What Is The Function Of Mitochondria In Eukaryotic Cells – Understand what cristae mitochondria are. Learn the function of cristae in mitochondria and understand why the inner mitochondrial membrane is folded.
Cristae folds within the inner mitochondrial membrane. Mitochondria have two membranes: an outer membrane without folds and an inner membrane with cristae.
What Is The Function Of Mitochondria In Eukaryotic Cells

Cristae are folded into the inner mitochondria membrane. These folds increase the area of the inner membrane where energy production occurs. Therefore, the increased surface area allows the mitochondria to produce more energy at a faster rate.
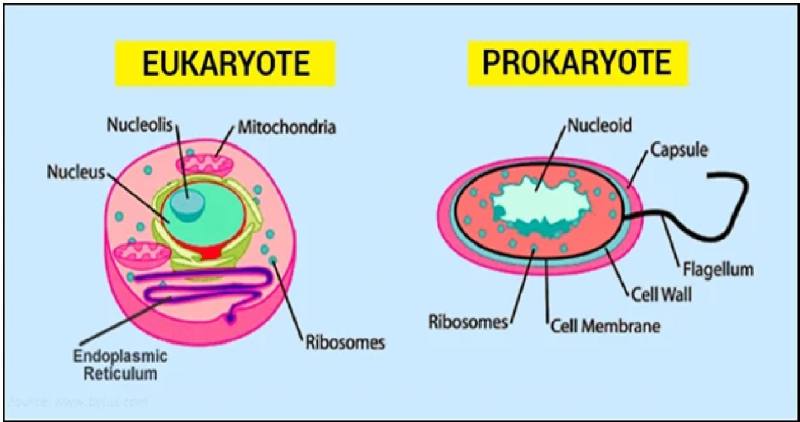
The Difference Between Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells
What are the cristae of mitochondria? Mitochondrial cristae is a folding in the inner mitochondrial membrane, and crista is one way of cristae. Mitochondria are eukaryotic organelles known for their function in energy production. Organelles are specialized structures that perform various functions within the cell, and eukaryotes are organisms (ie, humans, other mammals, plants, fungi, etc.) that have a nucleus, a nuclear envelope, and membrane-bound organelles inside. of their cells.
Mitochondrial cristae are folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane. These folds increase the area of the membrane and help make the mitochondrion more active.
In anatomy and zoology, the definition of cristae is a ridge or crest. Barriers within the mitochondrial membrane appear as ridges surrounding the mitochondrial matrix (the innermost layer of the mitochondria). These rows or folds go beyond aesthetics to serve a greater purpose.
Mitochondria are responsible for converting energy from food into available energy for the cell. This is accomplished through a series of coordinated movements known as cellular respiration. The result of these reactions is a very powerful molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is used in many biochemical reactions because it has enough energy within its bonds to drive those reactions. Reactions that occur in mitochondria include:
Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis are collectively known as oxidative phosphorylation, the final part of cellular respiration.
Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in and around the inner mitochondrial membrane. The form and function of the cristae facilitates the production of energy in this process. Oxidative phosphorylation involves the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Why is the mitochondrial inner membrane folded? Remember that oxidative phosphorylation occurs along the mitochondrial membrane, and the cristae is a folding within the same membrane. The addition of folds increases the surface area, allowing more of the membrane to fit inside the mitochondria. Increasing the surface area increases the number of oxidative phosphorylation reactions that can occur simultaneously. Therefore, an increase in surface area increases the ability of the mitochondrion to produce energy. Scientists also believe that the shape of the inner mitochondrial membrane constantly changes according to different physical conditions inside the cell.

The addition of folds to increase surface area is a common technique used for many body parts to increase performance. This appears in:
Mitochondrion Vector Illustration Stock Vector
Mitochondrial cristae are folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane that give rise to space. This allows a large area for processes to occur across the membrane. The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis are processes that help produce ATP in the final steps of cellular respiration. The following image is a mitochondrion, showing the inner membrane, including the cristae:
As a member, you’ll get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personal coaching to help you succeed.
I would definitely recommend to my colleagues. It’s like the teacher waved a stick at me and gave me a task. I feel like it’s a way of life.
Mitochondrial cristae activity ultimately produces more ATP at a faster rate and empowers cells to meet the body’s energy needs. Oxidative phosphorylation is the final part of cellular respiration and operates in response to the body’s need for energy. Mitochondrial cristae provide the structure, function, and flexibility needed to provide sufficient energy.
Comparing Mitochondrial, Chloroplast, And Prokaryotic Genomes
Cristae folds in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Mitochondria are organelles in eukaryotic cells. The main function of the cristae is to increase the surface area of the mitochondrial membrane. This allows membrane systems to produce more energy at a faster rate. In this case, energy is produced in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through a process called cellular respiration, a group of mechanisms that generate usable energy from simple food molecules. Basically, the cell needs cristae to make enough ATP.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the final part of cellular respiration that includes the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. The electron transport chain creates a proton potential in the inter-membrane space. Chemiosmosis is a process in which the electrochemical gradient of protons collected funnels through ATP synthase to produce ATP.
Therefore, mitochondrial cristae provide structural support and functional space to produce ATP and meet the body’s energy needs.

Before we explain the function of the crista (plural = cristae), we need to go back to what the mitochondrion does. A mitochondrion is a cellular organelle where cellular respiration occurs. Cellular respiration is a process that generates chemical energy in the form of ATP from simple food molecules. These food molecules, especially glucose, are first broken down in the cytosol outside the mitochondrion during glycolysis.
Eukaryotic Cells Definition And Examples
After glycolysis, the remains of glucose molecules form in the mitochondria. This initiates aerobic cell respiration. First, the citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix; this releases less ATP and creates NADH and FADH2 electron carriers that pass to the next step, the electron transport chain.
The electron transport chain uses electrons from NADH and FADH2. These electrons are transferred through proteins embedded in the membrane and produce H2O molecules. H+ ions (protons) from these carriers are bound ‘across’ the inner membrane and the inter-membrane space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes.
The formation of H + ions in the inter-membrane space creates a proton potential. During chemiosmosis, protons funnel through the protein ATP synthase to the inner membrane. As they do, ATP synthase cycles to create ATP from ADP and phosphate. Thus, the energy of the proton provides the energy to make ATP.
Cristae are folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane. The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis occur in this membrane as part of cellular respiration to make ATP and can be seen in the diagram:
Draw Two Eukaryotic Cells. Label The Structures Listed Here
The cristae increase the surface area of the inner membrane, allowing the rapid production of ATP because there are more places to do the process.
So, how do these folds increase the surface area? Imagine a square membrane with a perimeter of 800 nanometers. Each side is 200 nm (billionths of a meter) long. If the height were 25 nm, there would be exactly 20,000 square nm of surface area for ATP production. If the inner membrane of the mitochondrion were square, it would have limited space to produce ATP. In the following diagram, notice the ATP synthase molecule that allows the H+ ion to form.
Now, if we increase the perimeter of that membrane by including folding, we get more surface area without taking up a lot of space. Let’s say the new folder adds another 200 nm to the perimeter, for the same length of 25 nm. This increases the area of 5, 000 square nm, to 25, 000. The crista is a fold that allows the inclusion of ATP synthase molecules in the membrane, therefore, the production of more ATP at the same time.

Let’s take a closer look. Mitochondrial cristae are folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane that give rise to space. Having more cristae gives the mitochondrion more places for ATP production to take place. In fact, without them, the mitochondrion would not be able to maintain the ATP needs of the cell.
Mitochondria And The Art Of Dna Maintenance
This concept of large surface area also applies to other areas of the human body. For example, the lining of the intestine has structures called villi that increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients.
Cellular Respiration: Cellular respiration is a process that generates chemical energy in the form of ATP from simple food molecules.
Unlock Your Education See why 30 million people use Become a member and start learning now. Be a Member. They provide chemical energy to the cell in the form of ATP molecules. The definition of mitochondria in biology goes like this:
Mitochondria are round or egg-shaped, double-membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells that carry out the responsibility of keeping the cell charged with cellular activity through the production of energy units called ATP.
Loss Of Contact Between Mitochondria And Lysosomes Contributes To Genetic Parkinson’s Disease
A mitochondrion is a cell organelle that is actively involved in the production of energy or the basic biological fuel for the functioning of the cell. Now the question arises,
– A high energy compound that provides energy for cellular energy needs. It is produced by the cellular respiration process that takes place in the mitochondria. During cellular respiration, food is oxygenated, oxygen is consumed, and carbon dioxide is released.
Figure 1: Look at this diagram of a mitochondrial to understand its basic structure and internal organs. You can notice the double membrane structure and the different DNA of the mitochondria (

DNA) outside the nuclear DNA (DNA present in the nucleus) of the cell.
Mitochondrial Proteins: From Biogenesis To Functional Networks
Function of the mitochondria, what is the function mitochondria, what is the function of the mitochondria, mitochondria function in eukaryotic cells, what is the function of cyclin in eukaryotic cells, what is the function of mitochondria in cells, what is the function of eukaryotic cells, function of eukaryotic cells, function of mitochondria in cells, mitochondria of eukaryotic cells, what is the role of mitochondria in eukaryotic plant cells, what is the function of organelles in eukaryotic cells