What Is The Main Function Of Skeletal System – LO1 of Unit 4 – Understand the consultation process specific to gym-based exercise program planning and own professional role boundaries
LO3 of Unit 4 – Know the range of health and fitness assessments relevant to the gym-based client
What Is The Main Function Of Skeletal System

LO1 of Unit 5 – How to plan and tailor safe and effective gym-based exercise programs for a range of clients
Skeleton And Bones
Private: Level 2 – Certificate in Fitness Instruction (February 2021) Unit 1 – Anatomy and Physiology (2021) LO3 of Unit 1 – Skeletal System (2021)
Prefix ‘peri’ means ‘going around’ Prefix ‘endo’ means ‘found within’ Suffix ‘blast’ means ‘to build’ Example: osteoblast (
Sesamoid bones are embedded within tendons or muscles and act to reduce friction and change the direction of muscle pull—eg. patella
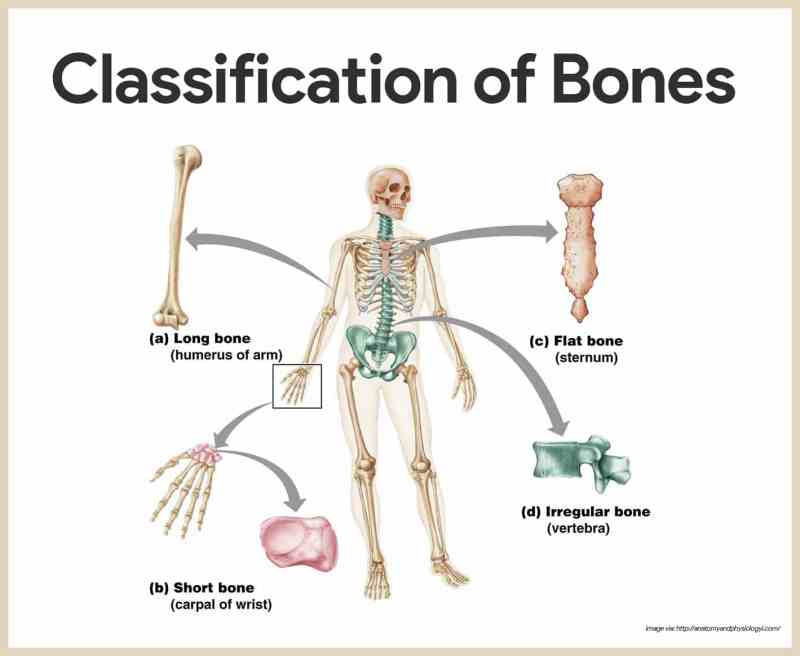
Long bones are longer than wide and have a hollow center. These bones act as levers to create movement, produce blood cells and store minerals—eg. Femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, metatarsals.
Types Of Bones
Segmental bones are as wide as they are long. Their primary function is to provide support and stability with little movement. E.g. Carpals and tarsals.
Flat bones are made up of a layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone. As their name suggests, these bones are ‘flat’ in appearance and have broad surfaces for muscle attachment. E.g. Skull, sternum, ribs
Irregular bones consisting of spongy bone lined with a thin layer of compact bone, their shapes depend on the functions they fulfill within the body. E.g. Provides significant mechanical support to the body, but protects many anchor points for skeletal muscle attachment. E.g. Vertebrae, facial bones, pubis, ischium

Spongy or cancellous bone has large open spaces for bone marrow. Red and white blood cells are produced here.
Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology
Location of longitudinal bone growth in children and adolescents. Once growth is complete, it is called the epiphyseal line.
A cellular layer lines the marrow cavity within the long bone shaft. Endosteum actively participates in bone growth and repair.
Connective tissue consisting of a fibrous outer layer and a cellular (osteogenic) inner layer surrounding bone; Actively participates in bone growth and repair.
Compact bone has a tough, calcified matrix with few spaces. This layer forms a protective shell around spongy bone tissue, but it also gives our bones their stiffness, strength and resistance.
Bones: Anatomy, Structure & Function
The word hyaline means ‘glassy’ and blue-grey in colour. It is the tissue that covers the ends of the bones and promotes smooth movement with less friction between the bones as they move. Hyaline cartilage is the most extensive cartilage in the body. It does not contain any nerves or blood vessels
An epiphysis is an enlarged end of a long bone that ossifies separately from the bone shaft but becomes fixed to the shaft when full growth is achieved. The epiphysis is made of spongy bone covered by a thin layer of compact bone.
The diaphysis is a long bone shaft. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue.

The process of bone formation called ossification begins with cartilage ossifying and converting to bone when calcium is deposited. There are two stages of development:
Types Of Skeletal Systems
The mineral calcium is of particular importance to bone health and, along with the protein collagen, gives bones their strength and flexibility.
During the first two months in utero, the immature skeleton forms and is composed entirely of hyaline cartilage.
Blood vessels grow around the edges of the cartilage (perichondrium), cartilage cells transform into osteoblasts, forming a thin layer of bone along the outer shaft.
Blood vessels enlarge and invade, supplying nutrients to the central region of the developing bone. Bone formations spread along the shaft towards the end of the bone in ‘primary ossification’.
Skeletal System 2: Structure And Function Of The Musculoskeletal System
Bone remodeling and growth continues; The bone elongates, forming a central medullary cavity. The bone thickens and the epiphyseal cartilage is replaced by bone called ‘secondary ossification’.
Cartilage remains only at the ends of bones and growth plates. The shaft continues to grow as the bone lengthens and thickens.
Bone remodeling occurs continuously throughout our lifetime. It is a dynamic process that involves a balance between bone resorption (where bone tissue is removed from the skeleton) by cells called osteoclasts and bone deposition (bone tissue formation) by cells called osteoblasts.

Around 10-15 years of age, girls and boys go through puberty, where rapidly increasing sex hormones influence bone growth. In girls, it is the hormone estrogen that greatly accelerates the growth of bone mass, leading to a change in posture. In boys, the hormone testosterone causes more significant bone mass growth. By age twenty, 90% of bone mass is achieved in both girls and boys.
The Musculoskeletal System And Disease
Bone mass increases by another 10% in the third decade of life. From the age of 30, bone mass begins to decline gradually in men and women as the level of sex hormones decreases.
Men can achieve more bone mass than women due to factors such as a larger skeleton, greater overall muscle mass, and ten times higher testosterone levels.
Hormone levels continue to decline as both men and women age, resulting in further loss of bone mass. However, women experience an acceleration of bone loss around 50 due to female menopause
Bone is a dynamic tissue that undergoes constant renewal throughout everyone’s life by bone remodeling. This physiological process is necessary for the following reasons:
Why Do We Have Bones?
2. Resorption phase. Osteoclasts adhere to the bone surface and begin to dissolve the bone. They excavate a cavity called a resorption pit in cancellous bone or burrow a tunnel in compact bone. Reabsorption requires two steps:
3. Reverse phase. Macrophage-like cells function to remove debris produced during matrix degradation. Mesenchymal stem cells, the precursors of osteoblasts, appear along the pit or pit, where they increase in number and transform into pre-osteoblasts.
4. Formative stage. Osteoblasts accumulate on the surface of the burrow or pit. Osteoblasts release a compound called osteoid at the site, forming a new soft non-mineralized (non-calcified) matrix. The new matrix is mineralized with calcium and phosphorus and the new bone is complete.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DigitalVision.-skeletonsovertime-5c77129446e0fb00019b8d27.jpg?strip=all)
99% of calcium in the body (average 1.2 kg) is deposited in bones; The other 1% is an essential component of other body tissues such as muscle. As a result, our bones act as our calcium reservoirs and can take up or release calcium.
Axial Skeleton: What Bones It Makes Up
Calcium regulation must be tightly regulated to maintain life-sustaining physiological functions such as heart rate, nervous system function, and muscle contractions. 1% is more important than 99%.
Calcium regulation is performed by a pair of hormones with opposite effects that together regulate the storage, absorption and excretion of calcium in the body.
Many hormones regulate bone density and are essential for bone health. The following hormones are involved in the regulation of bone growth and maintenance:
Regular weight-bearing physical activity such as resistance training exercises and short bouts of high-impact activity in childhood increases bone mass.
Skeletal Systems Worksheet
Physical activity during adulthood helps maintain bone mass and strength, and in later life, reduces the risk of losing bone mass.
The spine has 33 vertebrae, nine fused and 24 movable segments. Each vertebra varies in shape and size, with the largest in the lumbar region and the smallest in the cervical region.
The vertebrae form four natural curves. There are two anterior convex (backward bending) curves and two anterior concave (forward bending) curves. Separating each vertebra are vertebral discs composed of fibrocartilage. The discs work to allow some movement between the segments of the spine while acting as shock absorbers during movement.

During fetal development there is a single anterior concave curve, called the primary curve. When a baby is about three months old and holding their head upright, the cervical curve develops. The hip curve develops later when the child stands and walks. As the cervical and lumbar curves develop during the postpartum period, they are secondary curves.
How Bones Communicate With The Rest Of The Body
The spine is a flexible column capable of moving in all directions. When viewed from the side, it is clear that the spine is curved, with different areas bending in a forward or backward direction.
When prescribing exercises, look to maintain spinal posture in a neutral position or alignment, especially during heavy lifting exercises such as squatting and deadlifting.
A person’s spinal alignment is quickly assessed when viewed from the side. Ask the person to stand next to the plumb line. The line should be:
Maintaining good posture while exercising is essential. During exercise, good posture maintains the normal curves of the spine, allows the muscles to work more efficiently and reduces any unnecessary stress on the joints and ligaments and keeps the spine healthy.
Spotlight On: The Skeletal System
Any (or all) spinal curves that deviate from the spine’s natural posture can become exaggerated or extreme.
Reasons for the spine to deviate from the norm include genetic factors, sitting, driving, play (and other sedentary activities), psychological factors (eg self-confidence), sports and activity (eg: muscle imbalances and imbalances) and the effects of pregnancy. .
The lumbar curve increases during pregnancy due to the weight of the growing baby and weakening of the abdomen.

Lateral curvature characterizes scoliosis, which is either ‘S’ or ‘C’ shaped. It is usually hereditary, affecting young women more than boys. Typically, there
Functions Bones Images, Stock Photos & Vectors
What is the main function of skeletal muscles, function and structure of the skeletal system, what is not a function of the skeletal system, function of the skeletal and muscular system, what's the function of the skeletal system, what is function of the skeletal system, what are the 5 function of the skeletal system, explain the function of the skeletal system, what is the main function of the human skeletal system, main function of skeletal muscle, 5 function of the skeletal system, main function of skeletal system