What Is The Purpose Of Cholesterol In The Cell Membrane – Considering collagen drinks and supplements? Going through middle school is tough: How parents can help Is Internet Gambling Harmful? Preventable liver disease on the rise: What you eat – and avoid – counts Fall shots: Who’s most vulnerable to RSV, COVID, and the flu? Do you have immunity? Thank your thymus Easy ways to buy whole, low-cost foods When – and how – should you be screened for colon cancer? 7 organs or glands you can do well without How to help your child get the sleep he needs
Only about 20% of the cholesterol in your blood comes from the food you eat. Your body does the rest.
What Is The Purpose Of Cholesterol In The Cell Membrane

Cholesterol has a bad name, because of its known role in promoting heart disease. Excess cholesterol in the blood is a major contributor to artery-clogging plaque, which can accumulate and predispose to heart attack. However, the role of cholesterol in your body is not all bad.
The Effects Of Cholesterol On The Body
To fully explain cholesterol, you must realize that it is also important for your health. Although we measure the production of cholesterol in the blood, it is found in all cells of the body. The Harvard Special Report on Controlling Your Cholesterol describes cholesterol as a waxy, yellowish-white fat and an important building block in cell membranes. Cholesterol is also needed to make vitamin D, hormones (including testosterone and estrogen), and fat-dissolving bile acids. In fact, the production of cholesterol is so important that your liver and intestines make about 80% of the cholesterol you need to stay healthy. They only eat about 20 percent of the food. (See example.)
If you eat only 200 to 300 milligrams (mg) of cholesterol per day (one egg yolk contains 200 mg), your liver will produce an additional 800 milligrams per day from carbohydrates such as fat, sugar, and protein. .
Since cholesterol is a fat, it cannot travel alone in the bloodstream. It will end up as useless globs (imagine bacon fat floating in a pot of water). To get around this problem, the body packages cholesterol and other lipids into protein-coated particles that mix easily with the blood. These small particles, called lipoproteins (lipid plus protein), transport cholesterol and other fats throughout the body.
Cholesterol and other lipids circulate in the blood in many different ways. Of these, the one receiving the most attention is low-density lipoprotein—more commonly known as LDL, or “bad” cholesterol. But lipoproteins come in a range of shapes and sizes, and each type has its own functions. They also change from one form to another. These are the five main types:
Can Cholesterol Be Too Low?
Share This Page Share This Page On Facebook Share This Page On Twitter Share This Page By Email
As a service to our readers, Harvard Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the deadline for reviews or updates on all articles.
No content on this site, regardless of date, should be used as a substitute for medical advice from your doctor or other qualified practitioner.

Staying y Immune boost or explosion? From IV drips and detoxes to superfoods Diseases and Conditions y food to control blood sugar Nutrition Nourishing body and soul
Low Levels Of Hdl (the “good” Cholesterol) Appear Connected To Many Health Risks, Not Just Heart Disease
The best food for Cognitive Fitness, FREE when you sign up to receive alerts from Harvard Medical School
Subscribe for lifestyle tips, and ways to fight inflammation and improve cognition, as well as the latest advances in preventive medicine, diet and exercise, pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
Get helpful tips and guidance on everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss… from exercises to build a strong core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from experts at Harvard Medical School. The lock (lock symbol) or https:// means you are connected securely to a .gov website. Share sensitive information only with legitimate, secure websites.
Cholesterol is a fibrous, fat-like substance found in all the cells of your body. Your body needs cholesterol to make hormones, vitamin D, and other nutrients that help you digest food. Your body makes all the cholesterol it needs. Cholesterol is also found in foods from animal sources, such as eggs, meat, and cheese.
On World Heart Day, New Global Survey Reveals Confusion On Bad Cholesterol And Cardiovascular Risk
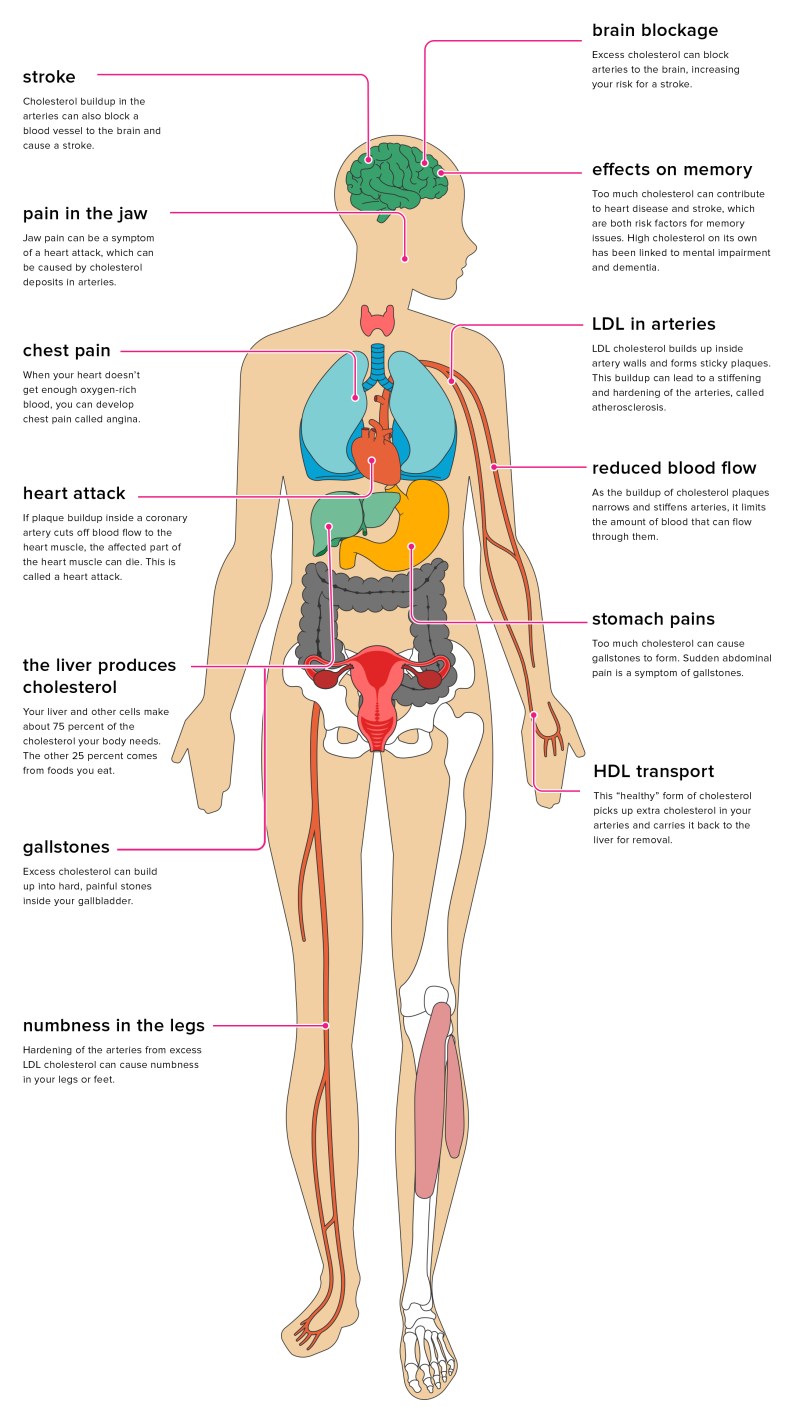
If you have too much cholesterol in your blood, it can combine with other substances in the blood to form plaque. Plaque sticks to the walls of your arteries. This plaque formation is called atherosclerosis. It can lead to coronary artery disease, where your coronary arteries become narrow or even blocked.
HDL, LDL, and VLDL are lipoproteins. They are a combination of fat (lipid) and protein. Lipids must be attached to proteins in order to travel through the bloodstream. Different types of lipoproteins have different purposes:
Genetics can predispose people to high cholesterol. For example, familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is an inherited form of high cholesterol. Some medical conditions and certain medications can also cause high cholesterol.
If you have large amounts of plaque in your arteries, the area of the plaque may rupture (rupture). This can cause a blood clot on the surface of the plaque. If the clot becomes large enough, it can partially or completely block the flow of blood in the coronary artery.
Solved The Role Of Cholesterol In The Plasma Membrane Of
If the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle is reduced or blocked, it can cause angina (chest pain) or heart disease.
Plaque can also build up in other arteries in your body, including the arteries that bring oxygen-rich blood to your brain and legs. This can lead to complications such as carotid artery disease, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease.
There are usually no signs or symptoms that you have high cholesterol. There is a blood test to measure your cholesterol level. When and how often you should get this test depends on your age, risk factors, and family history. The general recommendations are:
You can lower your cholesterol with healthy lifestyle changes. They include a hearty diet plan, weight management, and regular physical activity.
Contribution Of Serum Lipids And Cholesterol Cellular Metabolism In Lung Cancer Development And Progression
If lifestyle changes alone do not lower cholesterol enough, you may need to take medication. There are many types of cholesterol-lowering drugs available, including statins. If you are taking medication to lower your cholesterol, you still need to continue with lifestyle changes.
Some people with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) may receive a treatment called lipoprotein apheresis. This treatment uses a machine to filter LDL cholesterol from the blood. The machine then returns the remaining blood to the person.
Links to health information from the National Institutes of Health and other government agencies. it also links to health information from non-government sites. See our disclaimer about external links and our quality guidelines.

The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for medical care or advice. Consult a health care provider if you have questions about your health. Cholesterol is a lipid molecule that plays an important role in many biological processes, both physiological and pathological. It is an important structural component of cell membranes, and is important for the biosynthesis, integrity, and functions of biological membranes, including membrane trafficking and signaling. In fact, cholesterol is the main component of lipid rafts, a type of lipid-based structure that regulates the assembly and function of many cell signaling pathways, including those related to cancer, such as gastrointestinal cell growth, adhesion, migration, invasion, and cancer. apoptosis. Considering the importance of cholesterol metabolism, its homeostasis is strictly controlled at all levels: intake, synthesis, export, metabolism, and storage. Changes in this homeostatic balance are known to be associated with heart disease and atherosclerosis, but increasing evidence also links these behaviors with an increased risk of cancer. Although there is conflicting evidence about the role of cholesterol in the development of cancer, most studies show that a malfunction of cholesterol homeostasis can lead to the development of cancer. This study aims to discuss the current understanding of cholesterol homeostasis in normal cells and cancer, summarizing the main results from recent clinical and clinical studies that have investigated the role of the main players in the regulation of cholesterol and the organization of lipid rafts, which may represent promising therapeutic targets. .
Main Steps In Cholesterol Biosynthesis Pathway. Enzymes Catalyzing…
Cholesterol is the main lipid molecule that plays an important role in many biological processes, both at the physiological and pathological level (Maxfield and Tabas, 2005).
Cholesterol, in addition to being an important component of cell membranes, is important for their biogenesis, and is necessary for maintaining the integrity and functions of biological membranes, including endocytosis, membrane trafficking, and signaling (Maxfield and Tabas, 2005; Yamauchi and Rogers, 2018). Inside the cell, cholesterol, widely distributed among the organelles, modulates the immune system, and represents the precursor of hormones such as sex hormones and vitamin D (Mollinedo and Gajate, 2020; Figure 1).
Recently, cholesterol has played a central role in cancer research because of its potential therapeutic effects in prevention and treatment. However, the role of cholesterol in oncogenesis is still debated (DuBroff and de Lorgeril, 2015). Literature data have described the conflicting role of cholesterol depending on the type of tumor (Ding et al., 2019). Excess cholesterol is related
What's the purpose of a cell membrane, cholesterol structure in cell membrane, what is the purpose of proteins in the cell membrane, cholesterol function in the cell membrane, what is the purpose of cell membrane, the purpose of the cell membrane, what is the main purpose of the cell membrane, what is the purpose of cholesterol in the body, cholesterol in the cell membrane, is cholesterol found in cell membrane, what does cholesterol do in the cell membrane, what is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane