What Is The Function Of Dense Connective Tissue – Learn about the structure, location, and function of regular dense connective tissue in the human body with photos and histological diagrams. Updated: 10/03/2021
Dense connective tissue mainly stabilizes and supports the surrounding tissues and organs. Regular dense connective tissue has parallel fibers packed closely together and can be found in tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses, the respiratory tract, and blood vessel walls – just to name a few! Dense, irregularly oriented connective tissues have the appearance of woven fibers and comprise organ capsules, periostea, and perichondria.
What Is The Function Of Dense Connective Tissue

A tendon is an example of regular dense connective tissue. A tendon is a dense connective tissue of collagen (white) that serves to connect bones to muscles and has great tensile strength along its long axis.
Organization Of Connective Tissue
This lesson will guide your understanding of regular dense connective tissue. Through the sections below you will explore the components of the tissue and its overall structure, the unique functions of this particular type of tissue, and where in the body regular dense connective tissue can be found.
Connective tissues are found throughout the body and are extremely diverse in appearance and function. However, the structural components of connective tissue are consistent. All connective tissue contains specialized cells, extracellular protein fibers, and ground substance. The protein fibers and ground substance surround specialized cells in connective tissue and form what is called the matrix. The matrix is the bulkiest component of all connective tissues.
Connective tissues are categorized as (1) proper connective tissue, (2) supporting connective tissue, or (3) fluid connective tissue. The proper connective tissues are classified as tight and loose connective tissues. The supporting supporting tissues are cartilage and bone. The fluid connective tissues are blood and lymph. Tissues within these categories can perform the following functions:
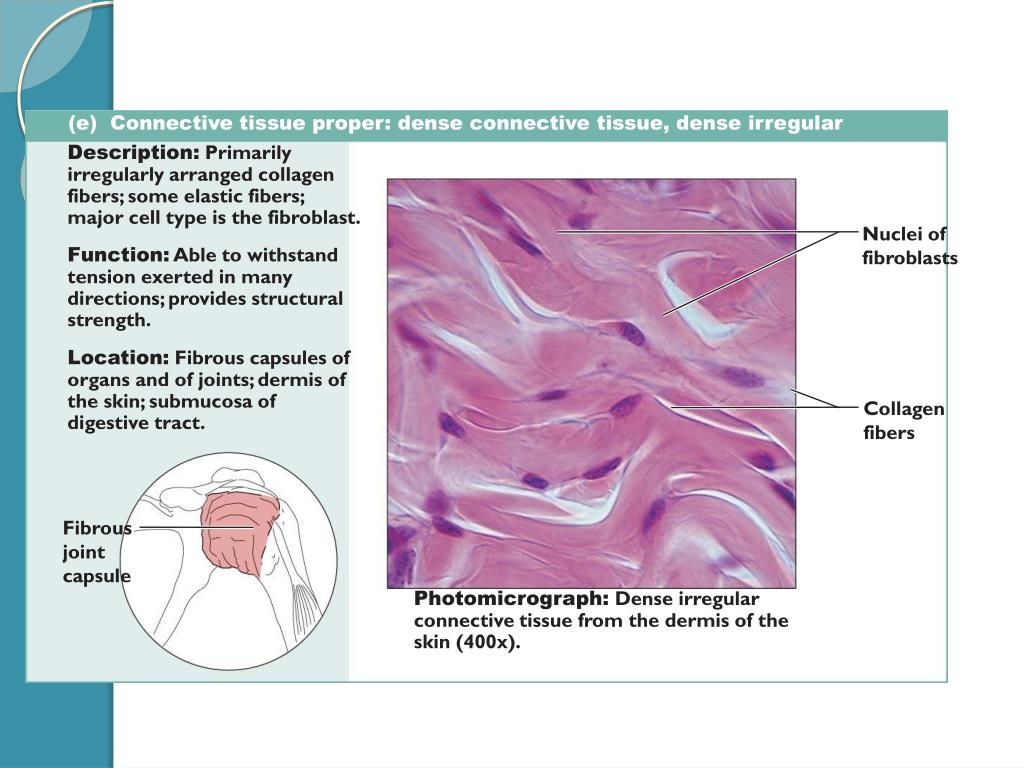
Dense connective tissues work to connect and stabilize other tissues and are mostly fibrous. This means that fibers, especially collagen or elastin fibers, comprise most of the volume of the tissue. Because of this fibrous composition, dense connective tissue is also known as fibrous connective tissue. Dense connective tissue can be regular or irregular. This distinction reflects the organization of fibers within a tissue structure. The fibers in regular dense connective tissue are aligned parallel to each other, whereas in irregular dense connective tissue the fibers have an inconsistent patterning and a woven appearance.
Dense Fibrous Connective Tissue Hi Res Stock Photography And Images
The photo on the left shows the parallel collagen fibers in regular dense connective tissue, this is a histological photo of a tendon at 200x magnification. The photo on the right shows the woven appearance of irregular dense connective tissue, this histological photo shows areolar tissue at 400x magnification.
Dense irregular connective tissues form the protective capsules that surround internal organs, the casing around some cartilages (i.e. perichondrium) and bones (i.e. periosteum), and also provide strength to the dermis. Alternatively, tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses are all forms of regular dense connective tissue that support or stabilize adjacent tissues. The rest of this lesson will focus on regular dense connective tissue.
Not just connective tissue, as the name suggests, but tissue that connects tissues or organs to each other; they are also responsible for anchoring, separating and encasing other tissues and organs within the body. Within the connective tissue category there are six types:
Here, we are going to explore one of the fibrous types known as regular dense connective tissue. Regular dense connective tissue is a very important type of connective tissue that provides the structures they join and/or includes a lot of protection because they are strong yet flexible. They can resist very large tensile and stretching forces along their fibers while remaining extremely flexible and flexible. You are probably familiar with regular dense connective tissue in the form of your tendons (tissue that connects muscle to bone) and ligaments (tissue that connects bone to bone).
Connective Tissue Types And Examples
Now, you might think that your muscles alone make you strong but it’s not. Your actual strength is the product of your muscles as well as the regular dense connective tissue of your tendons. These tendons attach your muscles firmly to your bones. Without your tendons, your muscles would detach easily when you moved or flexed because muscles, although they are strong fibers, are not great connective tissue.
As a member, you get unlimited access to more than 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you succeed.
I would definitely recommend to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waving a magic wand and doing the work for me. I think it’s a lifeline.
Protein fibers in regular dense connective tissue that run in tightly packed parallel bundles. Fibers often have a wavy appearance. The specialized cells in this type of tissue are called fibroblasts. They are often colored darker in histological slides and diagrams, they are scattered between the parallel fibers.
Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Connective Tissue Video Tutorial & Practice
The recognizable components of regular dense connective tissue are fibroblasts and protein fibers. Because of the dense, regular arrangement of the fibers, the ground substance is rarely visible on histological slides and diagrams. Regular dense connective tissue contains many more fibers than fibroblasts. Below are the components of this type of tissue.
Fibroblasts are stationary cells and are always found in proper connective tissue. Fibroblasts produce a cellular binding agent called hyaluronan and various proteins.
Collagen fibers are long, wavy, unbranched fiber bundles. Visible fibers are composed of many protein subunits that are tightly wound together, they are white in color, but will appear thick and light colored on most slides and histological diagrams. Collagen fibers are the most abundant fibers in proper connective tissue and provide strength and rigidity.

Elastin fibers are thinner than collagen fibers and usually stain darker in histological slides and diagrams. Elastin provides tissues with flexibility and recoil. The fibers appear yellow and are less abundant in proper connective tissue than collagen fibers.
Structure And Function Of Connective Tissue And Bone Lab
The ground substance is viscous in proper connective tissue due to proteoglycans. Proteogins are formed by interaction between extracellular fluid and fibroblast secretion of hyaluronan and protein subunits.
This histological photograph shows a long section of a tendon (regular dense connective tissue). Note the parallel arrangement and symmetry of the collagen fibers with fibroblasts.
There are two regular types of dense connective tissue: collagen dense connective tissue and elastin dense connective tissue.
The tight, parallel arrangement of fibers in regular dense connective tissue contributes to the tissue’s strength. Furthermore, the orientation of the tissue is always in line with the forces that the tissue will be subjected to. This is why dense connective tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses provide stability and resilience to the body.
Bio 372 Week 2 Lecture 4
Regular dense connective tissue can be found in many places throughout the body. It can be found in tendons that support the connection between muscles and bones, in ligaments that stabilize bone-to-bone connections and the position of internal organs, in aponeuroses that attach broad muscles to other muscles or multiple bones, and in fibrous sheaths and coverings. These sheaths surround some cartilage, organs, muscle and nerve fiber bundles, and bones. A more flexible subcategory of regular dense connective tissue, elastic tissue, provides stability to the body in areas that also require stretching and retraction such as in the walls of the aorta or around the spinal column.
The tensile strength and resistance of regular dense connective tissue gives it its function within the body as a means of support and stability for other tissues and structures. This strength is best understood by delineating the hierarchical composition of a regular dense structure of connective tissue, such as a tendon.
A tendon is made primarily of individual collagen strands called fibrils. These fibrils are tightly packed together parallel to each other in collagen fibrils. These fibers are bundled into larger groups called subfascicles, which are bundled with other subfascicles into fascicles. Fascicles join other fascicles into tertiary fiber bundles, which are then joined by other tertiary fiber bundles and covered to form a tendon. This nested bundle structure makes tendons very strong along the axis of muscular contraction and resists tearing.

Ligaments have a similar structure to tendons, and aponeuroses form sheets within a similar scheme to provide resistance and stability to other structures.
Solved 7, 8) Identify The Tissue A) Areolar Connective
This sketch shows the basic levels of tendon organization, from collagen to tendon. This hierarchical structure is critical to understanding the tensile strength of dense regular connective tissue.
Regular dense connective tissue works to transfer the force of one tissue to another to resist overload and injury. This type of tissue has great tensile strength, except along one axis, in the direction in which the collagen fibers are oriented. This means that strength is not only attributable to muscles, but is a product of muscles and the structure and composition of regular dense connective tissue. Regular dense connective tissue is prone to weakness if a force crosses the structure from any direction other than along the longitudinal axis. Therefore, although regular dense connective tissue provides support and stability to the body, it does not provide protection for cells and organs.
This type of tissue is also a
What is the function of dense regular connective tissue, what is the function of dense irregular connective tissue, examples of dense connective tissue, function of the connective tissue, structure of dense connective tissue, where is dense irregular connective tissue found, function of dense connective tissue, dense irregular connective tissue function, dense regular connective tissue function, collagen connective tissue function, where is dense connective tissue found, dense regular connective tissue






