What Is The Job Of The Vacuole – The structure of the vacuole is such that it helps the plant maintain its turgor pressure. Read on to know details about it…
The structure of the vacuole is such that it helps the plant maintain its turgor pressure. Read on to know details about it…
What Is The Job Of The Vacuole

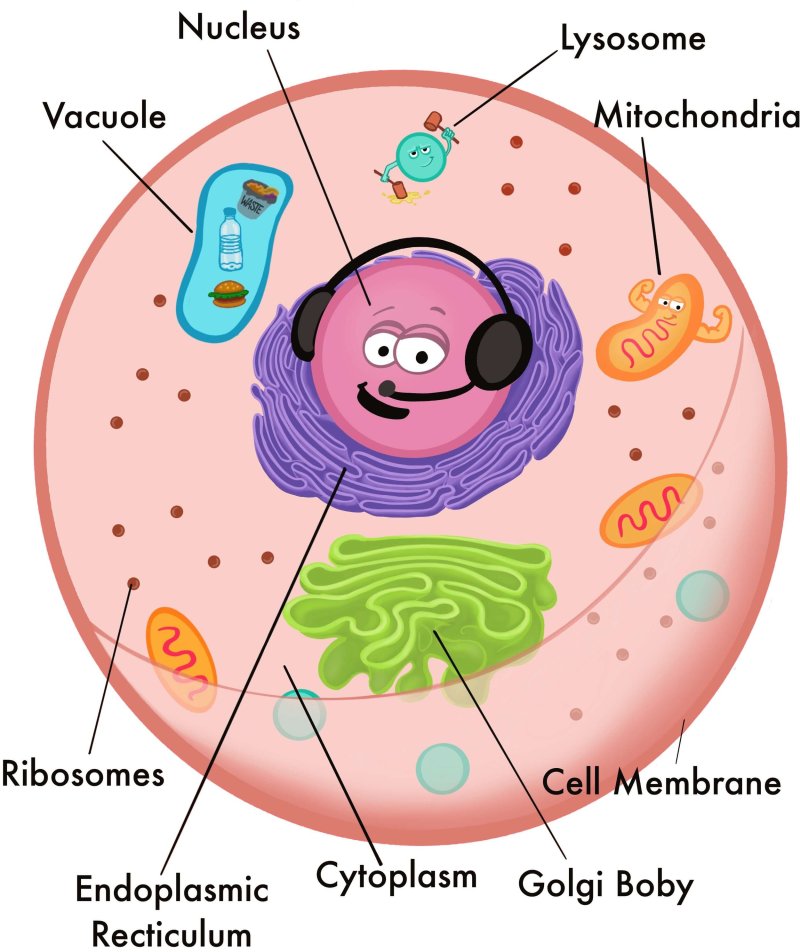
There are millions of cells in every multicellular living organism. These cells differ in their structure and functions. Moreover, the cells found in different living species also differ. There are many differences between animal cells and plant cells. A plant cell is photosynthetic in nature, so some of its organelles differ from those found in animal cells. One of the plant cell-like organelles unique to plants is the vacuole.
Question Video: Recalling The Functions Of A Plant Cell Wall
In plant cells, the vacuole occupies a large area. Sometimes it can be more than 90% of the plant cell space. They are said to usually result from the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles. Because of this, the vacuole does not have any specific size or shape. Its structure is such that it fulfills its function. Most mature and grown plant cells usually have a single large vacuole surrounded by a structure known as the tonoplast. This is said to be a very active and dynamic membrane for this all-important part of plant cell structure.
A vacuole contains a fluid known as cell sap in its central, hollow region. This fluid contains various compounds, some of which are secretory and some of which are excretory in nature. In addition, the middle one, depending on the cell type and requirements, contains concentrations of salts, sugars, and various types of soluble pigments. Cell sap, which is part of the central vacuole structure, also contains various enzymes that are even capable of digesting the cell itself. Although most mature plant cells contain a single large vacuole, when examining the cell biology of young plant cells, there are many vacuoles that slowly enlarge and eventually fuse together. This ultimately pushes the cytoplasm, nucleus, and other such structures to the plasma membrane and cell wall.
The structure of the vacuole is designed to support this important cell organelle, which is one of the main differences between plant and animal cells. Its membrane, the tonoplast, helps separate its contents from those floating in the cytoplasm. Thus, this membrane prevents harmful substances present here from entering and damaging the rest of the cell. Because the tonoplast is selectively permeable in nature, it also tends to maintain the pH and ion concentration of the cell by regulating what moves in and out of the vacuole. Also, because the structure is so large, it pushes the contents of the cell toward the boundaries near the cell wall and cell membrane and thus helps maintain the cell’s turgor pressure. Furthermore, vacuolar juice contains many different digestive enzymes capable of destroying the cell (which is handy when apoptosis is needed). The tonoplast also helps maintain turgor pressure, supporting plant leaf and flower structures.
This structure is designed to aid the function of the vacuole. There is usually a slightly acidic, i.e., low pH, maintained within this structure, as this aids the work of the degrading enzymes within it. In some cases, its structure may vary slightly depending on the cell type and function, for example, the vacuole in yeast cells is a very dynamic structure that can change its morphology. However, in general, it usually contains a tonoplast and cell sap within it.
Infographic: Intracellular Bacteria’s Tricks For Host Manipulation
Sign up to automatically receive (give or take) the latest and greatest articles from our site every week… straight to your inbox.
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We’ll assume you’re fine with this, but you can opt out if you’d like. Cookie settings Accept
This site uses cookies to improve your experience as you navigate the site. Of these cookies, cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser because they are essential for the operation of basic website functions. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will only be stored in your browser with your consent. You also have the option to opt out of these cookies. However, opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.

Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category includes only cookies that provide basic functionality and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Plant Piezo Homologs Modulate Vacuole Morphology During Tip Growth
Any cookies that may not be specifically necessary for the website to function and are used to collect user personal data through specific analytics, advertising, and other embedded content are called non-necessary cookies. User consent must be obtained before running these cookies on your site. Have you ever had a garden vegetable like a cucumber that didn’t get rained on, it dried up and died?
Cells, meaning they contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. One of the essential organelles in a plant cell is the vacuole. The membrane surrounding the plant vacuole is called the tonoplast.
Vacuoles are large in plant cells because their main function is to store water for the plant. The central vacuole of a plant cell can occupy up to 30-90 percent of the cell’s surface area. If you look at a plant cell under a microscope, the central vacuole looks like a bubble.
Water is vital to the plant cell’s daily processes, but it also provides the plant’s support. If the plant does not store enough water in the vacuoles, the plant will wither.
A List Of Main Functions Of The Vacuole
How does water support a plant? Water accumulated in the central vacuole exerts pressure on the cell wall when the vacuole is full. This is called turgor pressure. Turgor pressure keeps the plant upright.
With the help of the cell membrane, water enters the plant cell. The concentration of water in the plant is changed through the process of osmosis. During osmosis, water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane, in this case a plant cell membrane. Water molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Water is then stored in vacuoles where it exerts turgor pressure.
Plant vacuoles store carbohydrates such as sucrose, glucose, and fructose. Plants use these sugars to grow and develop. One benefit is that humans and animals can then eat the plant’s seeds, roots or stems for their own food.

Calcium is a mineral that plants need for the structure of their cell walls. Calcium is stored in cytoplasm or vacuoles.
Cells And The Versatile Functions Of Their Parts
Plant vacuoles contain special pigments that give flowers their distinctive colors that attract pollinators. Specialized pigments called anthocyanins
Which are stored in the vacuoles of plants give red, orange, purple and blue colors to food. Examples of foods that contain these colors are blueberries, blackberries, strawberries, cherries, and blood oranges.
These foods are healthy options for us. We also benefit from other substances stored in plant vacuoles, such as latex and rubber.
Plants have defensive adaptations that help them survive. One of these adaptations is the storage of bitter liquids in its vacuoles. Animals and insects avoid eating these horrible-tasting plants, which increases the plant’s survival rate.
Animal Cell Definition, Structure, Parts, And Functions
Hydrolytic enzymes in the plant’s central vacuole help control pathogens. Enzymes break down fungi and yeast cells that can harm the plant.
Vacuoles provide many functions for the plant. Without vacuoles, it would be difficult for the plant to survive.
Turgor pressure. fluid pressure in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall

Osmosis. the movement of water molecules from a solution with a higher concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules across a partially permeable cell membrane.
Lecturer Notes Plant Cell Structure And Function
Optionally permeable membrane. a membrane that allows only certain substances and molecules to pass into or out of a cell.
Concentration: The amount of a substance, such as a salt, present in a given amount of tissue or fluid, such as blood. The material becomes more dense when there is less water.
Adaptability. any inherited trait that helps an organism, such as a plant or animal, to survive and reproduce in its environment.
Hydrolytic enzymes. enzymes that break down proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fat molecules into their simplest units.
Glyoxisome ,glyoxylate Cycle , Vacuole , Turgour Pressure
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER ………. ………. Subscribe to our mailing list to receive updates in your email. the cells. Although the primary function is storage, there are a number of other roles it performs such as homeostasis, osmoregulation, maintenance of cell structure, autophagy, and pH maintenance.
By the end of this article, you should not only be able to define a vacuole, but also know the answers to frequently asked questions such as:
Where is the vacuole located, do animal cells have vacuoles, what is the function of the vacuole in animal cells, how do vacuoles contract

What is the central vacuole, what is the function of the vacuole, what is the definition of vacuole, what is the meaning of vacuole, what color is the vacuole in a plant cell, what is the function of central vacuole, what is the role of the contractile vacuole, what is the function of large central vacuole, what is the job of the vacuole in a cell, job of the vacuole, what is the job of the vacuole, what is the function of the contractile vacuole