Where Is Energy Stored In A Molecule – ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate and is the energy used by an organism in its daily activities. It consists of a
, the energy released from the breaking of a molecular bond is the energy we use to stay alive.
Where Is Energy Stored In A Molecule
This is done by a simple process, where one of the 2-phosphate molecules is broken off, reducing ATP from 3 phosphates to 2, forming ADP (adenosine diphosphate after one of the phosphates is removed). This is usually written as ADP + Pi.
Solved Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Atp
While ATP is constantly consumed by the body in its biological processes, the energy supply can be boosted by making new sources of glucose available through food which is then broken down by the digestive system into smaller particles that can be used by the body.
In addition to this, ADP is built up into ATP so that it can be used again in its more energetic state. Although this conversion requires energy, the process produces a net gain in energy, meaning that more energy is available by recycling ADP+Pi to ATP.
A lot of ATP is needed every second by a cell, so ATP is created inside them due to the demand and the fact that organisms like ourselves are made up of millions of cells.
Glucose, a sugar delivered through the bloodstream, is the product of the food you eat, and it is the molecule used to create ATP. Sweet foods provide a rich source of readily available glucose while other foods provide the materials needed to create glucose.
Overview Of Metabolic Reactions
This glucose is broken down in a series of enzyme-controlled steps that allow the release of energy to be used by the organism. This process is called respiration.
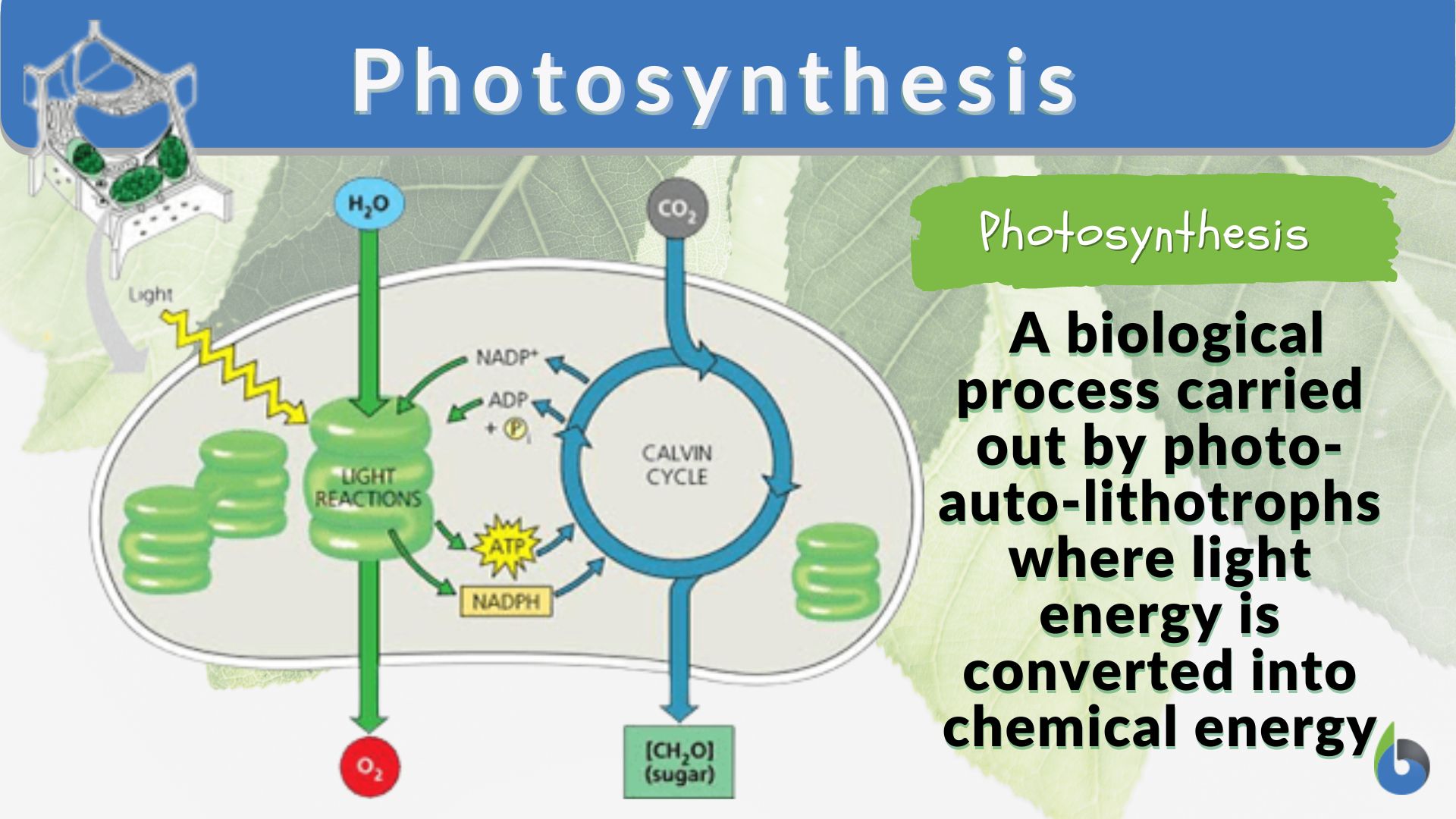
ATP is created via respiration in both animals and plants. The difference with plants is the fact that they get their food from elsewhere (see photosynthesis).
Essentially, materials are used to create ATP for biological processes. The energy can be created via cellular respiration. The breathing process takes place in 3 stages (when oxygen is present):

The following tutorial looks at the chemistry involved in respiration and the creation of ATP, and why oxygen is necessary for long-term respiration.
The Calvin Cycle
Nutrients in the soil are necessary for proper growth of a land plant. This tutorial is about the properties of soi..
This tutorial recognizes the importance of food as an energy source that will fuel many biological processes. A good d..
Plants produce hormones to regulate their growth. Auxins, for example, affect plant growth. Know the role of auxin in.. Food is basically solar energy stored in the form of complex biochemical substances. The process of releasing stored energy from food is almost as complex as the process of storing energy in food. This article will explain how this process works, as well as why it happens.
Chemical energy is simply energy stored in compounds or elements, specifically in the atomic bonds that connect atoms and molecules. In food, it is a form of potential energy because it is stored away. Then, through a process called chemical decomposition, the bonds containing the stored energy are broken, releasing energy that our bodies then use.
The Conversion Of Carbon Monoxide And Carbon Dioxide By Nitrogenases
Chemical energy can also be converted from one form to another. For example, when hydrogen gas is combined with oxygen, thermal energy and light energy are released through the combustion process. New covalent bonds are then formed between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms to form water.
Combustion is a simple, yet violent type of chemical reaction that releases heat, heat and sound energy. However, many chemical reactions are slow and barely noticeable, such as the rusting process, which is when metal oxidizes. Like combustion, roasting is a one-step process.
On the other hand, some chemical reactions are complex. These more complex processes are usually found in living organisms. The conversion of chemical energy from food, for example, is a multistep process that involves breaking down complex substances, such as carbohydrates and proteins, into their basic constituents, forming various intermediate compounds along the way.

Food is an example of stored chemical energy that is converted into usable energy by our cells. We all know what food is, but more specifically, it is any edible part of an animal, plant, algae, fungus, plankton, bacteria, or other organism that is absorbed by another organism as a source of nutrients and energy:
Plasmon Mediated Chemical Reactions
Fortunately for us, finding food is easier than that, but the process of how it is transformed in our bodies is just as complex. Food is used to make energy-rich molecules, such as ATP and NADPH. These molecules are then used by our cells to synthesize other molecules and form various biochemical products, such as enzymes and hormones. These complex metabolic processes synthesize proteins and other materials that eventually become parts of cells, tissues, and organs in all multicellular organisms (which includes us).
During this process, food is broken down into basic molecules, such as amino acids, lipids and glucose. These, among other organic molecular components, become the building blocks of the organism that ate the food. In humans, for example, amino acids from food are used to build up proteins that become part of our muscles.
At the most basic level, chemical energy in food is stored as molecular bonds. These molecular bonds represent potential energy, which is either very stable, such as in fat molecules, or very active and transient, such as in ATP molecules.
In living organisms, energy is also stored through the electron potentials across membranes, such as those in the thylakoid membranes during photosynthesis.
Ancient Chemistry: Why Living Things Use Atp As The Universal Energy Currency
There are several ways to store energy in food, including photosynthesis and chemosynthesis. Here on earth, the sun is the ultimate source of energy that is converted into food. Chemosynthetic bacteria that live in underwater darkness may seem to be the exception to this, but even these vampiric microorganisms are still indirectly dependent on the sun’s energy.
In our planet’s ecosystem, all organisms are potential food for other organisms. Therefore, all organisms are technically chemical energy storage units. Hierarchy is evident in all ecological systems, and you remember this interconnection of organisms as the food chain:
Then it is the turn of the decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi. These consume other organisms once they have died. The organic remains of other organisms are also taken up by producers as nutrients from the soil. That completes the cycle.

Food is used to make energy-rich molecules, such as ATP, the key molecule used by cells in metabolic processes
Adenosine Triphosphate (atp)
Cells release chemical energy from food through the process of respiration, which can be either aerobic or anaerobic. This process takes place mainly in the cells’ mitochondria.
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not. The release of energy is necessary to fuel the cells’ activities, such as biochemical synthesis, body repair and reproduction. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the key molecule used by cells in various metabolic processes.
Almost all activities in the cells require energy. These cellular activities are called metabolism, which can be divided into two categories:
The release of chemical energy from food is a catabolic process. But before cells can release energy, the food must first be digested, reduced to its basic components, absorbed by the cells and stored.
Atp Energy And The Proton Motive Force (pmf)
During aerobic respiration, oxygen reacts with the basic constituents of food, such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins. These are consumed as reactants to create ATP molecules. For example, ATP is produced when glucose reacts with oxygen during aerobic cellular respiration.
An energy transfer then occurs, which is used to break the molecular bond of ADP to add a third phosphate group, forming ATP molecules. NADH and FADH2 are also involved in the phosphorylation process at the substrate level.
Anaerobic respiration, on the other hand, is the main metabolic pathway in many species of bacteria and archaea. Since bacteria do not have specialized organelles, anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm. Instead of oxygen, anaerobic respiration uses sulfate, nitrate, sulfur, or fumarate as electron acceptors.

The chemical energy stored in food is released by cells through the process of respiration. This process has four steps and mainly produces ATP as the energy-carrying molecule that can be used by cells in their metabolic activities. The four steps in the process are:
We Need To Talk About The Energy In Chemical Bonds
The total ATP yield of respiration is 30 or 32 per glucose molecule. Although the theoretical yield is 38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule, some are lost because they are spent moving pyruvate from glycolysis, phosphate, and ADP into the mitochondria.
Chemical energy is stored in the food because of the different molecular bonds in the food and the electrochemical gradients they create. Depending on the type of food, these bonds can be either easy or difficult to break. The constituents of food, such as carbohydrates, fibers, minerals, fats and proteins, act as reactants.
They are broken down into basic molecules, such as amino acids and glucose, which are either used as energy or assembled and stored in other forms, such as glycogen. The presence of chemical energy in food is essential to give our bodies the energy they need to sustain
How is energy stored, energy stored in flywheel, where is the energy in an atp molecule stored, where in the atp molecule is energy stored, where is the energy stored in a capacitor, where is the energy in a glucose molecule stored, where is solar energy stored, where is energy stored, energy stored in capacitor, where is energy stored in a molecule, energy that is stored, the energy in this molecule is stored