What Is The Significance Of Stem Cells – Discover the importance of stem cells and their transformative potential in modern medicine. Discover the science behind these different cells and their uses in different treatments.
Stem cells are immature cells that can develop into many different types of cells in the body. They are responsible for tissue repair and regeneration, and scientists and researchers have been studying stem cells for many years in hopes of finding new ways to treat and cure diseases.
What Is The Significance Of Stem Cells

The study of stem cells is known as stem cell research and is considered one of the most promising areas of medicine today. In this article, we will delve into the world of stem cells, exploring what they are, how they are used, and their potential in the future of medicine.
Nutrition And Stem Cell Integrity In Aging
Stem cells are some types of cells that can develop into many different types of cells in the body. They have special functions such as self-renewal through cell division and division into different types of red cells, such as red blood cells, cells that produce insulin, neurons, or other blood cells.
Stem cells are often called the “building blocks” of the body, as they can develop into any tissue or organ. It is found in various parts of the body, including bone marrow, blood, and embryonic tissue. The abundance of stem cells allows them to build any type of cell.
According to a study conducted in 2019, Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in the human body that have the potential to become any cell in the body. They can also reproduce and replenish themselves, making them unique compared to other cell types. These cells can be found in both embryonic and adult stages. (1)
Stem cells are important in the field of regenerative medicine and medical research, providing new ways to treat a wide range of diseases and conditions. Their unique ability to self-renew and differentiate into specialized cells makes them valuable tools in tissue repair, drug discovery, disease simulation, gene therapy, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine. By harnessing the power of stem cells, researchers and physicians aim to develop treatments that promote healing, restore function, and improve patient health.
Brush Up: Hematopoietic Stem Cells And Their Role In Development And Disease Therapy
Stem cells are considered very important in medical research due to their ability to differentiate into different types of cells and tissues, as well as their ability to self-renew. This makes it important in a variety of treatments, including regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and treating diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, MS, Crohn’s, and heart disease.
In addition, studying stem cells can provide important information on the development and progression of various diseases and can help in developing new treatments and therapies. As such, stem cells have become an important area of focus in biomedical research, with many researchers and scientists working to unlock the full potential of these cells in the quest to improve human health.
This section will discuss the different types of stem cells in the human body and their different functions. These types include embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells. Understanding the different types of stem cells is important to understanding their potential applications in medical research and treatments.

These stem cells are taken from the early embryonic stage of human development, usually from the blastocyst stage of the embryo. They are pluripotent, meaning they have the potential to differentiate into any cell type in the body. Human pluripotent stem cells can make any cell in the body.
Facts About Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are taken from the innermost cells of the blastocyst, the first embryo. They have the unique ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body and have the potential to self-renew. This variety makes them important for medical research, since they have the possibility of being used to replace damage or loss of tissue in various diseases and injuries.
Embryonic stem cells used in research today come from unused embryos. This is due to the in vitro fertilization process. Embryonic stem cells have been shown to have a high degree of pluripotency, meaning they can differentiate into a variety of cell types. Using embryonic stem cells in research and medical applications also poses some risks. Another major concern is the ability of tumors to grow, as embryonic stem cells can divide and grow uncontrollably.
In addition, embryonic stem cells may not be compatible with the host, leading to rejection or an immune response. There are also ethical concerns and potential legal issues surrounding embryonic stem cells, since they are obtained from human embryos that have been destroyed in the process.
Embryonic and adult stem cells are immature cells that can differentiate into different types of cells in the body. However, some important differences between the two types of stem cells make stem cells more interesting for clinical use.
Hematopoietic Stem Cell
One important difference between embryonic and adult stem cells is the source of the cells. Embryonic stem cells develop from embryos, while stem cells are found in various tissues in the body, such as bone marrow, umbilical cord, adipose tissue (fat), and blood. This makes mature cells more accessible and less aggressive, which is important for clinical use.
In addition, embryonic stem cells can form tumors in therapy. This is because they can continue to divide and make new cells, leading to abnormal cell growth. Adult stem cells, on the other hand, have a lower risk of forming tumors because they tend to be larger and less capable of dividing.
Stem cell research suggests that adult stem cells are particularly suitable for clinical use due to their targeted differentiation ability, availability, and low risk of tumor formation. While embryonic stem cells have a wide range of differentiation, adult cells are more specific, easier to obtain, and less dangerous, making them a promising option for therapeutic applications.

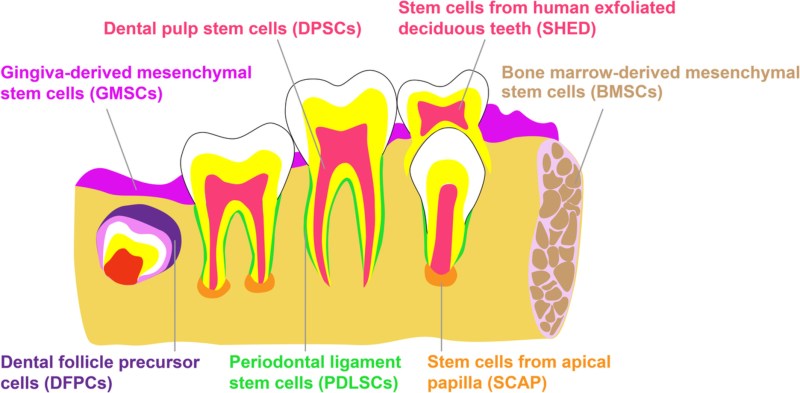
Somatic or adult stem cells (ASCs) are undifferentiated cells found throughout the body after regeneration. These cells are important in daily healing, growth, and replacement of lost cells. Some examples include:
Next Generation Stem Cells — Ushering In A New Era Of Cell Based Therapies
ASCs are undifferentiated cells found among differentiated cells in the body after regeneration. They can regenerate and differentiate into different types of cells, depending on their location in the body. Adult pluripotent stem cells may also prove useful in therapy; however, researchers are actively looking for ways to promote the cultivation of these cells in laboratory settings.
They have fewer differentiation options compared to embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells can be found in bone marrow, skin, and neural tissue. They play an important role in maintaining proper functioning and repairing body tissues. Human cells can also be used for therapeutic purposes in regenerative medicine.
Adult stem cells play an important role in healing and repairing the body by replenishing damaged or lost tissue. Unlike embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells have a more limited type of differentiation and can only create specific types of cells within the tissues in which they are found.
Research on stem cells has led to the development of various therapeutic applications, such as using hematopoietic stem cells to treat blood cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma and mesenchymal stem cells to treat bone and cartilage disorders such as osteoarthritis. Stem cells have also been used in the treatment of skin conditions such as burns and wound healing, as well as neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and spinal cord injuries.
Hc Allows Stem Cell Therapy For Autistic Kids
Clinically, stem cells are usually obtained from bone marrow, umbilical cord tissue, or adipose tissue through simple and minimal procedures. The cells are then separated, expanded, and differentiated in the laboratory before being returned to the patient’s body to treat a disease or injury.
In general, this provides a promising method for the development of regenerative medicine and has already shown good results in the treatment of various diseases. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential of stem cells and to develop safe and effective treatments for many conditions.
Induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPS cells, are cell lines created by reprogramming mature, specialized cells back to embryonic stem cell-like conditions using specific genetic factors. The first successful generation of PS cells in mice was created by introducing four key genetic factors, Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc, into cells using a retroviral vector. These stem cells are produced by modifying adult cells, such as skin cells, to a pluripotent state. They can differentiate into any cell in the body, similar to embryonic stem cells. (2)

IPS cells have been successfully derived from various types of cells, including fibroblasts, pancreas, leukocytes, hepatocytes, keratinocytes, neural stem cells, cord blood cells, etc. These findings show that many types of cells can be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state and that the average process of cell specialization can be reversed through experimental methods. Some types of cells, such as the so-called neuronal progenitors, which already express one or more important reprogramming factors, may be more suitable for reprogramming.
Significance Of Hla Typing In Stem Cell Transplantation
Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells are cells made from adult cells and reprogrammed to have the same characteristics as embryonic stem cells. These cells can differentiate into different types of cells and have the potential to regenerate. IPS cells
What is the use of stem cells, what is the job of stem cells, cryopreservation of stem cells, what is the role of stem cells, preservation of stem cells, what is the source of stem cells, significance of stem cells, what is the function of stem cells, what is the meaning of stem cells, production of stem cells, what is the stem cells, what is the definition of stem cells