What Is The Role Of Cholesterol In The Body – Biochemistry and Metabolism Amino Acid Metabolism Nitrogen and Urea Cycle Citric Acid Cycle Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation Glucogenesis Glycogen Metabolism Glycolysis Pentose Phosphate Pathway Physiological Changes During Exercise Cholesterol Metabolism T. Acid oxidation
Metabolic disorders Alkaptonuria Cystinuria (NORD) Hartnup disease Homocystinuria Maple syrup urine disease Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency Phenylketonuria (NORD) Essential fructosuria Galactosemia Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Deficiency lipoproteinemia Familial Hypercholesterolemia Hyperlipidemia Hypertriglyceridemia Glycogen storage disease type I Glycogen storage disease type II (NORD) Glycogen Storage disease type III Glycogen storage disease type IV Glycogen storage disease type V V Mucopolysaccharide storage disease type 1 (Holler syndrome) (NORD) Mucopolysaccharide storage disease type 2 (Hunter syndrome) (NORD) Fabry. Diseases Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism: Pathology Review Disorders of Fatty Acid Metabolism: Pathology Review Dyslipidemias: Pathology Review Glycogen Storage Disorders: Pathology Review Lysosomal Storage Disorders: Pathology Review
What Is The Role Of Cholesterol In The Body

A research study is conducted to better understand the function of a molecule that leads to hardening of the coronary arteries when high concentrations are found in mouse models. An adrenal biopsy isolates the compound with the chemical structure given below Which of the following describes a complex cellular function of this molecule?
Hyperlipidemia (high Cholesterol): Levels, Causes, Symptoms & Diagnosis
Cholesterol is a lipid molecule that helps maintain the structure of cell membranes and is a precursor to steroid hormones, bile acids, and vitamin D.
Next, the enzyme HMG-CoA synthase combines acetoacetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA to form a 6-carbon molecule called 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA or HMG-CoA—so 3 acetyls and one free CoA molecule.
Then, an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase reduces HMG-CoA to mevalonate, removing a CoA-SH and a water molecule.
In other words, the rate of this reaction determines the overall rate of cholesterol synthesis—the slowest step on the assembly line for a factory.
The Role Of Cholesterol In Health And Disease
Currently, cholesterol synthesis is controlled by a trio of proteins – sterol regulatory element binding protein – or SREBP and two others that go by only SCAP and INSIG-1.
In that situation, INSIG-1 is released from SREBP like pulling a pin from a grenade, and the SREBP-SCAP complex is then cleaved by cellular enzymes.
Once HMG-CoA reductase has made 6 carbons of mevalonate, it undergoes several additional enzyme-mediated transformations before becoming cholesterol.

Finally, mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase removes a carboxyl group from it to form a 5-carbon molecule called isopentenyl pyrophosphate.
Cholesterol Handout — Functional Health Research + Resources — Made Whole Nutrition
Next, geranyl transferase condenses 3 of these isopentenyl pyrophosphate molecules to form a 15-carbon molecule called farnesyl pyrophosphate.
Cholesterol is a lipid molecule that helps synthesize hormones, cell membrane integrity, and other important compounds. Cholesterol is synthesized in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of cells throughout the body, but mainly in the liver. The rate-limiting step of this reaction is the reduction of HMG CoA to mevalonate, which is catalyzed by HMG-CoA reductase.
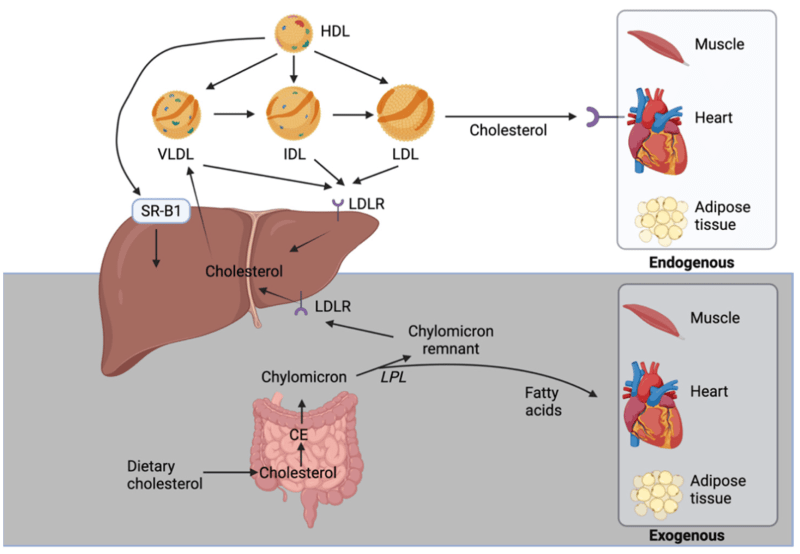
Some of the cholesterol in the blood comes from food Dietary cholesterol is found in meat, poultry, fish and dairy products Cholesterol is transported in the bloodstream and attached to proteins called lipoproteins, which carry it to the cells that need it.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier, its licensors and affiliates All rights reserved including text and data mining, AI training and similar technologies
Study Challenges
The USMLE® is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB) and the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME). COMLEX-USA® is the National Board of Osteopathic Medical Examiners, Inc. NCLEX-RN® is a registered trademark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc. Trademark holder None of the trademark holders are endorsed or affiliated with this website.
Open Access Policy Institutional Open Access Program Special Issue Guidelines Editorial Process Research and Publication Ethics Article Processing Charges Award Testimonials.
All published articles are immediately available worldwide under an open access license No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the published article, including figures and tables For articles published under an open access Creative Commons CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https:///openaccess

Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for further impact in the field A feature paper should be a substantial original article that covers several techniques or approaches, provides a perspective for future research directions, and describes possible research applications.
How Cells Handle Cholesterol
Feature papers are submitted by the Scientific Editor upon individual invitation or recommendation and must receive positive feedback from reviewers.
Editors’ Choice articles are based on recommendations from scientific editors of journals from around the world. The editors select a small number of recently published articles in journals that they believe will be of particular interest to readers or will be important in relevant research areas. Its aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the journal’s various research areas
Google Scholar Anna K. Hottinsky, Anya K. Google Scholar Brian J. Kus Skillet Printers dot.
Received: 8 May 2023 / Revised: 13 June 2023 / Accepted: 19 June 2023 / Published: 27 June 2023
What Is Ldl Cholesterol?
Cholesterol has many complex functions in cells It is a key component of membranes and cell-signaling processes, and acts as a chemical precursor in many biochemical pathways, such as vitamin D and steroid synthesis. Cholesterol has also been implicated in the development and progression of various cancers, including promoting cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is an example of a lipid-avid cancer that relies on lipid metabolism rather than glycolysis for cell proliferation. However, data regarding the role of cholesterol in CLL are conflicting Studies have shown that dyslipidemia is more common in CLL patients than in age-matched healthy controls, and CLL patients taking cholesterol-lowering drugs such as statins appear to have improved survival rates. Therefore, defining the role of cholesterol in CLL may emphasize monitoring and management of hyperlipidemia as part of the routine care of CLL patients. In this review, we discuss the role of cholesterol in the context of CLL by examining the literature on the trafficking, uptake, endogenous synthesis, and intracellular handling of this lipid. Data from clinical trials investigating different classes of cholesterol- and lipid-lowering drugs are also discussed.
It has been recognized for nearly a century that nutrition plays an important role in cancer. There is growing evidence that cholesterol, a type of lipid, plays a major role in carcinogenesis. Several studies, both in vitro and clinically, have shown that hypercholesterolemia may influence the development of cancer. For example, a 10mg/dL increase in cholesterol levels was associated with a 9% increase in prostate cancer recurrence. In a study of nearly 300,000 Danish patients, lowering cholesterol levels through the use of drugs such as statins showed a small reduction in cancer-related mortality in 13 different types of cancer.
There is evidence that serum cholesterol levels begin to decline 6 years before diagnosis in colon cancer and chronic myeloid leukemia [ 5 , 6 ], suggesting that cholesterol levels may be an early predictor of cancer development for some tumors. Conversely, epidemiological studies have shown that elevated serum cholesterol is positively associated with a higher incidence of certain cancers, such as those of the colon, prostate, and testes [2, 7]. Data from these studies suggest that cholesterol levels may be critical in some tumors, a review by Ding et al. [8] suggests that the link between cancer progression and cholesterol is more complex than a simple two-factor association, and that other factors such as cholesterol requirements for cancer origin and dietary habits may be more critical. For example, more aggressive disease was observed in bladder cancer patients receiving statins, and large studies conducted in the 1970s showed that low cholesterol levels were associated with colon and lung cancer [6, 10]. These studies, among others, point to the need for further research into whether targeting cholesterol metabolism may represent a promising therapeutic approach for cancer.

Cholesterol in humans can be produced endogenously or derived from exogenous dietary sources. Endogenous cholesterol production is regulated by the enzyme hydroxy—methylglutaryl co-enzyme reductase (HMG-CoA reductase) and is synthesized primarily in the liver, where it is packaged into low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Cholesterol can also be sourced from food
Cellular Itinerary Of Ldl Cholesterol
What is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane, what is the role of cholesterol, what is the purpose of cholesterol in the body, what is the role of hdl cholesterol, what is the function of cholesterol in the body, what is the role of stem cells in the body, what is the role of triglycerides in the human body, role of cholesterol, role of cholesterol in the body, what is the level of cholesterol in human body, what is the role of iron in the body, what is the role of collagen in the body