What Is Potassium Level In The Body – A group of researchers are studying the mechanisms of potassium homeostasis. They found that the movement of potassium across the cell membrane is controlled by many factors. Which of the following increases the movement of potassium from intracellular to extracellular?
Potassium or potassium is a positive ion, or a cation, identified with K. About 98% of total body potassium is found in the intracellular fluid, or ICF for short, making the intracellular potassium concentration about 150 milliequivalents per liter. .
What Is Potassium Level In The Body

The remaining 2 percent is in the extracellular fluid, or ECF, which includes plasma and interstitial fluid.
Potassium Benefits, Sources And Its Side Effects
However, we can only measure the plasma level of potassium, which is about 4.5 milliequivalents per liter, and that level is usually used to define the normal extracellular concentration of potassium.
Maintaining normal potassium concentrations in the ECF and ICF is essential for the normal functioning of excitable cells such as nerve cells and muscle cells, including cardiomyocytes.
Now, across all cell membranes, when there is no stimulus, there are negative electrical charges on the inside and positive electrical charges on the outside.
Once the muscle contracts, an electrochemical impulse is generated and propagates across the cell membrane, causing an action potential.
Potassium And Heart Failure: Regulating Potassium Levels
The daily recommended intake of potassium is about 40 to 50 milliequivalents per liter, which is about 1.6 to 2 grams of potassium — the equivalent of 5 bananas a day.
Once ingested, potassium is reabsorbed from the GI tract into the blood and moves unbound to plasma proteins.
Most of the potassium gets into the cells, some is lost through sweat and the GI tract, and the rest is filtered and excreted by the kidneys.

Potassium balance depends on the total amount of potassium in the body, which is determined by potassium intake and excretion and is called external potassium balance.
Serum Potassium And Mortality In High Risk Patients: Sprint
Potassium balance depends on the distribution of potassium between ECF and ICF and is also known as internal potassium balance.
On a daily basis, urinary excretion of potassium should equal dietary potassium, minus small amounts of potassium that may be lost through sweat or through the GI tract.
Now, if potassium excretion is less than potassium intake, this is a positive potassium balance and hyperkalemia or increased potassium levels in the blood can occur.
Potassium homeostasis is the body’s ability to maintain a constant balance of potassium in the body. Potassium is the most abundant intracellular cation and is essential for maintaining the function of excitable tissues. The kidneys play a fundamental role, being responsible for peripheral potassium balance, in particular the distal convoluted tubule cells and the collecting duct are considered fine-tuning units of potassium reabsorption and secretion. The kidneys remove excess potassium from the bloodstream and excrete it in the urine.
Hyperkalemia: Symptoms, Treatment Overview
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier, its licensors and contributors. All rights reserved including text and data mining, AI training and similar technologies.
The USMLE® is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB) and the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME). COMLEX-USA® is the National Board of Osteopathic Medical Examiners, Inc. NCLEX-RN® is a registered trademark. NCLEX-RN® is a registered trademark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc. Test names and other trademarks are the respective properties. Trademark holder. None of the trademark holders are endorsed by or affiliated with this website. Potassium is an electrolyte and a mineral. All muscles need potassium to work, including the muscles that control heart rate and breathing. We get potassium from the food we eat. Potassium needed by the body is absorbed and the kidneys remove excess potassium from the blood. When the kidneys do not remove excess potassium from the blood, excess potassium accumulates and this condition is called hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia is a dangerous condition and can lead to heart attack.
Symptoms Most people do not experience any symptoms of hyperkalemia. When they do, the most common are fatigue, muscle weakness, nausea, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, and chest pain.

Causes The main cause of hyperkalemia is chronic kidney disease and acute renal failure. If the kidneys are not working properly, they are unable to remove excess potassium from the blood. Potassium therefore moves back into the bloodstream instead of leaving the body through the urine. Over time, potassium levels in the blood increase. Other common causes of hyperkalemia are dehydration, uncontrolled diabetes, certain medications such as ACE inhibitors and beta blockers, certain injuries that cause excessive bleeding, and excessive use of potassium supplements. A hormone called aldosterone signals the kidneys to remove potassium. Certain diseases, such as Addison’s disease, reduce aldosterone production and lead to hyperkalemia. Excess potassium in the diet can also cause hyperkalemia. Treatment Treatment of hyperkalemia varies depending on the cause of the disease. Hyperkalemia is usually treated with diet and medication. Treating kidney disease is very important. Other treatments usually include going on a low-potassium diet, changing medications or stopping medications that cause hyperkalemia, and taking medications that lower potassium levels in the body. Medicines used to lower potassium levels are called potassium binders. It binds to potassium in the blood and prevents it from being reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
Low Potassium Meats (nutrient Rich Meats)
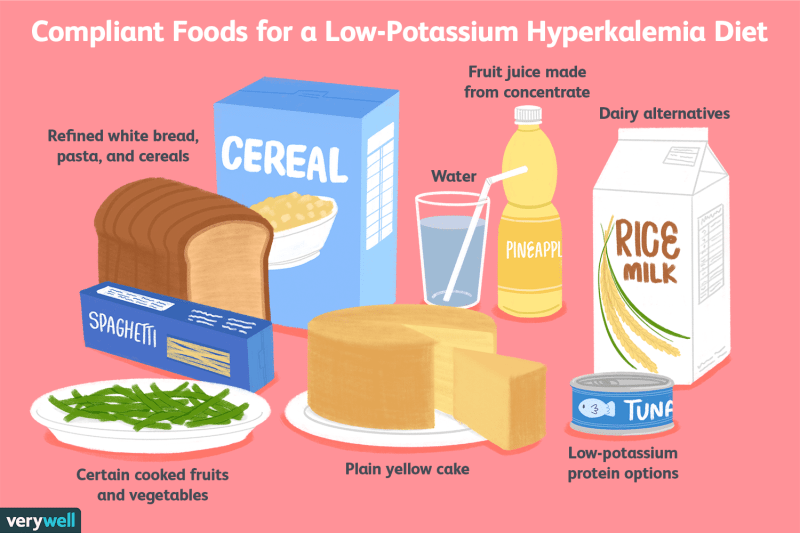
Foods high in potassium are bananas, oranges, grapefruits, tomatoes, asparagus, Brussels sprouts, beans, most meats, fish and salt substitutes.
Hyperkalemia should not be left untreated because it can cause changes in heart rhythm that can be life-threatening. It can cause paralysis.
Disclaimer: The information in no way constitutes or should be construed as medical advice. Nor is the above article an endorsement of any of the research findings discussed in the article or an endorsement of any of the original publications.
Bed Wetting: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Many people think that bed wetting only happens to children, but it is a problem that can happen to adults as well. They may feel embarrassed to wet the sheets, but it’s not their fault, it could be due to a medical condition, medication or their bladder problem. Read more..
Potassium (k+) In Blood And Its Significance
Carolyn Bertozzi, a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) investigator, discovered that a modified trehalose sugar molecule penetrates the cell wall of TB bacteria as a diagnostic marker. The method can potentially help in early detection and treatment. The research is reported in the journal
This website uses cookies. We use cookies to personalize content and ads, provide social media features, and analyze our traffic. If you continue to use our website you consent to our cookies.OkDoes Does Gluten Cause Potassium Deficiency? Should those with a celiac diagnosis or gluten sensitivity be concerned about getting enough potassium in their diet? The simple answer is yes, but before we dive into the connection between gluten sensitivity and potassium deficiency, let’s take a look at why this electrolyte is such an important mineral for your body’s health and well-being.
Potassium is both a mineral and an electrolyte. It dissolves in the water content of your body fluids and creates positively charged ions. And many important functions in your body rely on these electrically charged ions to occur efficiently and effectively.

So let’s take a closer look at the important roles that potassium plays. Then we’ll discuss how gluten can cause potassium deficiency and the problems that arise following a list of healthy, potassium-rich foods to boost your intake.
High Blood Levels Of Potassium In Patients With Kidney Disease
Your body contains different fluids. Some are inside your cells (intracellular) and others, like blood, are outside your cells (extracellular). And all these liquids contain water. So electrolytes like potassium and sodium help maintain an optimal balance of water between your intracellular fluids and extracellular fluids.
You’ve probably heard that your body is made up mostly of water, and it’s true. 60% to be exact. Additionally, most of this water is found in your cells. And potassium is the main electrolyte in your intracellular fluid. So potassium controls the amount of water inside your cells, while sodium controls the concentration of water outside your cells.
If your cells lose too much water due to a lack of potassium, they become dehydrated. They can shrink and become inactive. On the other hand, too much potassium can cause your cells to swell.
Thus, potassium is essential for balancing the fluids in your body. So your cells can function properly. So they are able to get the nutrients and oxygen they need to function and eliminate waste. Fluid and electrolyte balance helps maintain optimal ph. .
Amazon.com: Now Supplements, Potassium Gluconate Pure Powder 175 Mg, Essential Mineral*, 1 Pound
When potassium ions move out of the cell and sodium ions move into the cell, the cell voltage changes. This creates nerve impulses, which means that nerve cells communicate with each other and trigger events such as muscle contractions and heartbeats. So your nervous system needs potassium to send important signals
What is the normal level of potassium in human body, potassium level in body, what is the potassium level, what is the normal potassium level, potassium level is high, what is the potassium level in human body, potassium level in blood, what is the normal level of potassium in your body, what is the normal potassium level in the human body, potassium level in the blood, what is the normal potassium level in the body, what is high potassium level