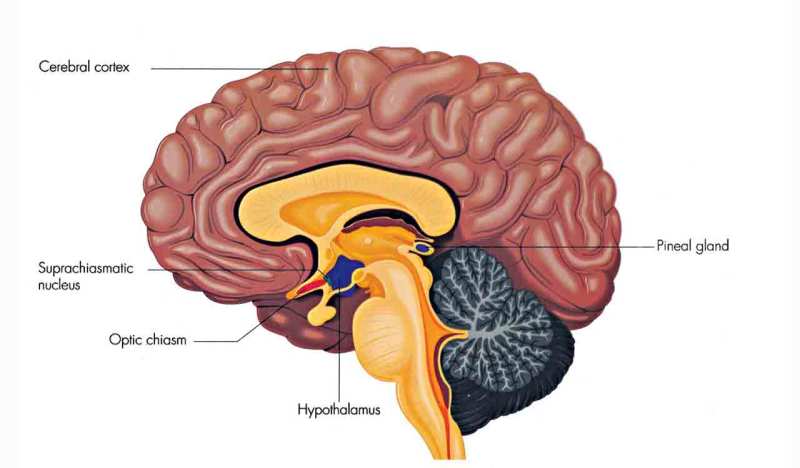
What Is The Main Function Of The Pineal Gland – The pineal gland is a small pineapple-shaped neuroendocrine organ whose primary function is to secrete melatonin at night. Melatonin regulates the sleep-wake cycle known as circadian rhythms. The pineal gland receives light information from the retina, which is why the pineal gland is sometimes referred to as the third eye. The pineal gland releases melatonin during the dark.
The pineal gland is located in the brain behind the third cerebral ventricle in the middle and between the two cerebral hemispheres. It is attached to the roof of the third ventricle by a short stalk. The pineal gland originates from an embryonic structure known as the diencephalon, which develops into the epithalamus, thalamus, subthalamus, and hypothalamus. It can release hormones into the bloodstream because it is not covered by a blood-brain barrier, a physiological barrier made up of endothelial cells.
What Is The Main Function Of The Pineal Gland

The primary function of the human pineal gland is to regulate the night-time secretion of melatonin, thereby regulating the circadian system and sleep patterns. In addition, the pineal gland plays a role in protecting cells, protecting the nervous system and mental illness (for example, schizophrenia and depression). It is also necessary for reproduction and in the management of sexual maturity. The pineal gland has been found to inhibit gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus, which ultimately controls the onset of puberty, sexual development and ovulation in women.
Pineal Xt Reviews: Do Not Buy Pinealxt Until Truth Exposed!
Abnormalities of the pineal gland can occur due to aging, injury and developmental conditions. Examples include pineal tumors, craniopharyngiomas; Injuries affecting the inner part of the sympathetic part of the pineal gland; And rare congenital diseases. Conditions that affect the pineal gland alter melatonin secretion and disrupt the circadian cycle.
As we age, the pineal gland begins to gain weight, which increases with age. Calcium of the pineal gland may be associated with decreased age-related melatonin production and sleep patterns in the elderly. Also, some studies have found that the level of calcification is higher in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Tumors of the pineal gland are abnormal, forming about 3 percent of brain tumors. Among the types of tumors that can form in the pineal area, viral cell tumors are the most common. They are more common in children between the ages of 1 and 12 and those born in men. Pineal tumors can lead to hydrocephalus, a condition that leads to a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. Hydrocephalus is manifested by headache, drowsiness, and other signs of increased intracranial pressure, such as blurred vision, vomiting, behavioral changes, and weakness when moving or speaking. The majority of individuals with pineal tumors have Parinaud syndrome. This neurological condition makes it difficult for an individual to look upwards due to pressure on the protective areas of the brain (eg, the posterior part of the upper midbrain).
Other types of tumors affecting the pineal gland are craniopharyngiomas, which are rare brain tumors that form near the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Craniopharyngiomas can occur at any age, but are most common in children 5 to 14 years of age and adults 50 to 74 years of age. It usually forms from solid tumors and fluid-filled sections. As these tumors grow, intracranial pressure increases, which can cause headaches, nausea, and vomiting. They can also expand to narrow the pituitary gland and lead to hormonal abnormalities. In addition, it can compress other neighboring structures, such as the optical chiasm, through which two optical nerves pass through Leads to blurred vision.
The Anatomy Of The Nervous System, From The Standpoint Of Development And Function . Ose, Mouth, And Tongue Andhe Concerned With Feeding Reflexes. The Pineal Body Is A Small Mass, Shaped Like
The pineal gland receives innervation from the hypothalamus through the spinal cord and the apex cervical ganglion. If a spinal cord injury occurs, the circuit that affects the production of pineal gland hormones may be disrupted. This causes tetraplegia, the inability to move the upper and lower parts voluntarily. It can also be absent in the pineal production of melatonin, which causes sleep problems, poor quality of life, increased oxidative stress and loss of anti-inflammatory and anti-nervous effects.
Finally, examples of congenital pineal gland problems include pineal agenesis or failure of the pineal gland to develop. This has been linked to mutations in the PAX6 gene that lead to abnormalities of the pineal gland and other brain and eye disorders. PAX6 is responsible for brain development processes, including cell proliferation, nerve migration, and axial guidance. The extent to which pineal agenesis affects human growth and development has not yet been widely explored. Further study of the nervous system, endocrine and sleep can help provide more insight into the effects on normal human growth and development.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most useful initial study to identify tumors and other pineal gland abnormalities and determine their relationship to adjacent structures. For example, if a pineal tumor grows and extends into the third ventricle, it can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and cause hydrocephalus blockage, which is visible on MRI. Computed tomography (CT) scans can also detect pineal abnormalities. Tumors in the Pineal region usually appear as solid masses lit by contrast. In addition, CT can detect calcification of the pineal gland due to increasing age.

Treatment of pineal gland tumors and craniopharyngiomas is surgical if possible. Surgery aims to perform an autopsy and obtain a tissue to determine the type of tumor and whether it is cancerous. The surgeon will usually remove as many tumors as possible without causing any additional symptoms for the individual. Postoperative treatment may include radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Treatment of pineal gland problems due to injury and chemotherapy.
Can The Pineal Gland Dmt Explain Natural Mystical Experiences?
The pineal gland is a small gland located in the center of the brain and attached to the roof of the third ventricle. The pineal gland is sometimes called the third eye because of its ability to perceive light and dark through the retina. The primary function of the pineal gland is to release melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep. When the environment is dark, the retina sends force to the pineal gland to release melatonin and begin the sleep cycle. Abnormalities of the pineal gland affect sleep, wakefulness, regeneration and mood. Examples of pineal gland diseases include pineal tumors, craniopharyngiomas; Injuries affecting the internal sympathy of the glands; And congenital malformations. Abnormalities can be found on MRI and CT images. Treatment of pineal gland tumors usually involves surgery and chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In addition, external administration of endocrine secreted hormones, such as melatonin, may be therapeutic approach.
Aulinas, A. Physiology of the pineal gland and melatonin. [Updated 10 December 2019]. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al., Editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc .; 2000-. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK550972/
Avery, D. (n.d.). Seasonal diseases: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, evaluation and diagnosis. Stylish. Retrieved July 10, 2022 from https://www-uptodate-com.rosalindfranklin.idm.oclc.org/contents/seasonal-affective-disorder-epidemiology-clinical-features-assessment-and-diagnosis ? search = pineal + gland + & source = search_result & selectedTitle = 3 ~ 34 & usage_type = default & display_rank = 3
Devesa, J., Segade, N.L., Jacobo Isorna, et al. Is It Proper To Use Growth Hormone And Melatonin In Spinal Injuries? MOJ Anat Physiol. 2017; 4 (2): 258–262. DOI: 10.15406 / mojap.2017.04.00128
Solved Incorrect Question 30 Which Structure Is Highlighted?
Sapède, D., Cau, E. pineal gland from development to function. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2013; 106: 171-215. doi: 10.1016 / B978-0-12-416021-7.00005-5. PMID: 24290350.
Srinivasan, V. pineal gland: its physiological and pharmacological role. Indian, J. Physiol Pharmacol. 1989 October-December; 33 (4): 263-72. PMID: 2695464.Renee Descartes describes the pineal gland as the “altar of the soul.” It is located in the center of the brain. The primary function of the pineal gland is to receive signals about the state of the light-dark cycle from the atmosphere immediately and then transmit this information by producing and secreting melatonin. Melatonin is produced and secreted in a rhythmic pattern.
Melatonin is mostly secreted during the dark hours of the day and serves extensively as a marker of the circadian clock.
Melatonin has also been used as a treatment for some sleep problems, such as jet lag, 24-hour insomnia and sleep-deprived phase symptoms.
Pineal Gland: All You Need To Know About Pineal Gland Function
Melatonin may have more therapeutic uses in the future, considering that many physiological functions are presumed to be melatonin. Physiological effects of melatonin are released overnight or at night. It is also effective when administered appropriately during the day when melatonin levels are at their lowest. Melatonin is also involved in nerve protection, cell protection, the reproductive system and other functions. Physiological function of the pineal gland can be impaired by developmental and accidental conditions, including craniopharyngiomas, pineal tumors, injuries affecting the pineal sympathetic innervation, as well as congenital diseases affecting the secretion of melatonin. This article presents the anatomy and physiology of the pineal gland.
The pineal gland is a neuroendocrine structure that includes part of the epithalamus (part of the diencephalon). Other components of the epithalamus are the habenular nuclei, stria medullaris, paraventricular nuclei, and posterior commissure.
The pineal gland begins with an external projection from the posterior wall of the third ventricle below the splenium of the corpus callosum. It is located in the groove between the apex colliculi and has a bilateral relationship to the posterior aspect of both thalami.
The pineal gland is innervated by the sympathetic nervous system. The inner sympathetic of the pineal gland arises from the cervical ganglia.
A Simple Guide To The Pineal Gland (the Third Eye) And Its Function By Kenneth Kee
Both the anterior and posterior arteries supply the arteries of the pineal gland, the main arteries supplying the posterior pineal arteries, starting from the posterior.
Main function of pineal gland, function of melatonin in pineal gland, what is the main function of the thyroid gland, what is the pineal gland, function of the pineal gland, what is the function of pineal gland, pineal gland function test, pineal gland spiritual function, what is the main function of the prostate gland, what is the main function of the adrenal gland, what is the main function of the pituitary gland, location and function of pineal gland