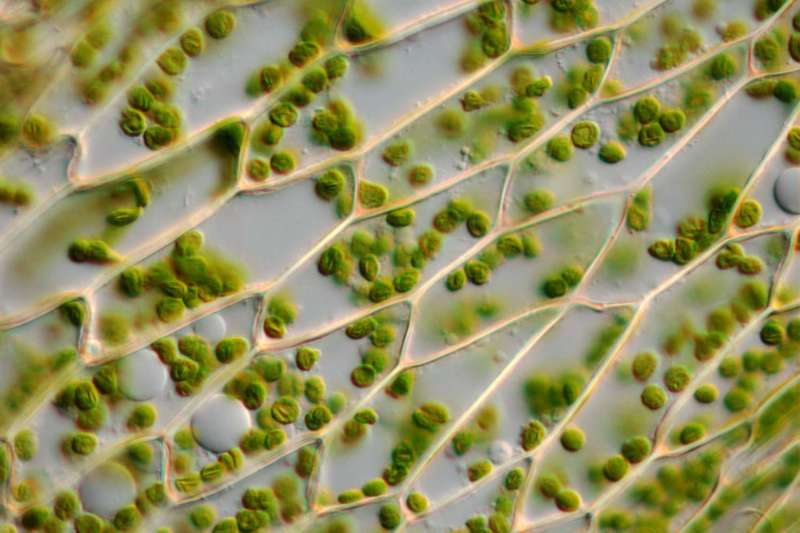
What Is The Main Function Of A Cell Membrane – The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is a type of organelle (i.e., a structure located in a cell) that processes and packages proteins and lipid molecules (i.e., fat molecules). They are subsequently transported to other cellular compartments (for example, lysosomes or the plasma membrane) or secreted from the cell.
When Camillo Golgi discovered the Golgi apparatus in 1898, it was one of the first cell organelles discovered. He discovered it while researching the nervous system. Camillo Golgi called his discovery the “inner reticular apparatus”, and the organelle was named after him only in 1910.
What Is The Main Function Of A Cell Membrane

The Golgi apparatus is a series of stacked membranes found within the cytoplasm (ie, the gel-like fluid found in the cell membrane) in all eukaryotic cells (ie, complex cells). It can usually be found near the nucleus and rough endoplasmic reticulum (organelles involved in protein synthesis).
This Picture Shows A Model If A Cell. What Is The Main Function Of The Part Labeled Z In The Model?
The function of the Golgi apparatus is to process and package proteins that have left the rough endoplasmic reticulum for further transport inside and/or outside the cell. In plant cells, the Golgi body also serves as a site for the synthesis of complex polysaccharides.
The Golgi body contains Golgi stacks, which can be thought of as a series of trafficking pathways that work by modifying proteins and other complex polysaccharides. The number of Golgi stacks a cell has depends largely on the cell type. These Golgi stacks contain from 3 to 20 flattened membrane sacs, called cisternae. These Golgi cisternae are usually classified based on what they import and export to the Golgi body, each containing a different set of processing enzymes. Therefore, Golgi cisternae are a very important part of the packaging and processing that takes place in the Golgi body.
Transport vesicles usually pick up molecules from the rough endoplasmic reticulum and transport them to the cis face (ie, the region of the Golgi apparatus adjacent to the endoplasmic reticulum) of the Golgi stacks, where they fuse with the Golgi membrane and are sorted based on their next destination. They are then moved through Golgi cisternae as they undergo remodeling and other modifications. The modified protein or lipid molecules then leave the transface (ie, the area of the Golgi apparatus facing the plasma membrane) of the Golgi stack where they are either secreted from the cell, or transported to another cell compartment.
The complex network of membranes and vesicles in the Golgi stacks into which molecules enter is also known as the cis Golgi network.
Which Are The Main Points Of The Cell Theory? Select All That Apply. A. Cells Are The Basic Units Of
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is an organelle that processes and packages proteins and lipid molecules (i.e., fat molecules) that are later exported to other cellular compartments or secreted from the cell. The Golgi body has Golgi stacks, which are involved in modifying proteins and other complex polysaccharides. Transport vesicles take up molecules from the rough endoplasmic reticulum and transport them to the cis face of the Golgi stacks, where they fuse with the Golgi membrane and are sorted. They are then moved through the Golgi cisternae and undergo remodeling and other modifications. The modified protein or lipid molecules then leave the transfacial Golgi stack where they are either secreted from the cell or transported to another cell compartment.
Day, K. J., Staehelin, L. A., & Glick, B. S. (2013). A three-step model of Golgi structure and function. Have you ever heard the phrase “form follows function?” It’s a philosophy practiced in many industries. In architecture, this means that buildings should be built to support the activities that will be carried out inside them. For example, a skyscraper should be built with several rows of elevators; the hospital should be built so that emergency care is easily accessible.
Our natural world was created by the principle of shape-following function, especially in cell biology, and this will become clear as we explore eukaryotic cells. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: (1) a membrane-bound nucleus; (2) numerous membrane-bound organelles—such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and (3) several rod-shaped chromosomes. Because the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is surrounded by a membrane, it is often said to have a “true nucleus”. The word “organelle” means “small organ” and, as mentioned before, organelles have specialized cellular functions, just as the organs of your body have specialized functions.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png?strip=all)
Figure 1. These images show the major organelles and other cellular components of (a) a typical animal cell and (b) a typical eukaryotic plant cell. A plant cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, plastids, and a central vacuole—structures not found in animal cells. Plant cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes.
What Is A Neuron? Diagrams, Types, Function, And More
Before we start looking at individual organelles, we need to briefly address the matrix in which they are located: the cytoplasm. The part of the cell called the cytoplasm is slightly different in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. In eukaryotic cells, which have a nucleus, the cytoplasm is everything between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope. In prokaryotes, which lack a nucleus, cytoplasm simply means everything inside the plasma membrane.
One major component of the cytoplasm in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the gel-like cytosol, a water-based solution containing ions, small molecules, and macromolecules. In eukaryotes, the cytoplasm also includes membrane-bound organelles, which are suspended in the cytosol. The cytoskeleton, the network of fibers that supports the cell and gives it shape, is also part of the cytoplasm and helps organize cellular components.
Although the cytosol is mostly water, it has a semi-solid, jelly-like consistency due to the many proteins suspended in it. The cytosol contains a rich broth of macromolecules and smaller organic molecules, including glucose and other simple sugars, polysaccharides, amino acids, nucleic acids, and fatty acids. Ions of sodium, potassium, calcium and other elements are also found in the cytosol. Many metabolic reactions, including protein synthesis, take place in this part of the cell.
Figure 2. The nucleus stores chromatin (DNA plus proteins) in a gel-like substance called the nucleoplasm. The nucleolus is a condensed region of chromatin where ribosome synthesis takes place. The boundary of the nucleus is called the nuclear envelope. It consists of two phospholipid bilayers: outer and inner membrane. The nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. Nuclear pores allow substances to enter and leave the nucleus.
Cell Structure And Functions: Parts, Plant & Animal Cell, Videos, Examples
) contains the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins. Let’s look at it in more detail (Figure 2).
The nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure that forms the outermost part of the nucleus (Figure 2). Both the inner and outer nuclear envelope membranes are phospholipid bilayers.
The nuclear envelope is riddled with pores that control the passage of ions, molecules and RNA between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm. Nucleoplasm is a semi-solid liquid inside the nucleus, where we find chromatin and nucleolus.

To understand chromatin, it is helpful to first consider chromosomes. Chromosomes are structures inside the nucleus that consist of DNA, the hereditary material. In prokaryotes, DNA is organized into a single circular chromosome. In eukaryotes, chromosomes are linear structures. Each eukaryotic species has a certain number of chromosomes in the nucleus of its body cells. For example, humans have 46 chromosomes, while fruit flies have eight. Chromosomes are visible and mutually recognizable only when the cell is preparing to divide. When a cell is in the growth and maintenance phases of its life cycle, proteins are attached to chromosomes and resemble an unwound, tangled bunch of threads. These uncoiled protein-chromosome complexes are called chromatin (Figure 3); chromatin describes the material that makes up chromosomes both when condensed and decondensed. Later we will focus on chromatin and chromosomes in more detail.
Cell Notes For Exams
Figure 3. (a) This figure shows the different levels of chromatin organization (DNA and protein). (b) This image shows paired chromosomes. (credit b: paper modification by NIH; scale data by Matt Russell)
We already know that the nucleus directs ribosome synthesis, but how does it do it? Some chromosomes have sections of DNA that code for ribosomal RNA. A darkly stained area within the nucleus called the nucleolus (plural = nucleoli) aggregates ribosomal RNA with associated proteins to assemble ribosomal subunits that are then transported through pores in the nuclear envelope to the cytoplasm.
Figure 4. Ribosomes consist of a large subunit (top) and a small subunit (bottom). During protein synthesis, ribosomes assemble amino acids into proteins.
Ribosomes are cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. When viewed through an electron microscope, ribosomes appear either as clusters (polyribosomes) or as individual, tiny dots floating freely in the cytoplasm. They can be attached to the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane or the cytoplasmic side of the endoplasmic reticulum and the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. Electron microscopy has shown us that ribosomes, which are large complexes of protein and RNA, consist of two subunits, aptly named large and small (Figure 4). Ribosomes
Cell Membrane Function And Structure
What is function of the cell membrane, main function of cell membrane, what is cell membrane function, what is the function of a cell membrane, what is the main function of plasma membrane, the main function of the cell membrane is to, what is the function of glycoproteins in the cell membrane, what is the function of carbohydrates in the cell membrane, what is the main function of a cell membrane, what is not a function of the cell membrane, what is the primary function of a cell membrane, what is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane