What Is The Role Of A Nerve Cell – Neurons (or nerve cells) are the main functional units of the brain and nervous system. They are messengers and use electrical impulses and chemical signals to transmit messages between different regions of the brain, between the brain and the rest of the nervous system.[1] There are thousands of types of neurons, but scientists classify them into three broad types based on function:[2]
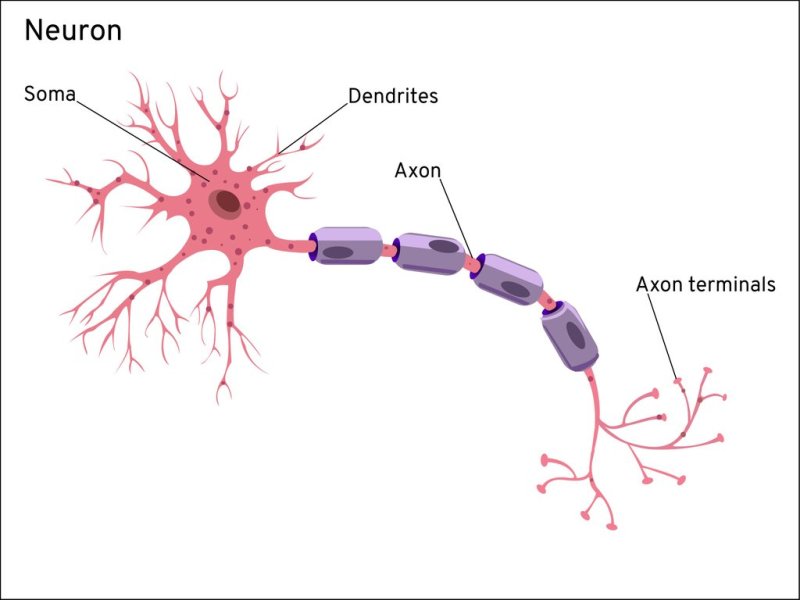
Neurons are structured and function differently than other types of cells – they are specially designed for the purpose of communication between cells. A neuron has three main parts: a body (or soma), dendrites, and an axon.
What Is The Role Of A Nerve Cell

The cell body (soma) is the base of the neuron. It contains genetic information, maintains the structure of the neuron, and provides the energy to carry out the neuron’s functions.[3]
Peripheral Nervous System: What It Is And How It Works
An axon is a long thin membrane that carries information from its home neuron to another neuron by electrical impulses. Many axons contain a fatty substance called myelin, which helps axons conduct electrical signals.[4]
Dendrites are where the neuron receives information from other cells. They branch out from the body like antennae and receive and process signals from the axons of other neurons. Neurons can have multiple sets of dendrites, depending on the function of the neuron.[5]
The junction where two neurons meet is called a synapse, and is the site of communication. Neurons communicate with each other through action potentials (changes in the electrical potential of the neuron) and neurotransmitters.[6]
When an action potential is triggered in a neuron, it travels down the axon and releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft, the gap between the axon Neuron A and the dendrite on the B Neuron.[7] Neurotransmitters travel across the synaptic cleft and attach to receptors on the dendrite of Neuron B. Depending on the neurotransmitter released, positive or negative ions pass through the membrane of the dendrite, create an electrical signal at Neuron B. Basically, the synapses convert the electrical signal (action potential) into chemical signals (neurotransmitters) and back in. an electrical signal when it encounters the next neuron.[8]
What Are Glial Cells: Types And Functions
As key players in neuron communication, neurotransmitters are an important part of daily functioning. Scientists have discovered over 100 different neurotransmitters, each of which has a different effect on the human brain chemistry. Abnormal levels of certain neurotransmitters may contribute to mental health conditions.[9]
Serotonin is the main chemical that stabilizes the mood and emotions of life. It also helps regulate appetite, digestion, and sleep. Many antidepressants are SSRIs, or selective reuptake inhibitors, and reduce depression and anxiety by increasing serotonin levels in the brain.[10]
Dopamine is important for memory, learning, behavior, and motivation. It is sometimes called the “reward” neurotransmitter because it produces positive feelings associated with accomplishments that motivate us to continue with a task. Dopamine is also associated with pleasure and is released during pleasurable activities.[11]

Norepinephrine, also known as noradrenaline, helps the body respond to stress and increases as part of the fight or flight response. It also helps signal the body when to wake up each morning, increase attention to tasks, and aid in memory storage. Low levels of norepinephrine are associated with depression, anxiety, PTSD, and substance abuse, but substance abuse can lead to euphoria and even panic attacks.[12] Some mental health medications are SNRIs (serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) and act on both neurotransmitters.
Teaching The Nervous System
Scientists believe that abnormalities in the functioning of certain brain circuits lead to the development of many mental health conditions. Connections between neurons along specific brain pathways can contribute to challenges in how the brain processes information, sometimes resulting in negative moods, thoughts, or behaviors.[13] It’s not just brain chemistry that affects the brain – the brain also responds to signals from the gut, or “second brain.” The brain and gut communicate through chemicals such as hormones and neurotransmitters, and those chemical messengers are affected by gut bacteria (called the “gut microbiome”). To learn more about the gut-brain connection and other non-pharmacological approaches to managing mental health challenges, visit MHA’s Science Hub. Neurons are responsible for carrying information throughout the human body. Using electrical and chemical signals, it helps coordinate all of the world’s activities.
In short, our nervous system detects what is happening around us and in us; it determines how we act, changes the state of the internal organs (heart rate changes, for example), and allows us to think and remember what is going on. To do this, it depends on an advanced network – neurons.
Each neuron is connected to another 1,000 neurons, creating a very complex network of communication. Neurons are considered the basic units of the nervous system.
Neurons, sometimes called nerve cells, make up about 10 percent of the brain; the rest are glial cells and astrocytes that support and nourish neurons.
Myelin Sheath: What They Are, Their Function, & Damage
Dendrites — these thin fibers carry information from other neurons to the soma. They are the “input” part of the cell.
Axon — this long projection carries information from the soma to other cells. This is the “outside” part of the cell. It usually terminates with many synapses that connect to the dendrites of other neurons.
Axons vary in length. Some are small, while others can be more than 1 meter long. The longest axon is the

(DRG), a group of nerve cells that carry information from the skin to the brain. Some of the axons in the DRG go from the toes to the brainstem – up to 2 meters in a tall person.
Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology
Efferent neurons — take messages from the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and send them to cells in other parts of the body.
Afferent neurons — receive messages from the rest of the body and send them to the central nervous system (CNS).
If a neuron receives too many inputs from other neurons, these signals are added until a threshold is reached.
When this threshold is exceeded, the neuron is allowed to send an impulse along its axon – this is called an action potential.
Structure And Functions Of Neurons
Neurons at rest are more negatively charged than the fluid that surrounds them; this is called the membrane potential. This means -70 millivolts (mV).
When a nerve cell receives signals large enough to fire, the portion of the axon near the cell body decreases – the membrane potential falls faster (in 1,000th of a second ). This change begins to reduce the length of the axon along the edge, and so on, until the control increases and decreases along the entire length of the axon.
After each unit is fired, it enters a short state of hyperpolarization, and its threshold is lowered, which means that the immediate stimulus will be less.
) ion that produces the work force. Ions move in and out of axons through voltage-gated ion channels and pumps.
Cancer And The Nervous System
The characteristics of the works are called “all or nothing” because they are of the same size. The intensity of the stimulus is released with frequent use. For example, if the stimulus is weak, the neuron will fire less, and for a strong signal, it will fire more.
There are small areas in the myelin coating, called nodes of Ranvier. As the energy jumps from place to place, the signal moves faster.
Neurons connect with each other and tissues so that they can communicate; however, they do not physically affect each other – there is a space between cells, called a synapse.
Synapses are either electrical or chemical. In other words, the signal is carried from the first nerve fiber (presynaptic neuron) to the next (postsynaptic neuron) by an electrical or chemical signal.
Motor Neuron Research Could Broaden Understanding Of Nerve Cells
When the signal reaches the synapse, substances (neurotransmitters) are released into the space between the two neurons; this area is called the synaptic cleft.
The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and interacts with receptors on the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron, causing a response.
Glutamergic — releases glutamine. They are often motivated, which means they are more motivated to work.

GABAergic — releases GABA (gamma-Aminobutyric acid). They are often inhibitory, which means they reduce the chance that the postsynaptic neuron will fire.
The Peripheral Nervous System
Are rare but can be found throughout the CNS. Channels called gap junctions connect the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes. In gap junctions, the post- and presynaptic membranes are much closer to the chemical synapses, which means that electrical current can be transferred directly.
Electrical synapses work faster than chemical synapses, so they are found in places where they need to work quickly, for example in barrier mirrors.
Chemical synapses can trigger complex reactions, whereas electrical synapses can produce simple responses. However, unlike chemical synapses, they are bidirectional — information flows in one direction.
Neurons are one of the most interesting types of cells in the human body. It is essential for every function our body and brain perform. The complexity of neuronal connections gives us our personality
Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception And Response
What is the role of cytoplasm in the cell, what is the role of enzymes in the cell, what is the nerve cell, what is the role of a nerve cell, role of vagus nerve, what are the types of nerve cell, what is the role of a red blood cell, what is the role of proteins in the cell membrane, role of optic nerve, what is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane, what is the role of the white blood cell, what is atp role in the cell