What Is Enzymes Function In The Human Body – We often hear that certain nutrients are involved in hundreds or thousands of enzymatic reactions, but what does this mean? What is an enzyme?
An enzyme is a protein that usually ends in the suffix “-ase”, which activates a chemical reaction in the body but is not “consumed” in the process. Enzymes are essential for proper metabolism at the cellular and tissue-specific levels. Different enzymes are produced for specific activities based on their amino acid sequence.
What Is Enzymes Function In The Human Body

Enzymes range from less than 100 to over 2,000 amino acids and come in all different shapes and sizes. They can be synthesized in the body based on functional needs or can be consumed through diet or supplement sources. The correct function of the enzyme depends on the optimum pH and temperature conditions.
What Is The Function Of Digestive Enzymes?
Some enzymes need enzymes or co-nutrients to help them function. This is where vitamins and minerals come into play. If one lacks any of the vitamins or minerals needed to carry out the enzyme reaction, the enzymes will not be able to function properly and pathological conditions may occur. Provides several different tests to determine if certain vitamin and mineral levels are in the right range to perform normal metabolic functions, including its role in enzyme function.
The diagram below shows a general picture of how the enzyme works. The substrate represents the substance that is changing to form the final product.
Here we will describe some of the metabolic processes in which vitamin D, magnesium, zinc, selenium and copper are involved.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. It binds to vitamin D receptors on target tissues (such as intestines, bones, kidneys) and helps regulate calcium absorption, immune function, insulin sensitivity, and cell proliferation and differentiation. Vitamin D requires many enzymes to be converted into various forms, and some of these metabolism requires the presence of magnesium as a co-nutrient. Adequate vitamin D levels (40-60 ng / ml) reduce the risk of breast cancer, colorectal cancer, autoimmune allergies, colds and flu, osteoporosis, inflammation, mental illness and intestinal microbial imbalances.
Enzymes (a Level) — The Science Hive
Magnesium is an important mineral that plays a key role in more than 300 enzymatic reactions, including muscle and nerve function, blood pressure control and blood sugar control. Magnesium helps enzymes use ATP, a chemical in all living organisms that provides energy and thus aids in ATP-dependent reactions such as glucose metabolism, protein activation and ion transport through the inner membrane.
Zinc is an important mineral found in every tissue of the body that acts as a cofactor for about 3,000 proteins and enzymes and is essential for health. Zinc is involved in protein synthesis, DNA synthesis, immune function, antioxidant protection, and cell division.
Superoxide dismutase, the enzyme responsible for the breakdown of reactive oxygen species, is one of many enzymes that rely on zinc (and copper) for proper functioning. Thus, zinc deficiency can lead to an increased risk of oxidative stress and inflammation.

Copper is an important mineral that helps in the formation of collagen and has an effect on cardiovascular function, skin integrity, wound healing and bone strength. Copper is a co-factor for cytochrome c oxidase, an important enzyme in energy production. It is also involved in superoxide dismutase function (as mentioned above) and about 95% of the copper in the blood is bound to ceruloplasmin, an enzyme that transports copper and reduces oxidative stress by reducing Iron to its most stable form.
The Importance Of Digestive Enzymes To Gut Health
Selenium is an important trace element that plays an important role in thyroid function, reproduction, DNA synthesis and antioxidant defense mechanisms. Selenium is incorporated into proteins (called “selenium proteins”), such as glutathione peroxidase, a powerful antioxidant responsible for promoting the reduction of hydrogen peroxide into water. Selenium is important for the activation of this enzyme and therefore it helps in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. The enzymes responsible for regulating thyroid maturation and thyroid activation also depend on selenium. Selenium deficiency is more common in people with high levels of oxidative stress and can contribute to inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and thyroid disorders.
D * action Magnesium + Safety Project tests serum magnesium, vitamin D and other essential nutrient levels, and uses an online monitoring tool to monitor the effectiveness of serum levels on certain health conditions.
Make sure you know your vitamin D level and take steps to keep it within the target range of 40-60 ng / ml or 100-150 nmol / L! Through the Nutrition Research Institute, you can also test your key elements: magnesium, copper, zinc and selenium, toxins such as lead, mercury and cadmium, as well as omega-3 levels, inflammation levels and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. Find out your level today! Go to the test selection page (click on the link below) to get your test and see for yourself if your level can be improved.
To help you track your nutritional intake and nutrient levels, we have created an online tracking system called myData-myAnswers. For each specific supplement, you can keep track of how many days you take it and how many more details. This will help you to know your exact diet and how to use the process for you to reach and maintain optimal nutrient levels. Check it out today!
Digestive Enzymes — Science Learning Hub
Having and maintaining a healthy vitamin D and other nutrient levels can help improve your health now and for your future. Measurement is the only way to make sure you get enough!
Step 1 Order your home blood test kit to measure vitamin D and other nutrients you are concerned about, such as omega-3s, magnesium, essential elements, and toxins (zinc, copper, selenium, lead, cadmium, mercury); Incorporate hsCRP as an anti-inflammatory or HbA1c marker for healthy blood sugar
Step 3 Using our educational materials and tools (such as our dose calculator) Evaluate your results to determine if you are within your desired target range or if action should be taken to get there.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-943787340-ef154c538abe4e188571cbc1a425578a.jpg?strip=all)
Step 4 After 3-6 months of implementing your transition, try again to see if you have achieved your goal level.
Digestive Enzymes And The Food Enzyme Concept For Health
Reduce the risk of Kovid-19 and improve patient survival – a summary of research on vitamin D, other nutrients, and immune system health with vitamin D supplemented with additional measures. Familiar Need for Nutrition – Infographic to share! Can vitamin D intake eliminate nutrient imbalances?
AA: EPA Ratio Asthma Bone Health Cancer Breast Cancer C-reactive Protein (CRP) Cadmium Cancer Children Cold & Flu Community Action Copper Coronavirus (COVID-19) D for Health Diabetes Disease Prevention Elements Panel Cohort Data Heart Health Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Health Immunity, inflammation, lead, magnesium, mental health, mercury, nutrition and multiple sclerosis Omega-3 omega-3 omega-6: omega-3 ratio Pregnancy, breastfeeding and infant prostate cancer Research Selenium skin cancer, special programs, stroke, Alzheimer’s and dementia, solar testing, now thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), vitamin D (25 (OH) D), zinc
Get 10% off your blood test kit! Plus, get a free copy of our new Breast Cancer Research Summary with any purchase or donation with code BCP23. This offer ends on October 31, 2023 at 11:59 PM PST. Offer not valid on T1D Prevention Test KitAn The enzyme is a type of protein located in cells that stimulates chemical reactions in the body that support life. The function of enzymes is to perform important tasks. These involve muscle growth, detoxification, and the destruction of molecules in food throughout digestion. High temperatures, diseases or chemical conditions can harm the enzyme and change its form. If this happens, the enzyme does not work, so it affects various physiological functions. Enzymes are made naturally in the body. Effective performance of the digestive system involves enzymes.
Metabolic enzymes facilitate and regulate any biochemical reactions in the human body, making them essential for optimal cell function and safety. Digestive enzymes convert the food we use into energy that the body can use for various biochemical purposes. In general, our body produces both digestive enzymes and metabolism as needed.
Digestion: Anatomy, Physiology, And Chemistry
Diagnosis also uses calculations of specific enzymes in body fluids to assess the location and degree of tissue injury. In addition to diagnostic functions, enzyme activity can also provide predictive knowledge (mostly measured by improvement in enzyme levels over time).
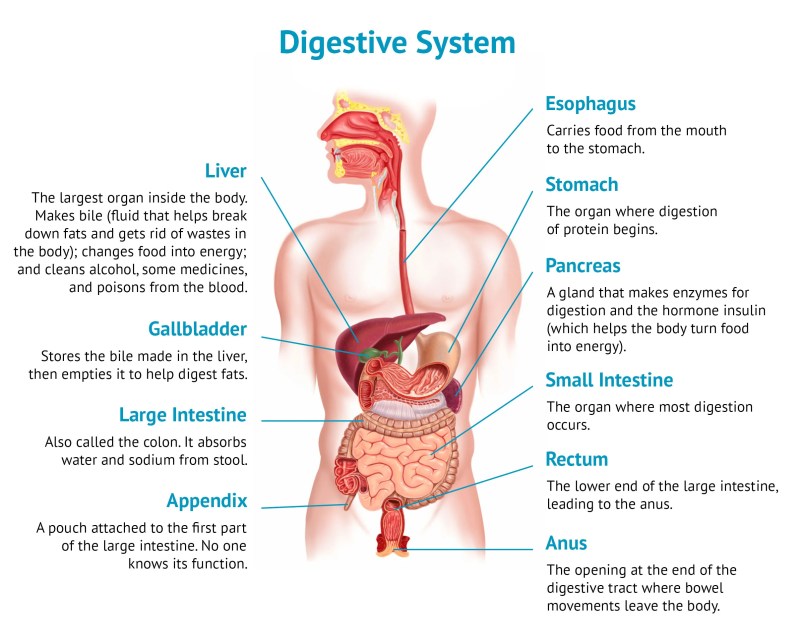
Amylase is formed in the salivary glands, pancreas and small intestine. A form of amylase called ptyalin is produced in the salivary glands and begins to work on carbohydrates when food is already in the mouth. And after you swallow it, it is still alive. Pancreatic amylase is formed in the pancreas and transferred to the small intestine. Their starches begin to break down into carbohydrates, which are gradually broken down into glucose by other enzymes. It is then drained through the membranes of the small intestine into the circulatory system of the body.
Protease emerges from the stomach, pancreas and small intestine. Most biochemical reactions occur in the small intestine and stomach. Pepsin is the main type of enzyme that breaks down proteins in the gut. As the protein particles enter the small intestine, the digestive function of the enzyme begins.

Lipase develops in the pancreas and small intestine. In breast milk, the form of lipase is
Why Are Enzymes Important For Digestive Health?
What is liver function in human body, function of enzymes in human body, what is the function of enzymes in the human body, what is the function of magnesium in the human body, what is the function of water in the human body, what is function of the liver in human body, what is the function of kidney in human body, what enzymes are in the human body, what is the function of digestive enzymes, what is the pancreas function in the human body, what is the function of gallbladder in human body, enzymes in the human body