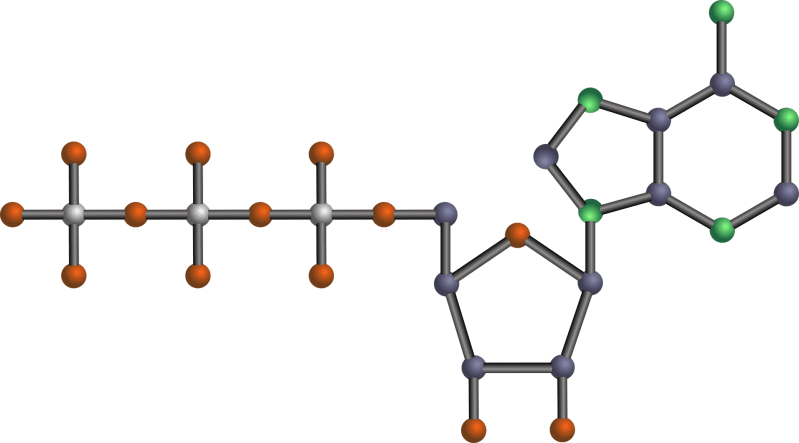
What Is The Role Of Atp In Energy Transfer – ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. It consists of a
, the energy released from breaking a molecular bond is the energy we use to keep us alive.
What Is The Role Of Atp In Energy Transfer

This is done by a simple process, where one of the 2 phosphate molecules is broken, thus reducing ATP from 3 phosphates to 2, forming ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate after removal of one of the phosphates). This is commonly written as ADP + Pi.
Atp: Energy Currency Of The Cell
While ATP is constantly being used by the body in its biological processes, the energy supply can be sustained by new sources of glucose that are available through the consumption of food which are then broken down by the digestive system into smaller particles that can be used by the body. body.
In addition, ADP is built back into ATP so that it can be used again in its more energetic state. Although this conversion requires energy, the process produces a net energy gain, meaning that more energy is available by recycling ADP+Pi back into ATP.
Many ATPs are needed every second by a cell, so ATP is created within them due to demand and the fact that organisms like us are made up of millions of cells.
Glucose, a sugar that is delivered through the bloodstream, is the product of the food you eat, and this is the molecule that is used to create ATP. Sweet foods provide a rich source of readily available glucose, while other foods provide the materials needed to create glucose.
Magnesium In Biology
This glucose is broken down in a series of enzyme-controlled steps that allow the release of energy to be used by the body. This process is called respiration.
ATP is created through respiration in both animals and plants. The difference with plants is that they get their food from somewhere else (see photosynthesis).
Essentially, materials are harnessed to create ATP for biological processes. Energy can be created through cellular respiration. The breathing process takes place in 3 stages (when oxygen is present):

The following tutorial looks at the chemistry involved in respiration and the creation of ATP and why oxygen is essential for long-term respiration.
Atp (adenosine Triphosphate) — Structure & Function
The Earth’s ecosphere is changing rapidly and is creating a wide range of ecological niches for new adaptive organisms.
Mātauranga Māori is the living knowledge system of the indigenous people of New Zealand, including the relationships t..
This tutorial looks at the relationship between organisms. It also explores how energy is transmitted in the food chain and…
According to Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection, preferred genes are favored by nature in the genetic background and…
Solved] All Organisms Utilize Adenosine Triphosphate (atp) As Their Major…
Various pregnancy and birth control strategies are described. Read this tutorial to learn each of the…
Organisms use different strategies to enhance their defenses against antigens. Humans have an immune system to fight pat..) An organic compound that is composed of adenosine (an adenine ring and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups, hence the name; a nucleotide with the chemical formula C
A nucleotide is an organic compound consisting of three subunits: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. The sugar component can be either

With a phosphate group. Depending on the number of phosphate groups attached to the sugar moiety, a nucleotide can be called
Atp—the Universal Energy Currency
. Also, depending on the nucleobase component, nucleosides can be grouped into either “double-ring” purine or “single-ring” pyrimidine.
Phosphate groups. It means it has a ribose attached as a sugar and three phosphate groups. Its structure consists of a purine base, specifically adenine that is linked at the 9′ nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a ribose sugar and three phosphate groups. Removal of one or two phosphate groups produces adenosine monophosphate or adenosine diphosphate, respectively.
In eukaryotes, ATP is biosynthesized by three major pathways: (1) glycolysis, (2) Krebs cycle, and (3) beta-oxidation. The first pathway occurs in the cytoplasm, while the next two pathways occur in the mitochondria.
Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic processes in which biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance (eg glucose) and stored in energy carriers such as ATP. Glycolysis is the initial step of cellular respiration that is involved in the cellular breakdown of the simple sugar glucose to pyruvate to produce high-energy molecules such as ATP and NADH.
Nad+ Metabolism: Pathophysiologic Mechanisms And Therapeutic Potential
The Krebs cycle is a step of cellular respiration after glycolysis and is characterized by the decarboxylation of pyruvate. It involves a cyclic series of enzymatic reactions by which pyruvate – transformed into acetyl coenzyme A – is completely oxidized to CO
With this, a hydrogen ion is removed from the carbon molecules, transferring the hydrogen atoms and electrons to electron-carrying molecules (eg NADH and FADH).
From the complete oxidation of pyruvate is removed from the cell into the blood. The electron and hydrogen carriers, NADH and FADH
, donates these electrons to the electron transport chain to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, the final metabolic pathway of cellular respiration.
Atp Definition And Importance In Metabolism
In eukaryotes, the Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria, while in prokaryotes, it takes place in the cytoplasm.
In plants, ATP can also be produced by photosynthesis in chloroplasts. It is also formed as one of the end products of photophosphorylation and fermentation. Fermentation is a cellular process used by certain cells and organisms (eg, yeast) to convert organic foods into simpler compounds. By doing so, chemical energy (eg ATP) is generated.
Fermentation differs from cellular respiration in a way that it uses organic compounds such as carbohydrates as (endogenous) electron acceptors instead of molecular oxygen (which is an exogenous electron acceptor in cellular respiration). However, compared to oxidative phosphorylation (of cellular respiration), fermentation produces less ATP.
In mammalian muscles, they switch from oxidative phosphorylation to fermentation when oxygen supply becomes limited, especially during intense activity such as vigorous exercise.
Molecular Mechanism On Forcible Ejection Of Atpase Inhibitory Factor 1 From Mitochondrial Atp Synthase
ADP is converted to ATP by the addition of a phosphate group. This occurs in processes such as substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation, and photophosphorylation.
ATPs are vital in intracellular energy transport for various metabolic processes, including biosynthetic reactions, motility, and cell division. It is also used as a substrate by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids and by adenylyl cyclase to produce cyclic AMP.
ATP can be degraded into AMP and pyrophosphate: ATP → AMP + PPi by hydrolysis. AMP can be further degraded by its conversion to uric acid which in mammals is excreted from the body.

ATP contains a large amount of chemical energy stored in its high-energy phosphate bonds. Releases energy when broken down (hydrolyzed) into ADP (
Adenosine Triphosphate (atp) Energy Transport Molecule Stock Illustration
). Energy is used for many metabolic processes. Therefore, ATP is considered the universal energy currency for metabolism. Its functions are intracellular transport of energy for various metabolic processes, including biosynthetic reactions, motility and cell division.
ATP also serves as a source for ADP and AMP. ADP is essential in photosynthesis and glycolysis. It is the final product when adenosine triphosphate ATP loses one of its phosphate groups. The energy released in this process is used to fuel many vital cellular processes. ADP is also important during platelet activation. It is stored inside platelets and is released to interact with ADP receptors (eg, P2Y1 receptors, P2Y12 receptors, etc.) on platelets.
Plant cells have plastids essential in photosynthesis. They also have an extra layer called a cell wall on the outside of their cell. Although animal cells lack these cellular structures, both have a nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. Read this tutorial to learn the structures of plant cells and their roles in plants…
Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. Plant processes such as photosynthesis, photophosphorylation, chemiosmosis, carbon fixation reactions, respiration are presented in this tutorial…
Adenosine Triphosphate (atp) Molecule. Functions As Neurotransmitter, Rna Building Block, Energy Transfer Molecule, Etc Skeletal Stock Illustration
A typical eukaryotic cell consists of cytoplasm with various organelles such as nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria and so on. The cell contents are surrounded by a double layer, the cell membrane. These cell structures and cell junctions are elaborated in this tutorial…
Proteins play a crucial role in various biological activities. Learn how proteins can function as enzymes, cofactors or regulators. In this tutorial, you will also learn about the common metabolic pathways of biomolecules such as glucose and other carbohydrates, fats, proteins and essential amino acids and nutrients… What is adenosine triphosphate: ATP is a nucleoside, which serves as one of the essential energy carriers in the cell. It also plays a vital role in energy storage and transfer. ATP exists in both organic and inorganic forms. The organic structure of the molecule comprises adenine, ribose and phosphate groups, and the inorganic form comprises ATP with two or three phosphates attached. Addition or removal of phosphate results in adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
In atp adenosine triphosphate, the energy released when ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and AMP is used to power metabolic reactions and other cellular processes, such as the movement of proteins within cells through active transport across plasma membranes and muscle contraction. ATP is constantly produced in cells by various cellular metabolisms; however, when more energy is needed for a particular process, ATP could be

How is the energy in atp released, what is the role of atp in photosynthesis, what is the role of atp in energy production, is atp energy, where is the energy stored in atp, what is the role of atp synthase in photosynthesis, what is atp energy, role of atp in muscle contraction, what is the role of atp, what is the role of atp in cross bridge cycling, what is the role of atp synthase, the role of atp in cells