What Is The Function Of Nerve Cells – Medical opinion of Nancy Hammond, M.D. – Carly Vandergriendt and Rachael Zimlich, RN, BSN – Updated February 28, 2022
Neurons, also known as nerve cells, send and receive signals from your brain. While neurons share much in common with other cell types, they are structurally and functionally unique.
What Is The Function Of Nerve Cells
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1286811004-f6718158f93d418d838933042068cd06.jpg?strip=all)
Specialized projections called axons allow neurons to transmit electrical and chemical signals to other cells. Neurons can also receive these signals through root extensions known as dendrites.
What Are Glial Cells: Types And Functions
. The formation of new nerve cells is called neurogenesis. Although this process is not well understood, we know that it is much more active when you are an embryo. However
As researchers gain insight into neurons and neurogenesis, many are also working to uncover links to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
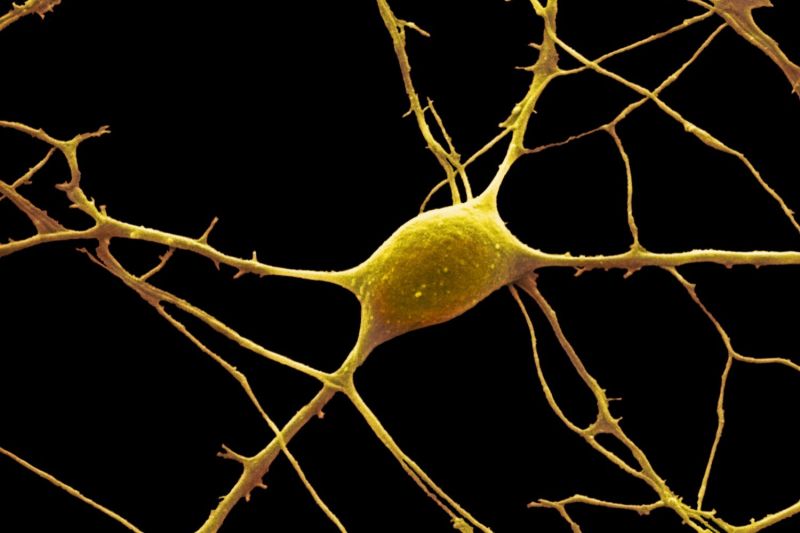
Neurons vary in size, shape and structure depending on their role and location. However, almost all neurons have three basic parts: the cell body, the axon, and the dendrites.
Also known as the soma, the cell body is the nucleus of a neuron. The cell body contains genetic information, maintains the neuron’s structure, and provides energy to drive activities.
Peripheral Nervous System (pns): What It Is & Function
Like other cell bodies, the neuron soma contains a nucleus and specialized organelles. It is enclosed by a membrane that protects it and at the same time allows it to interact with its immediate surroundings.
An axon is a long tail-like structure. It connects to the cell body at a specialized junction called the axon hillock. Many axons are insulated by a fatty substance called myelin. Myelin helps axons conduct electrical signals.
Dendrites are fibrous roots that branch out from the cell body. Like antennae, dendrites receive and process signals from the axons of other neurons. Neurons can have more than one set of dendrites, known as dendritic trees.

Their number depends on their role. For example, Purkinje cells are a special type of neuron found in a part of the brain called the cerebellum. These cells have highly developed dendritic trees that allow them to receive thousands of signals.
What Function Do Nerve Cells Perform
Neurons differ in structure, function and genetic makeup. Due to the huge number of neurons, there are thousands of different types, just as there are thousands of species of living organisms on Earth.
Sensory neurons are triggered by physical and chemical inputs from your environment. Sound, touch, heat and light are physical inputs. Smell and taste are chemical inputs.
For example, stepping on hot sand activates sensory neurons in the feet. These neurons send a message to your brain that makes you aware of heat.
Motor neurons play a role in movement, including voluntary and involuntary movements. These neurons allow the brain and spinal cord to communicate with muscles, organs, and glands throughout the body.
Red Blood Cells Red Blood Cells Structure: Large Surface Area
There are two types of motor neurons: lower and upper. Lower motor neurons transmit signals from the spinal cord to smooth and skeletal muscles. Upper motor neurons transmit signals between your brain and spinal cord.
When you eat, for example, lower motor neurons in the spinal cord send signals to smooth muscles in the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. These muscles contract, allowing food to move through your digestive tract.
Interneurons are neural transmitters found in your brain and spinal cord. They are the most common type of neuron. They carry signals from sensory neurons and other interneurons to motor neurons and other interneurons. They often form complex circuits that help you respond to external stimuli.

For example, when you touch something sharp like a cactus, sensory neurons in your fingertips send a signal to interneurons in your spinal cord. Some interneurons relay a signal to motor neurons in your hand, allowing you to move your hand away. Other interneurons send a signal to the pain center in your brain and you feel pain.
Text Book Of Nervous Diseases; Being A Compendium For The Use Of Students And Practitioners Of Medicine . M The Chromatic Substance Of The Cell. While Most Nervecells Have These Granules, Some,
Neurons send signals using action potentials. An action potential is a shift in the potential electrical energy of a neuron caused by the flow of charged particles in and out of the neuron’s membrane. When an action potential is generated, it is transmitted along the axon to the presynaptic terminal.
Action potentials can trigger both chemical and electrical synapses. Synapses are where neurons can transmit these electrical and chemical messages to each other. Synapses are made up of a presynaptic terminal, a synaptic cleft, and a postsynaptic terminal.
In a chemical synapse, a neuron releases chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These molecules pass through the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors in the postsynaptic end of the dendrite.
Neurotransmitters can trigger a reaction in the postsynaptic neuron, causing it to generate its own action potential. Alternatively, they may inhibit activity in the postsynaptic neuron. In that case, the postsynaptic neuron does not generate an action potential.
Motor Neuron: Function, Types, And Structure
Electrical synapses can only excite. These synapses are formed when two neurons are connected by a gap junction. This gap is much smaller than a chemical synapse and is formed by ion channels that help transmit a positive electrical signal.
Because of the way these signals travel, signals travel through electrical synapses much faster than chemical synapses. However, these signals can decrease from one neuron to another. This makes them less efficient at transmitting repeated signals.
Although research over the past century has advanced our understanding of neurons, there is still much we do not understand.

For example, until recently scientists believed that neuron formation occurred in adults in a region of the brain called the hippocampus. The hippocampus is involved in memory and learning.
Question Video: Describing The Function Of Nervous Tissue
Reports that the production of neurons in the hippocampus declines rapidly after birth. This means that practically no new neurons are created in adulthood. More research is needed to better understand what is really going on.
Experts viewed the discovery as a roadblock to using neurogenesis to treat diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. These conditions result from neuronal damage and death.
However, there is still hope that neural stem cells can be used to create new neurons. Neural stem cells can produce new neurons
. However, scientists are still trying to find the best way to use these stem cells to produce specific types of neurons in a laboratory setting.
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review
If successful, these nerve cells could be created to replace those lost through age, damage and disease.
Many clinical trials are currently underway to test the use of the newly created nerve cells. This one focuses, for example, on people who have experienced an ischemic stroke.
Used fluorescent probes to observe activity in mouse nerve cells in real time. This technology could help map brain activity, detect problems that lead to neurological disorders, and advance the field of artificial intelligence.

Want to see how much you learned today? Use the resources below to test yourself (or your students) on the anatomy and different types of neurons.
Neuron Anatomy, Nerve Impulses, And Classifications
The cells of the nervous system are called neurons. They have three distinct parts, including the cell body, axon, and dendrites. These parts help them send and receive chemical and electrical signals.
Although there are billions of neurons and thousands of types of neurons, they can be divided into three basic groups based on function. They are motor neurons, sensory neurons and interneurons.
There is still much we do not know about neurons and their role in the development of certain brain conditions. But many research projects and clinical trials are underway to try to find those answers.
Has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using third-party links. Learn more about how we ensure the accuracy and timeliness of our content in our editorial policy.
Neuron Structure And Classification
Our experts continuously monitor the health and wellness space and we update our articles as new information becomes available. Home Quizzes and games History and society Science and technology Biographies Animals and nature Geography and travel Art and culture Videos for money
A breakthrough in all studies of the nervous system was the observation of the Spanish scientist Santiago Ramón y Cajal in 1889, who stated that the nervous system consists of individual units that are structurally independent of each other and whose internal content is not direct. contact. According to his hypothesis, now known as neuron theory, each nerve cell communicates with others through contiguity rather than continuity. This means that communication between adjacent but separated cells must take place through the space and barriers that separate them. Cajal’s theory has since been proven not universally true, but his central idea—that communication in the nervous system is largely communication between independent nerve cells—remained the precise guiding principle for all subsequent studies.
It is estimated that there are 85 to 200 billion neurons in the human brain. Each neuron has its own identity, expressed by its interactions with other neurons and its secretions; each also has its own function depending on its intrinsic properties and location, as well as its inputs from other selected groups of neurons, its ability to integrate these inputs, and its ability to transmit information to another selected group of neurons.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-the-peripheral-nervous-system-2795465-FINAL-b69e1bb803654212a83d9e68eb4847d0.png?strip=all)
With few exceptions, most neurons consist of three distinct regions, as shown in the diagram: (1) the cell body or
Mammalian Nervous System (14.1.1)
Function of the nerve cells, what is the function of trigeminal nerve, what is the function of b cells, what is the function of goblet cells, what is the main function of nerve cells, what is the function of t cells, what is the function of stem cells, what is the function of myelin in nerve cells, what is nerve cells, structure and function of nerve cells, what is the function of nerve tissue, what is the function of vagus nerve