What Is The Function Of Ribosomes In Cells – Definition: A minute definition, a spherical structure composed of protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA) that is the site of protein synthesis
A biological cell is made up of many components called organelles. These organelles serve their specific purposes to make the cell a whole living unit. The
What Is The Function Of Ribosomes In Cells

. By that definition, the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and chloroplast (plastid) fall under the category of organelles, but lysosomes, vacuoles, ribosomes, and nucleosomes may not because they do not have such a layer. their lipids. Lysosomes and vacuoles are bound by a single membrane but ribosomes and nucleosomes do not have membranes around them.
Unique Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cells
There is another way we can classify cell organelles. An organelle is a special subunit within the cell that
Organelle ribosome, nucleosome, spliceosome, cell, proteasome, DNA polymerase III holoenzyme, RNA polymerase II holoenzyme, photosystem I, ATP synthase, centriole, microtubule organizing center, cytoskeleton, flagellum, nucleolus, stress granule,
Now that we know the basic classification of cell organelles, let’s move on and learn in detail about ribosomes which is the main topic of this article. We will also answer some common questions and doubts about the topic, so keep reading…
It is a minute and spherical cytoplasmic structure. It is composed of protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA). As the famous analogy of ribosomes to factories suggests, they are the site of protein synthesis; protein factories.
Common Parts Of Cells
With his electron microscope. He discovered these cell organelles which are the protein factories inside a cell. In 1958, the word “ribosome” was proposed by the scientist Richard B. Roberts.
Figure 1: George E. Palade, the scientist who discovered the ribosomes inside a living cell, received the prestigious Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1974. Image Credit: Nobelprize.org.
Figure 2: Richard B. Roberts was the scientist who named the organelle “ribosomes” in 1958. Image Credit: NASonline.

Figure 3: The “central dogma” of life governs the conversion of genetic code from DNA to RNA to proteins. The process of converting DNA into RNA is called transcription and the process of converting RNA into proteins with the help of ribosomes in a cell is called translation. Image Credit: MolBioReview.
Why Is The Ribosome So Important? · Get A Professor
Now that we know how to define ribosomes and are clear about the basic knowledge, let’s move on and learn about it in some detail.
There are several ideas and hypothetical theories about the origin of ribosomes. There is no single, conclusive, evidence-supported hypothesis for the origin of ribosomes. However, the best explanation given so far appears among many scientists. Some indications of the theory are:
Figure 5: Electron micrograph of a limited area in the basal region of an acinar cell of the rat pancreas. cell membrane cm, m-mitochondria, g-particles in the cytoplasmic matrix that have a special affinity for the ER membrane. This ribosome image clearly shows the granular bodies. Image Credit: Palade GE, 1955.
Ribosomes are made up of two basic components as discussed earlier: ribosome RNA (rRNA) and ribosomal proteins (R-proteins). There are different types of protein and their amounts vary from species to species. These 2 components are arranged in different bases in 2 different ribosomal units.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (rough)
The two ribosomal subunits join together and work as one to build proteins according to the genetic sequence contained within the messenger RNA (mRNA). Ribosomes are usually composed of two subunits: the
. They come together as one during translation; together, they catalyze the translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain during protein synthesis, and since their active sites are made of RNA, ribosomes are also referred to as “ribozymes.” “
Figure 6: The picture shows the 70S Ribosome of prokaryotic E. coli. The large subunit is red here (50S) and the small subunit is colored blue here (30S) these are the 2 subunits that make up the ribosome. Image Credit: Vossman, CC licensed.

Represented by the Svedberg (S) unit. The S units do not constitute because they represent levels of sediment, not mass.
Mechanisms And Functions Of Ribosome Associated Protein Quality Control
Figure 8: Plastoribosomes and mitoribosomes in various prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Image Credit: ETH Zurich, The Ban Lab.
. Scientists and pharmaceutical industries manipulate these differences as ways to create drugs that specifically target the prokaryotic 70S ribosomes of the pathogenic agent’s cells but do not affect the eukaryotic 80S ribosomes in the patient’s cells.
Do these antibiotics affect and target the mitoribosomes as well? (Because they are structurally similar to the prokaryotic ribosomes!!!)
ANSWER: No, because mitochondria are double membrane bound organelles, therefore antibiotics cannot enter and shut them down.
Solved 3. If You Were Describing The Function Of Ribosomes
Figure 9: There are several antibiotics available in the market that target the ribosomal subunits for their action. They turn down or reverse the different steps of translation by binding to the ribosomal subunits. Source: Wilson, D.N., 2013.
The high-resolution structures of the ribosomes have been revealed by studies from various scientific organizations around the world. They were able to differentiate these structures into their atomic configurations by studying them from specific organisms. Here is a list of the same.
Ribosomes perform vital functions within cells. Ribosomes in plant cells and ribosomes in animal cells are organelles with major responsibility for the normal functioning of cells and life processes.

Ribosomes can be distributed in the cytosol or can be attached to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. And so, ribosomes are sometimes classified as either
Ribosomal Rna 2′ O Methylations Regulate Translation By Impacting Ribosome Dynamics
In fact, the bound ribosomes are attached to the ER transiently. They can come and go. They attach to the endoplasmic reticulum (through the
) when a signal peptide is synthesized by protein translation at the ribosome, and then recognized by a
In eukaryotes, the ribosomes can be classified as ‘free’ or ‘bound’. Free ribosomes can be found hanging in the cytosol but bound ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (so called rough endoplasmic reticulum). The function of free ribosomes is to create proteins, especially proteins that function in the cytosol.
. Linked ribosomes are involved in the synthesis of proteins that are to be exported or used within the cell membrane.
The Cell: Organelles
Ribosome biogenesis refers to the biosynthesis of ribosomes. In eukaryotes, the sites of ribosome formation are the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The ribosome of eukaryotes is the 80S compared to the ribosome of prokaryotes, which is 70S. The 80S ribosome is composed of a large subunit (60S) and a small subunit (40S). Each of these subunits is composed of ribosomal protein and rRNA(s). The ribosomal proteins are synthesized in the same way as other proteins are produced, i.e. first by transcription within the nucleus and then moved into the cytoplasm for translation and maturation .
Mature ribosomal proteins are transported back into the nucleus, especially in the nucleolus for ribosomal subunit assemblies, ie 60S or 40S assembly. As for the rRNA components of the 60S or 40S, they are produced in the nucleus.
In mammals, the 18S, 28S, and 5.8S rRNAs are transcribed in the nucleolus organizer region into a single unit

. The result is a large pre-rRNA composed of 18S, 28S, and 5.8S, which after processing would be released individually. As for the 5S rRNA, the genes that code for it are transcribed into pre-5S rRNA by the
Eukaryotic Cytosolic Ribosomes
To form the large subunit (ie 60S) of the ribosomal complex, 5S rRNA combines with 28S and 5.8S rRNA. 18S, in turn, forms the small subunit (ie 40S) by combining with the ribosomal proteins. These subunits would then be translocated from the nucleolus into the cytoplasm to assemble a complete and active 80S ribosome.
Therefore, when you are asked about the site where ribosomes are made, they are made in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm.
The heterogeneous nature of ribosomes helps in gene regulation. It has also been suggested to help with translational control of protein synthesis. It helps maintain the structure and function of the ribosomes.
Genes are expressed through the process of protein synthesis. This comprehensive tutorial provides an in-depth review of the various steps of biological protein production starting from the gene up to the secretion process. Also included are topics on DNA replication during cell cycle intervals, DNA mutation and repair mechanisms, gene assembly, variation, and disease.
Animal Cell Diagram, Structure, Parts, Definition And Functions
Plant cells have plastids that are essential in photosynthesis. They also have an extra layer called a cell wall on the outside of the cell. Although animal cells do not have these cellular structures, they both have a nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. Read this tutorial to learn the structures of plant cells and their roles in plants.
A typical eukaryotic cell consists of cytoplasm with various organelles, such as nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and so on. Cell contents are surrounded by a double layer, the cell membrane. These cell structures and cell junctions are explained in this tutorial…
Part of the genetic information depends on the synthesis of proteins. mRNA, a type of RNA, is produced as a transcript that carries the code for protein synthesis. Read this tutorial for more information…
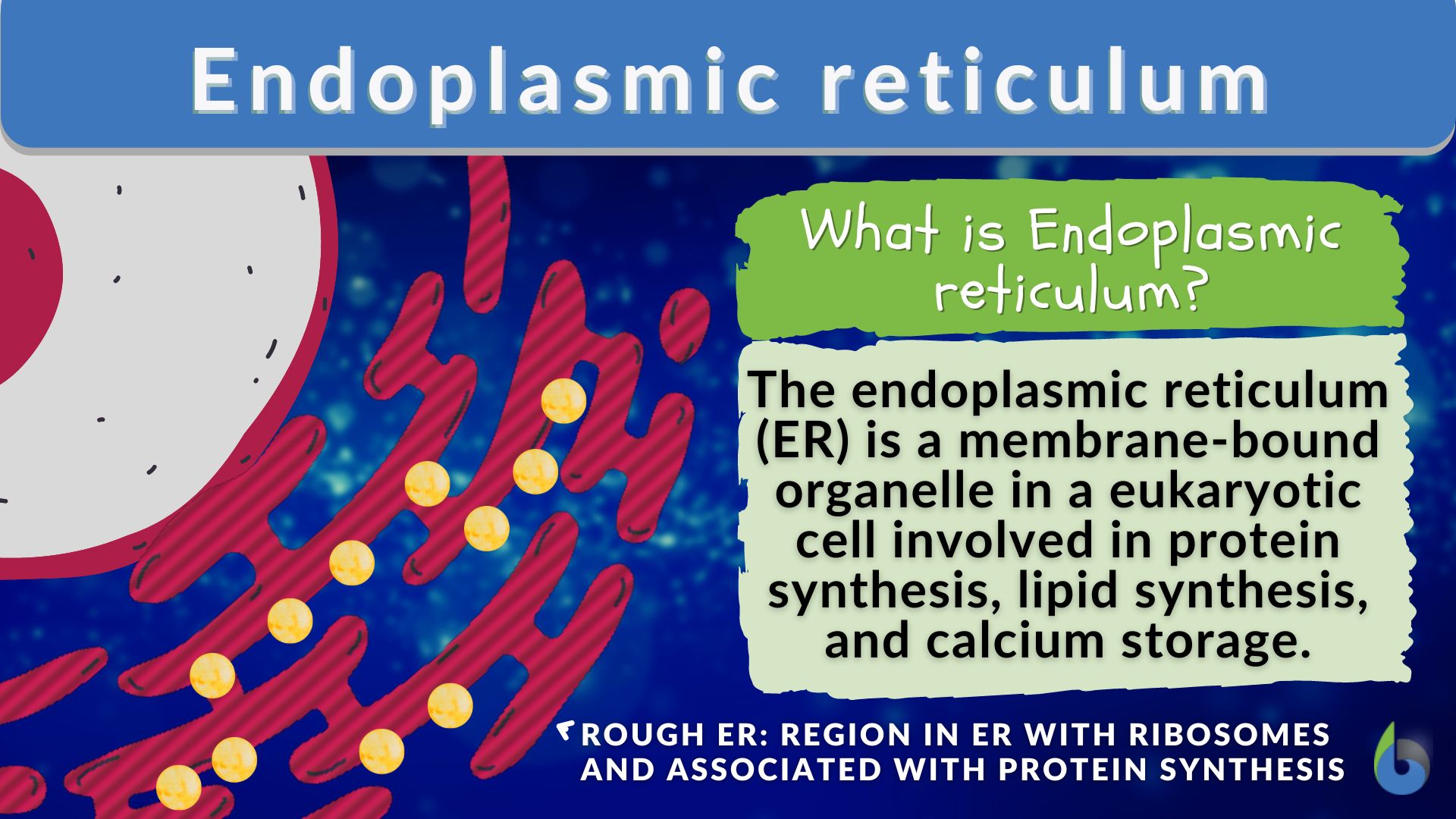
The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus are the organelles involved in the translational step of protein synthesis and the subsequent post-translational steps. Read this tutorial for more information…The Ribosome is an essential part of cells. Cells are a fundamental part of any living organism. So it is not wrong at all to say that every living organism has Ribosomes in its body. That too in millions.
Developing Cell Free Ribosomes In A Test Tube
Ribosomes are often considered
What is the function of ribosomes in a plant cell, the function of ribosomes is to synthesize, what is the main function of ribosomes, what is the function of ribosomes in an animal cell, function of ribosomes in points, ribosomes in prokaryotic cells, function of ribosomes in chloroplast, explain the function of ribosomes and why cells need them, function of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells, ribosomes function in prokaryotic cells, the function of ribosomes is to, what is the function of ribosomes






