What Is The Function Of Water In Photosynthesis – Photosynthesis is the process by which primary producers (mostly plants) obtain energy through light energy. The energy obtained from the light can be used in the various processes mentioned below for the production of the energy needed by the plant to survive and grow.
Photosynthesis is a reduction process, in which hydrogen is reduced by a coenzyme. This is in contrast to respiration when sugar is oxidized.
What Is The Function Of Water In Photosynthesis

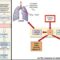
(photochemical stage) and the Calvin Process (decomposition stage). The diagram below is a summary of the reaction, where light energy is used to catalyze the reaction in its presence;
Engineering Artificial Photosynthetic Life Forms Through Endosymbiosis
Chloroplast where light is absorbed by chlorophyll; a type of photo pigment that converts light into chemical energy. This reacts with water (H
From this splitting of water, oxygen is released as a by-product as the small hydrogen carrier proceeds to the second stage of photosynthesis, the Calvin cycle.
Overall, as water is oxidized (hydrogen is removed) the energy in photolysis is released as needed in the Calvin cycle.
Of chloroplasts. Carbon freed from respiration in carbon dioxide undergoes this cycle, as shown below:
Where Does The Oxygen Liberated During Photosynthesis Come From?
In respiration, a substrate is manipulated into various forms of carbon to produce energy. In the case of photosynthesis, the following processes occur, which create glucose for respiration from the oxygen introduced into the cycle;
The energy used in the Calvin cycle is the energy available during photosynthesis. The sugar produced by GP can be used as breath or as a synthetic block
In general, growth is produced in such a way that it provides a source of glucose for respiration and the building blocks for more complex materials. While animals get their energy from food, plants get their energy from the sun.

This course looks at some of the communities in freshwater habitats. For example, symbiosis occurs in commun..
Photosynthesis Definition, Equation, Diagram, Process
In order to avoid the extinction of human species, successful adults must reproduce in order to be productive.
The hominid family diverged from the apes about 6 to 8 million years ago. Since then, it has been tested by the way of development..
Plants produce hormones to control their growth. Auxins, for example, influence plant growth. Understand the role of auxin in..
If New Zealand has many unique animals, it also has many unique plants. Find out more about some of them, ..All living organisms on earth have one or more cells. Each cell runs on chemical energy found mostly in carbohydrate (food) molecules, and most of these molecules occur in one process: photosynthesis. Through photosynthesis, some organisms convert the energy of the sun (solar) into chemical energy, which is used to make carbohydrate molecules. The energy used to maintain these molecules is released when the food is broken down by the organism. Cells use this energy to perform functions, such as cell respiration.
Chlorophyll Definition And Role In Photosynthesis
The energy used from photosynthesis goes directly into our planet’s ecosystem and is transferred from one organism to another. Therefore, rightly or wrongly, the process of photosynthesis accounts for most of the energy needed by living things on earth.
Photography also causes the release of oxygen into the atmosphere. In short, to eat and breathe, humans are almost entirely dependent on the organisms that carry out photosynthesis.
Some organisms can carry photos, while others cannot. An autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food. The Greek roots of the word

). Plants are the most common autotrophs, but others exist, including some bacteria and algae (Figure 5.2). Food and oxygen are essential in global food chains. Plants are also photoautotrophs, a type of autotroph that uses sunlight and carbon dioxide to synthesize chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. All organisms that carry out photosynthesis need sunlight.
Photosynthesis Is Nearly 100% Efficient. A Quantum Experiment Shows Why
Figure 5.2 (a) Plants, (b) algae, and (c) some bacteria, called cyanobacteria, are photoautotrophs capable of photosynthesis. Algae grow over large areas of water, sometimes covering the entire surface. (credit a: Steve Hillebrand, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service; credit b: “eutrophication&hypoxia”/Flickr; credit c: NASA; site-scale data from Matt Russell)
Heterotrophs are organisms that cannot synthesize nutrients, so they must obtain energy and carbon from food by eating other organisms. The Greek roots of the word
), meaning that their food comes from other organisms. Although the food organism is another animal, this food derives its origin from autotrophs and the process of photosynthesis. Humans are heterotrophs, like all animals. Heterotrophs depend on autotrophs, directly or indirectly. Deer and wolf are heterotrophs. Deer get energy by eating plants. A wolf that eats a deer gets energy that originally came from the plants that deer ate. The plant’s energy comes from photosynthesis, so it is the only autotroph in this model (Figure 5.3). Using this logic, all the food that humans eat is also linked to the autotrophs that carry out photosynthesis.
Figure 5.3 The energy stored in carbohydrate molecules from photosynthesis travels through the food chain. The predator that eats these deer gets energy from the photogenic herbage consumed by the deer. (credit: Steve VanRiper, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service)
Water Definition And Examples
Figure 5.4 Depicting the origin of products containing the main ingredients of human consumption. (credit: Associação Brasileira de Supermercados)
Large stores in the United States are organized in rooms, such as milk, meat, fruit, bread, butter, and more. Each aisle has hundreds, if not thousands, of different products to buy and eat (Figure 5.4).
Although there are many species, each property is related to photosynthesis. Meat and dairy products are linked to photosynthesis because the animals were fed plant foods. Bread, butter, and pasta come from seeds, which are the seeds of photosynthetic plants. What are the desserts and drinks? All of these products contain sugar—the basic carbohydrate molecule that results directly from photosynthesis. Photonic association affects each and every food that people eat.

The reaction involves sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water as the starting reaction (Figure 5.5). After the process is complete, photosynthesis releases oxygen and produces carbohydrate molecules, mostly glucose. These sugar molecules contain the energy that living things need to survive.
Photosynthesis: Surviving On Low Energy Light Comes At A Price
Figure 5.5 Illustration uses sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to release oxygen to produce energy-storing sugar molecules. Photosynthesis is the origin of the products that are the main components of the human diet. (credit: Associação Brasileira de Supermercados)
Figure 5.6 The process of photosynthesis can be represented by the equation, carbon dioxide and water produce sugar and oxygen using solar energy.
Although the equation looks simple, the many steps that take place during photosynthesis are very complex, such as the type of reaction that summarizes cellular respiration as a number of individual reactions. Before learning the details of how photoautotrophs convert sunlight into food, it is important to understand their physical structure.
In plants, photosynthesis occurs in leaves, which have many layers of cells, with different upper and lower sides. The process of photosynthesis does not take place on the surface layers of the leaf, but in the middle layer called the mesophyll (Figure 5.7). The gas exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen occurs through small openings called stomata.
How Photosynthesis And Its Light And Dark Reactions Work
In all autotrophic eukaryotes, photosynthesis occurs in an organelle called a chloroplast. In plants, the cells in the chloroplast are located in the mesophyll. Molecules are two (internal and external) molecules. The chloroplast contains a third membrane structure, disk-shaped structures called thylakoids. The thylakoid membrane contains molecules of chlorophyll, a pigment (molecule that absorbs light) that initiates the entire process of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of plants. The thylakoid membrane is surrounded by an inner space called the thylakoid space. Other pigments are involved in photosynthesis, but chlorophyll is the most important. As shown in Figure 5.7, the stack of thylakoids is called the granum, and the space surrounding the granum is called the stroma (not to be confused with stomata, the openings of leaves).
Figure 5.7 Not all cells in a leaf are photoconductive. The cells in the middle layer of the leaf are chloroplasts, which contain the photosynthetic apparatus. (credit “hundreds”: adaptation of work by Cory Zanker)
On a hot, dry day, plants close their stomata to conserve water. How does this affect the description?

There are two parts to photosynthesis: the light-reactions and the Calvin cycle. In light-dependent reactions that occur in the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll absorbs energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy using water. Moon-light reactions release oxygen from the water’s hydrogen as a byproduct. In the Calvin cycle, which occurs in the stroma, the chemical energy derived from light-reactions drives the capture of carbon in carbon dioxide molecules and the assembly of molecules sugar. Both reactions use carrier molecules to transfer energy from one to the other. Catalysts that transfer energy from light-reactions to Calvin cycle reactions can be considered “full” because
Stages Of Photosynthesis And Factors Influencing It
Guard cells function in photosynthesis, function of carotenoids in photosynthesis, what is the role of water in photosynthesis, what is the function of plant pigments in photosynthesis, main function of photosynthesis, function of photosynthesis, stomata function in photosynthesis, function of water in photosynthesis, what is the source of water in photosynthesis, what is the function of chlorophyll in photosynthesis, what is the energy source of photosynthesis, what is the function of photosynthesis