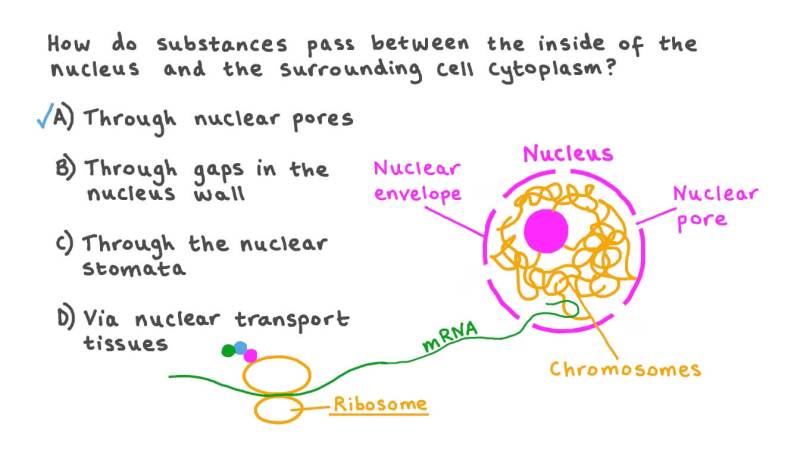
And the nucleoplasm. Cytoplasm, in turn, is the protoplasmic material between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope. Thus, a strict definition of cytoplasm is that which excludes the nucleus.
Human Cell Structure Showing Cytoplasm, Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Mitochondrion Stock Photo
Cytoplasm is defined as the cellular compartment within the cell between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope of the nucleus.
Cytoplasm is found inside the cell. In a eukaryotic cell—such as an animal cell and a plant cell—the cytoplasm is between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope. As for a prokaryotic cell—such as a bacterial cell—which lacks a well-defined nucleus, the cytoplasm is everything that is inside the cell, surrounded by a cell membrane. Figure 1 below shows a diagram of a cell with the cytoplasm annotated.
All cells contain cytoplasm. However, the size of the cytoplasm can vary from one cell to another. A fully-differentiated sperm cell, for example, will lose many of its cytoplasmic organelles. At maturity its head has very little cytoplasm and a very compact nucleus for a more streamlined structure for motility. In contrast, the ovum is a large cell because it has a large cytoplasm. It is, in fact, considered to be the largest cell in the human body, about 10,000 times larger than a sperm cell. The reason the ovum grows is because it contains enough nutrients to support life if it is fertilized and gives birth to a zygote.
Organisms contain a rich, mucilaginous fluid enclosed by a cell membrane. It is composed of the cytosol, intracellular structures, mitochondria, and other organelles. While cytoplasm can be used as a synonym for protoplasm, there is a subtle difference. Protoplasm is the living material of the cell composed of cytoplasm and nucleoplasm (the fluid inside the nucleus). The cytoplasm, in turn, excludes the nucleoplasm and, therefore, is the protoplasmic material between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope. Vocabulary:
Animal Cell Definition And Examples
The main purpose of the cytoplasm is to be the suspension medium of the cell. Cytoplasm in animal cells preserves cell organelles and aids in cell motility. Cytoplasm functions in a plant cell are almost identical to those of an animal cell. The
Where is the cytoplasm located in a plant cell, where is cytoplasm found in a cell, where is the cytoplasm, cytoplasm function in plant cell, where is the cytoplasm in a cell, where is the cytoplasm located in a animal cell, what is in the cytoplasm of a cell, what cell is cytoplasm found in, what does the cytoplasm do in a cell, where is the cytoplasm located in an animal cell, cytoplasm in the cell, what does the cytoplasm do in an animal cell