- What Is The Difference Between Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis
- Cellular Respiration: What Is It, Its Purpose, And More
- Sketch And Label A Diagram Showing The Relationship Between
- Please Help!!) How Does The Diagram Illustrate The Relationship Between Respiration And Photosynthesis?
- Describe The Similarities Between Photosynthesis And Respiration
- What Is Respiration
What Is The Difference Between Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis – Definition: A series of metabolic processes in a cell in which biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance (eg, glucose) and then stored in an energy-carrying biomolecule (eg, ATP).
. Biochemical energy is harvested from organic substances (eg, glucose, a six-carbon molecule) and then stored in energy-carrying biomolecules (eg, adenosine triphosphate, or ATP) for the cell’s energy-requiring functions. The main function of cellular respiration is to break down glucose to generate energy.
What Is The Difference Between Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis

Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic processes that take place in the cell, where biochemical energy is collected from organic matter (for example, glucose) and then stored in energy-carrying biomolecules (for example, ATP) for energy-requiring functions of the cell.
Cellular Respiration: What Is It, Its Purpose, And More
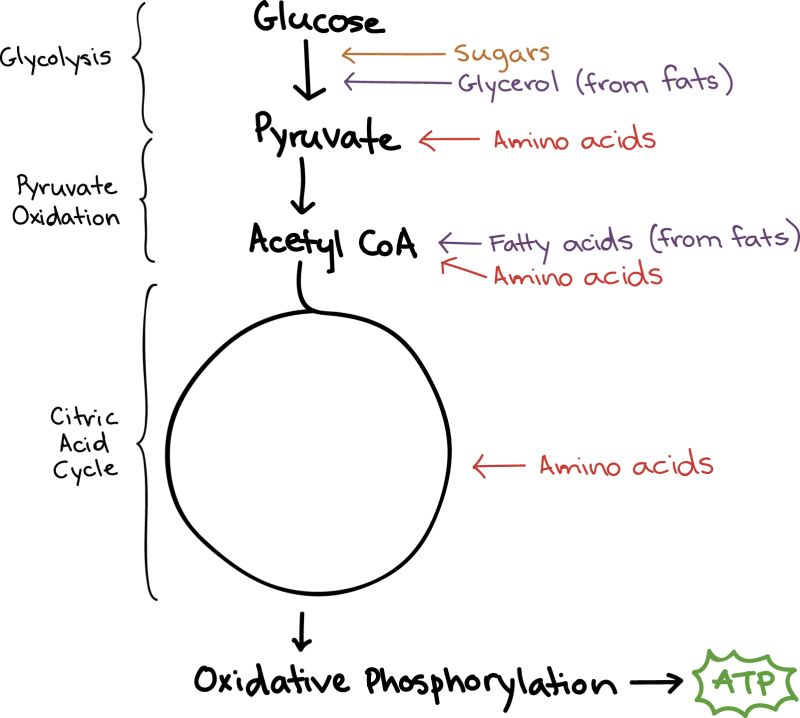
In prokaryotic cells it takes place in the cell cytoplasm, in eukaryotic cells it starts in the cytosol and then takes place in the mitochondria. In eukaryotes, the four steps of cellular respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation.
If the final electron acceptor is not oxygen, it is defined as anaerobic. Anaerobic respiration is carried out primarily by anaerobic organisms (eg, anaerobic bacteria) that use certain molecules as electron acceptors instead of oxygen.
In other anaerobic processes, such as fermentation, pyruvate is not converted in the same way as in aerobic respiration.
The pyruvate molecules produced are not transported into the mitochondria. Instead, they remain in the cytoplasm, where waste products from the cell are converted.
Pdf) Understanding Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration: Encouraging A View Of Biological Nested Systems
The main function of cellular respiration is to synthesize biochemical energy. Cellular respiration is very important for both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells because this biochemical energy is generated to stimulate many metabolic processes such as biosynthesis, locomotion and transport of molecules across fields.
Specific products for cellular respiration: Skip to section – What are cellular respiration products? For a diagram of cellular respiration, see the next section below.
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytosol and mitochondria of cells. Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol, pyruvate oxidation, the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation occur in the mitochondrion. Figure 1 shows the locations of the main biochemical reactions involved in cellular respiration.
Figure 1. Diagram of cellular respiration showing how the process produces ATP and other metabolic products. Credit: Thoughtco.com
Sketch And Label A Diagram Showing The Relationship Between
The energy produced by mitochondria is stored as potential energy in molecules called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The main chemical produced in cellular respiration is ATP. ATP is the standard unit of energy produced during respiration. Mitochondrion can be called “.
Due to its important role in cellular respiration, the cell. Mitochondria contain several enzymes that help with this process.
And it is transferable to molecules and ions (eg ATP). Cellular respiration of the inner membrane contains complex components involved in the electron transport chain step, which will be discussed in detail below.
Cellular respiration in the presence of oxygen is known as aerobic respiration. If it occurs in the absence of oxygen, it is known as anaerobic respiration.
Please Help!!) How Does The Diagram Illustrate The Relationship Between Respiration And Photosynthesis?
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are responsible for breaking down organic molecules (usually carbohydrates or lipids). During these enzyme reactions, a small amount of energy is transferred to the ATP molecules.
ATP is found in every living cell and can move energy to where it is needed. Energy can be released from ATP by dephosphorylation to adenosine diphosphate (ADP). See Figure 2 for the structure of ATP.
Oxygen is used in cellular respiration. It is a diatomic molecule (ie it is joined by two oxygen molecules in a covalent bond) and is electronegative, meaning it attracts electron bond pairs. When it attracts electrons to it, it releases energy from the chemical bond. The potential energy from our food combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide products (CO

For example, the monosaccharide glucose, (the most basic form of carbohydrate) can combine with oxygen. The high-energy electrons in glucose are transferred to oxygen and a potential energy is released. The energy is stored in the form of ATP. This final process of cellular respiration takes place on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Instead of releasing all the energy at once, the electrons move down the electron transport chain.
Describe The Similarities Between Photosynthesis And Respiration
The energy is released in small pieces and this energy is used to create ATP. See below to learn more about the steps of cellular respiration, including the electron transport chain.
Cellular respiration can be written as chemical equations. An example of the equation for aerobic respiration can be found in Figure 3.
Most prokaryotes and eukaryotes use the process of aerobic respiration. As mentioned above, oxygen is the process of cellular respiration. Water and carbon dioxide along with energy are the end products of this reaction. (See Figure 3)
During lactic acid fermentation, 6 carbon sugars such as glucose are converted to energy in the form of ATP. However, during this process, lactate is also released, which becomes lactic acid in the solution. See Figure 4 for an example of a lactic acid fermentation equation. It can occur in animal cells (such as muscle cells) as well as some prokaryotes. In humans, the accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles can occur in the absence of oxygen during intense exercise. Aerobic respiration is converted to lactic acid fermentation in the mitochondria, although it also produces ATP. It is not as efficient as aerobic respiration. Accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles can also cause pain.
Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Diagram Illustration Stock Vector Image & Art
Alcoholic fermentation (also known as ethanol fermentation) is a process that converts sugars into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. It is done by yeast and some bacteria. Alcoholic fermentation is used by humans in the process of making alcoholic beverages such as wine and beer. During alcoholic fermentation, sugars are broken down, creating pyruvate molecules in a process called glycolysis. Two molecules of pyruvic acid are formed during glycolysis of one glucose molecule. These pyruvic acid molecules are reduced to two ethanol molecules and two carbon dioxide molecules. Pyruvate can be converted to ethanol under anaerobic conditions, which begins by converting to acetaldehyde, which releases carbon dioxide, and acetaldehyde is converted to ethanol. In alcoholic fermentation, the electron acceptor NAD+ is reduced to form NADH and this exchange of electrons helps create ATP. Figure 5 shows the equation for the fermentation of alcohol.
Methanogenesis is a process carried out exclusively by anaerobic bacteria. These bacteria belong to the phylum Euryarchaeota and they include Methanobacteriales, Methanococcales, Methanomicrobiales, Methanopyrales and Methanosarcinales. Methanogens occur in oxygen-depleted environments, such as sediments, aquatic environments, and the guts of mammals. There are 3 pathways for methanogenesis:
(1) Acetoclastic methanogenesis. This process involves the activation of acetate to acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), then a methyl group is transferred to the central methanogenic pathway. Acetoclastic methanogens break down acetate in the following way:
Acetoclastic methanogenesis is carried out by Methanosarcina and Methanosarcinales and is often found in freshwater sediments. Here, acetate is thought to contribute two-thirds of the total methane formation on Earth each year.
Aerobic Respiration: Definition, Equation And Examples
(2) Methiotrophic methanogenesis. In methiotrophic methanogenesis, methanol or methylamines are used instead of acetate. This process can be seen in marine sediments where methylated substrates can be found. Some acetoclastic Methanosarcinales and at least one member of Methanomicrobials can use this second pathway.
(3) Hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis. Finally, hydrotrophic methanogenesis is a process used by Methanobacteriales, Methanococcales, Methanomicrobiales, Methanopyrales and Methanosarcinales (i.e. all five orders). In this reaction, hydrotrophic methanogens use hydrogen for carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, or formate as follows.
Although methanogenesis is a form of respiration, a simple electron transport chain is not used. Methanogens instead rely on several coenzymes, including coenzyme F420, which is involved in hydrogen activation, and coenzyme M, which is involved in the terminal reduction of CH3 groups to methane (Figure 6.).
The cellular respiration process has 4 stages. These are glycolysis, transition reactions, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with chemiosmosis.
What Is Respiration
The literal meaning of glycolysis is ‘split sugar’. Glycos comes from the Greek word for ‘sweet’ and lysis means ‘to split’. Glycolysis is a series of reactions that release energy by splitting glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules. Glycolysis is a biochemical pathway that evolved a long time ago and is present in most organisms. In organisms that perform cellular respiration, glycolysis is the first step of the process. However, glycolysis does not require oxygen, and many anaerobic organisms also have this pathway.
Before glycolysis can begin, glucose must be transported into the cell and phosphorylated. In most organisms, this occurs in the cytosol. The most common form of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis involves other pathways, one
What is the difference between photosynthesis and respiration, the similarities between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, what is the difference between cellular respiration and breathing, what is the difference between cellular respiration and fermentation, the connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, what is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration, photosynthesis and cellular respiration, difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, what is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, what is the difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, what is the connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration