What Is The Word Formula For Cellular Respiration – ATP production Cell metabolism Electron transport chain Energy conversion Glycolysis Krebs cycle Mitochondria Oxidative phosphorylation
Cellular respiration is a fundamental process that occurs in every living organism, from the smallest bacteria to complex multicellular organisms like humans. It is the process by which cells convert energy from nutrients into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the molecule that drives cellular activities.
What Is The Word Formula For Cellular Respiration

In this article, we’ll explore 15 interesting facts about cellular respiration that will not only improve your understanding of this vital biological process, but also spark your curiosity about the intricate mechanisms that sustain life.
Monosaccharide Definition And Examples
From the role of mitochondria in energy production to the different stages of cellular respiration, get ready to immerse yourself in the fascinating world of how our cells generate the energy they need to perform their functions. So let’s dive in and discover the remarkable things that make cellular respiration a truly fascinating area of biological study.
13 The rate of cellular respiration can be affected by factors such as temperature and nutrient availability.
Cells require a constant supply of energy to perform their functions, and cellular respiration provides them with the necessary fuel.
Glycolysis is the initial step, followed by the Krebs cycle and finally oxidative phosphorylation, where most ATP is generated.
Modeling Cellular Respiration Diagram
Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, leading to the production of ATP.
These by-products are expelled from cells through exhalation and help maintain the balance of gases in the environment.
This is different from anaerobic respiration, which can occur in the absence of oxygen and usually produces lactic acid or alcohol as waste products.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/cellular_respiration-8fcc3f1ad3e54a828dabc02146ce4307.jpg?strip=all)
During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to release energy that is stored and transferred in the form of ATP.
Question Video: Defining The Term “oxygen Debt”
Without this process, cells could not reproduce and organisms could not grow.
The rate of cellular respiration can be affected by factors such as temperature and nutrient availability.
Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of respiration, while a lack of nutrients can lead to a decrease in energy production.
In conclusion, cellular respiration is a fascinating process that is necessary for the survival of all living organisms. It provides the energy needed to perform various biological activities and is a fundamental process in the study of biology. Understanding the intricacies of cellular respiration allows us to appreciate the complexity of life and the interconnectedness of living systems.
Intriguing Facts About Cellular Respiration
From the production of ATP to the role of mitochondria, there are countless interesting things about cellular respiration. Research not only deepens our knowledge of biology, but also gives us insight into the beautifully orchestrated mechanisms that allow life to thrive.
Whether you are a student, a biology enthusiast, or simply curious about how organisms produce energy, entering the world of cellular respiration is an exciting journey that reveals the wonders of life.
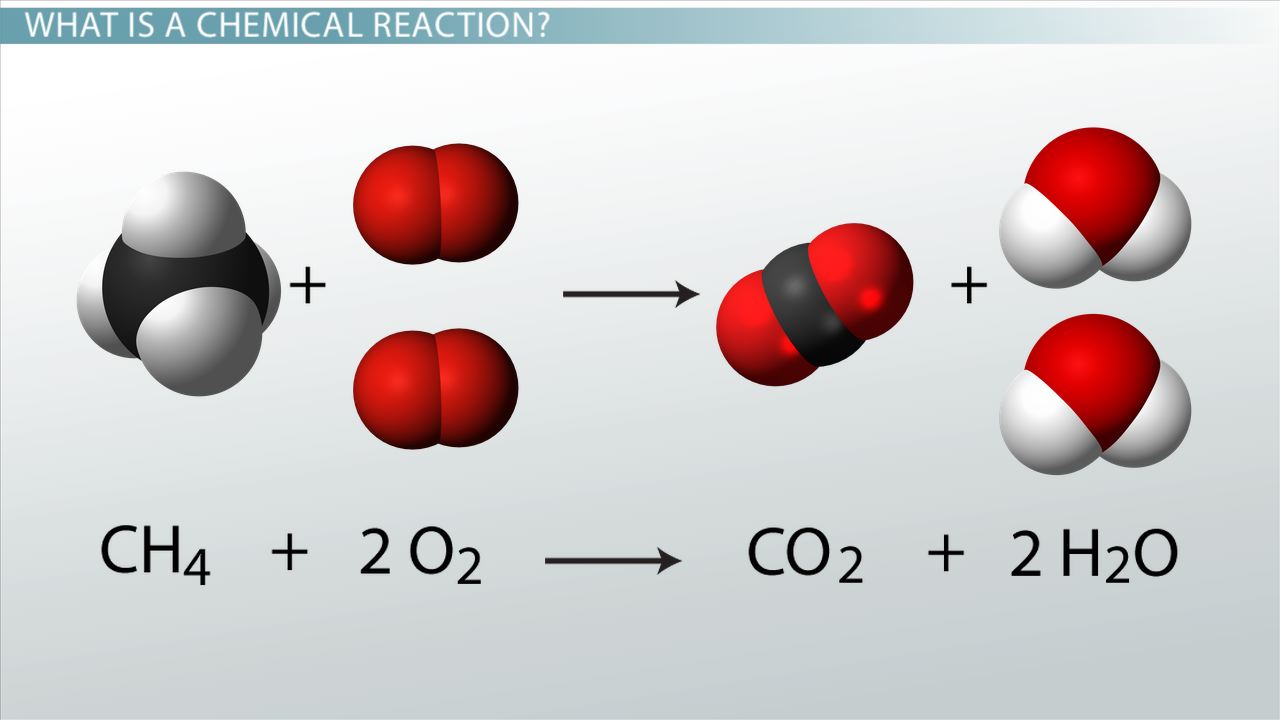
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide, water and energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).

Cellular respiration is essential for providing energy to carry out essential biological functions, such as growth, repair and movement. It is of vital importance for the survival of all living organisms.
Solved: Aerobic Respiration Is Represented By The Following Equation: C8h12o6 + 6 O2 → 6 Co2 + 6 H2o. Discuss Four Reasons Why This Equation Does Not Fully Represent Respiration. (4 Marks)
Cellular respiration takes place primarily in the mitochondria, which are often called the powerhouse of the cell. However, some initial reactions also occur in the cytoplasm.
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are interconnected processes. While cellular respiration involves breaking down glucose to produce energy, photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Yes, cells can perform a form of cellular respiration called anaerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen. This process produces less energy and creates lactic acid or ethanol as by-products. Home Games & Quizzes History & Society Science & Technology Biographies Animals & Nature Geography & Travel Arts & Culture Money Videos
Although every effort has been made to follow the rules of citation style, some deviations may occur. Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions.
Solved: 2. Write The Chemical Equations For Aerobic Respiration And Anaerobic Respiration
Encyclopedia Editors Encyclopedia editors oversee subject areas in which they possess extensive knowledge, whether through years of experience working on that content or through study for an advanced degree. They write new content and review and edit content received from contributors.
Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with food molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances to life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen break down food in a process called fermentation. (For longer treatments of various aspects of cellular respiration,
The three processes of ATP production include glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. In eukaryotic cells, the latter two processes occur within the mitochondria. Electrons passing through the electron transport chain eventually generate free energy capable of driving ADP phosphorylation.
One of the goals of breaking down food is to convert the energy contained in chemical bonds into the energy-rich compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which captures the chemical energy obtained by breaking down food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. In eukaryotic cells (that is, any cell or organism that has a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles), the enzymes that catalyze the individual steps involved in respiration and energy conservation are located in highly organized rod-shaped compartments called mitochondria. In microorganisms, enzymes occur as components of the cell membrane. A liver cell has about 1000 mitochondria; the large egg cells of some vertebrates have up to 200,000.
How Much Do You Know About Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration releases the stored energy in glucose molecules and converts it into a form of energy that cells can use.
Biologists differ somewhat on the names, descriptions, and number of stages of cellular respiration. The overall process, however, can be distilled into three major metabolic stages or steps: glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (phosphorylation of the respiratory chain).
Glycolysis (which is also known as the glycolytic pathway or the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnassus pathway) is a sequence of 10 chemical reactions that take place in most cells that break down a molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate (pyruvic acid). The energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during glycolysis is captured and stored in ATP. In addition, the compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD
). The pyruvate molecules produced during glycolysis then enter the mitochondria, where each is converted to a compound known as acetyl coenzyme A, which then enters the TCA cycle. (Some sources regard the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A as a separate step, called pyruvate oxidation or transition reaction, in the process of cellular respiration.)
What Is The Chemical Equation For Cellular Respiration?
The TCA cycle (which is also known as the Krebs cycle or the citric acid cycle) plays a central role in the breakdown or catabolism of organic fuel molecules. The cycle consists of eight steps catalyzed by eight different enzymes that produce energy in several different stages. Most of the energy derived from the TCA cycle, however, is captured by NAD compounds
And flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and later converted to ATP. The products of one turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NADs
) to the same number of NADH molecules and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to one FADH

Molecules. These molecules further drive the third phase of cellular respiration, while carbon dioxide, which is also produced by the TCA cycle, is released as a waste product.
Aerobic Respiration Developing: Describe What Respiration Is.
It provides a pair of electrons that – through the action of a series of iron-containing hemoproteins, cytochromes – eventually reduces one atom of oxygen to water. In 1951, it was discovered that the transfer of one pair of electrons to oxygen results in the formation of three molecules of ATP.
A series of steps by which electrons flow to oxygen allows for a gradual lowering of the electron energy. This part of the oxidative phosphorylation phase is sometimes called the electron transport chain.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the main mechanism by which large amounts of energy in food are stored and made available to the cell. A series of steps by which electrons flow to oxygen allows for a gradual lowering of the electron energy. This part of the oxidative phosphorylation phase is sometimes called the electron transport chain. Some descriptions of cellular respiration that focus on the importance of the electron transport chain have changed the name of the oxidative phosphorylation phase to the electron transport chain. Respiration is the process by which our bodies break down glucose to release energy. Energy is generated in the form of ATP to drive processes such as muscle contraction and cell division.
Aerobic respiration consists of four phases: glycolysis, bond reaction, Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. During aerobic respiration, glucose is efficiently burned in our bodies (reacts with oxygen) to produce carbon dioxide, water, and lots of energy in the form of ATP. The overall equation for aerobic respiration is:
Aerobic Respiration: Definition, Overview & Equation I Studysmarter
The first stage of aerobic respiration is glycolysis, which takes place in
What's the formula for cellular respiration, formula for aerobic cellular respiration, formula for cellular respiration, general formula for cellular respiration, what is cellular respiration, aerobic cellular respiration formula, what is the formula for cellular respiration, what is the formula for photosynthesis and cellular respiration, what is the chemical formula for cellular respiration, chemical formula for cellular respiration, the formula for cellular respiration, word formula for cellular respiration






