What Is The Function Of Nerve Tissue – Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous tissue. Nerve cells are specialized cells that are responsible for receiving and transmitting nerve impulses or action potentials from one nerve cell to the next. Dendrites and axons are two types of cellular projections found in nerve cells.
Living things’ structural and functional units are cells. They perform fundamental body functions. A group of these specialized cells work together to produce tissue. Animals and plants have different tissues. There are four types of tissues in animals which include muscle, epithelial, connective and nervous tissue.
What Is The Function Of Nerve Tissue
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/glialcellsillustration-5a94d585642dca00362568c4.jpg?strip=all)
Nerves, the spinal cord and the brain all include nervous tissue. Many body functions are coordinated and under its direction. It stimulates muscle contraction, increases environmental awareness and is essential for emotions, memory and thinking.
Unit 6: Tissue Structure And Functions
To perform all these duties, cells in nervous tissue must be able to communicate with each other via electrical nerve impulses. Neurons, also known as nerve cells, are the cells in the nervous system that generate and conduct impulses. The dendrites, the cell body and the axon are the
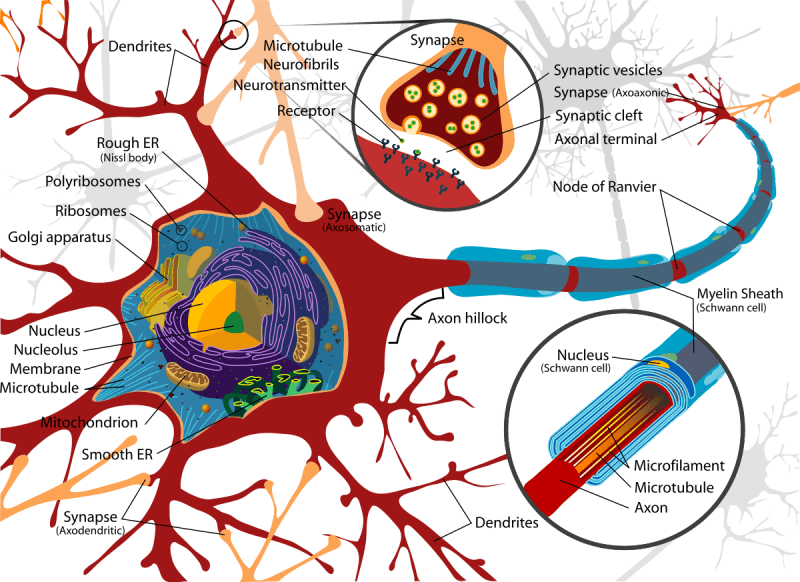
The cell body is the primary component of the cell and performs all of its fundamental tasks. Dendrites are cytoplasmic processes that transmit impulses to the cell body. The axon is a mechanism or extension that transmits impulses from the cell body. The axon forms synaptic connections that run through the neurons. The synaptic connections are a neural net’s learned information is contained in the interconnections between its neurons.
In addition, nervous tissue contains cells that support the functions of the neurons rather than transmitting impulses. These are the neuroglia, also known as glial cells (neuroglia cells). The neurons are connected and insulated by glia, or supporting cells. Some glial cells are capable of immune protection by being phagocytic; others act as tubes that deliver nutrition as they connect the blood vessels to the neurons.
The nervous tissue is a type of animal tissue that consists mainly of nerve cells and neuroglia cells. It is one of the most important types of animal tissue, the others being epithelial tissue, muscle tissue and connective tissue. The nerve cells are specialized cells that receive and transmit nerve impulses or action potentials from one nerve cell to the next. The nerve cells have characteristic cellular projections (dendrites that receive the electrochemical signals from another nerve cell and axons that transmit the action potential to the next nerve cell). The neuroglia cells help in protecting and providing nutrients to the nerve cells. They also help maintain homeostasis and form myelin.
Peripheral Nervous System: What It Is And How It Works
Neurons, commonly known as nerve cells, and neuroglial cells make up nervous tissue. Astrocytes, microglial cells, ependymal cells and oligodendrocytes are the four different forms of neuroglia that can be found in the central nervous system (CNS). Whole Schwann cells and satellite cells are two varieties of neuroglia found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The autonomic nervous system is a peripheral nervous system component that controls involuntary physiological functions such as heart rate and many other things.
The somatic nervous system is another component of the peripheral nervous system that is related to the voluntary regulation of body movements via skeletal muscles. Gray matter and white matter are the two tissue types found in the CNS. The tissue’s neuronal and neuroglial components are used to classify it.
The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) is one of the autonomic nervous system’s (ANS) two functionally distinct and constantly active divisions. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system (CNS).

Reaction in stressful situations. The primary function of the PNS is to conserve energy for later use and to control bodily activities such as digestion and urine.
Structure And Function Of The Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system consists of a network of nerves associated with activating the body’s “fight-or-flight” response. This system becomes more active when you are anxious, in danger, or physically engaged. Its effects include increased heart rate and respiratory capacity, improved vision and a slowing of functions such as digestion.
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a component of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that can regulate gastrointestinal behavior without the need for input from the central nervous system (CNS). Mammalian neurons can be found in the CNS (brain and spinal cord) or the PNS (cells with soma outside the brain and spinal cord).
The blood brain barrier (BBB) is an important immunological component of the human central nervous system (CNS). The dendritic blood brain barrier, which is made up of many different cell types, acts as a structural and functional barrier to pathogens such as bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites that may circulate in the bloodstream.
The central nervous system (CNS) requires a number of amino acids found in protein diets to function properly. The brain uses amino acids including tryptophan, tyrosine, histidine and arginine to synthesize various neurotransmitters and neuromodulators.
Nervous Tissue Chapter 3
The peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of branching peripheral nerves, and the central nervous system (CNS), which consists of the spinal cord and the brain, are the two main components of the nervous tissue that control and regulate the body’s functions and activities.
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless, watery fluid that circulates around your brain and spinal cord. The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. It controls and coordinates everything you do, such as your ability to move and breathe.
The central nervous system organs such as the brain and spinal cord as well as the peripheral nerves throughout the body contain nervous tissue. Neurons, or nerve cells, make up the nervous tissue. Axons, which are elongated projections that extend from the cell body of neurons, are how these specialized cells respond to stimuli by sending out messages. This is done by means of signaling molecules.
Signaling molecules play an important role in the nervous tissue. However, sometimes there are excess signaling molecules and the body must go through the process of removing excess signaling molecules.
Understanding Neurons’ Role In The Nervous System
Below is a diagram of each of the types of nervous tissue, a neuron and a neuroglia.
By carrying electrical signals through tissue, nervous tissue serves as the nervous system’s network of communication. Gray matter, which houses the synapses in the CNS, is crucial for processing information. Between gray matter regions in the CNS, white matter connects with myelinated axons and promotes nerve impulses. Unmyelinated axons will not perform this function. The myelin sheath is a type of connective tissue covering.
Relay sites for nerve tissue impulses are found in the ganglion tissue of the PNS, which also contains cell bodies and dendrites. Bundles of myelinated axons carry action potential nerve impulses fiber bundles and axons in the nervous tissue.
The two main types of cells that predominate in the nervous tissue present in organisms are neurons and neuroglia.
Cells Of The Nervous System
Neurons are specialized cells that can receive and promote the transmission of nerve impulses, or action potentials, across their membrane to the next neuron. They have an axon, dendrites and a large cell body (soma), which houses the cell projections.
Thin branching projections called dendrites receive electrochemical communication from neurotransmitters to change the cell’s voltage. The action potential is carried by long extensions called axons from the cell body to the next neuron.
A small space known as a synaptic cleft separates the bulbous end of the axon, or the axon terminal, from the dendrite of the neuron. Neurotransmitters are released across the synapse and attach to the post-synaptic receptors at the axon terminal, which continue the nerve impulse.

, is the most important part of a neuron. The nucleus and the majority of the major organelles are found in the cell body. But what distinguishes neurons is that they contain numerous extensions of their cell membranes known as processes.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Nervous System Notes: Diagrams & Illustrations
Axons, which are nerve fibers that emerge from the cell body and project to target cells, are commonly seen in neurons. A single axon can branch repeatedly to communicate with a large number of target cells. The axon is responsible for transmitting the nerve impulse to one or more cells.
Dendrites, which receive information from neighboring neurons via specific contact areas known as synapses, are the neuron’s other operations. Dendrites are typically strong branching processes that allow other neurons to connect with the cell body.
From the dendrites to the cell body and down the axon, information passes through a neuron. This gives the neuron polarity, meaning that information only flows in one direction.
Multiple processes arise from the cell bodies of multipolar neurons (hence the name). They have dendrites attached to their cell bodies and in certain cases a single long axon. Many CNS neurons, including motor neurons, are multipolar.
Nervous System: Structure And Function
Two opposing processes (bipolar cells) extend from each end of the cell body in bipolar cells. The first is an axon, and the second is a dendrite. Bipolar cells are extremely rare. They are mostly present in the olfactory epithelium (where odor stimuli are detected) and as a component of the retina in the eye.
The non-neural cells in nervous tissue known as neuroglia (or glial cells) serve a variety of vital support roles for neurons. They differ in structure depending on their function and are
Function of nerve tissue, what is the function of trigeminal nerve, what is the function of nerve tissue in the skin, what is the function of vagus nerve, structure and function of nerve tissue, what is the nerve tissue, what is the function of olfactory nerve, what is the function of bone tissue, what is the function of nerve cells, what is the function of vascular tissue, what is the function of auditory nerve, what is the function of connective tissue