What Is A Dangerously Low White Blood Cell Count – White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, make up less than 1% of your blood cells, but are critical to health and protection against disease. These are cells that protect the body from viruses and bacteria. A low or high white blood cell count can indicate a variety of disorders related to the blood and bone marrow.
A low white blood cell count is also sometimes called leukopenia (or leukocytopenia). The number of white blood cells varies from person to person.
What Is A Dangerously Low White Blood Cell Count

The normal range is usually 4,000 to 11,000 white blood cells per microliter of blood. Anything below 4,000 is generally considered a low white blood cell count.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Low White Blood Cell Count?
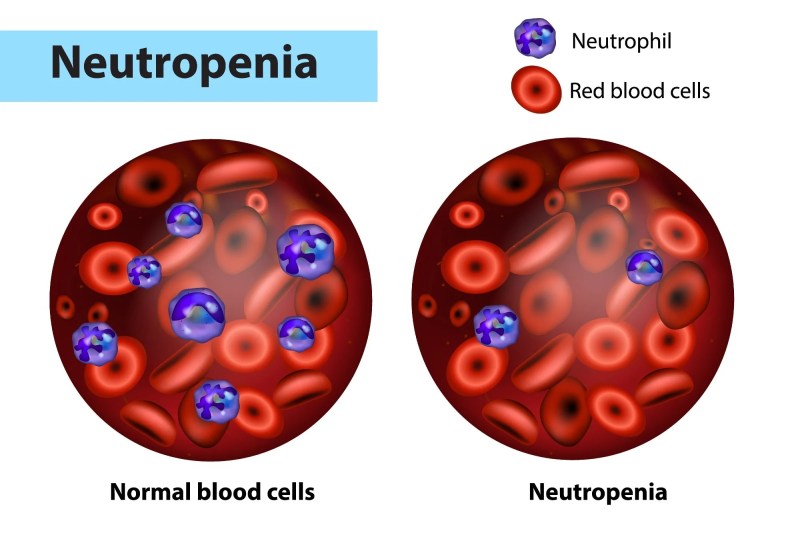
Low white blood cell counts are often caused by problems with the bone marrow where they are made. Bone marrow is the tissue inside the bones that is responsible for making most of the body’s blood cells.
Certain types of cancer, such as leukemia, and treatments such as chemotherapy can impair the bone marrow’s ability to produce white blood cells. Chemicals such as benzene and certain pesticides can also damage bone marrow.
Another common cause of low white blood cell counts is infection. The infection can affect the bone marrow and make it difficult to produce white blood cells. Also, when the body is fighting a particularly severe infection, the rate at which white blood cells are produced, even with an increased response, may not match the rate at which white blood cells are used to fight the disease.
Other causes of leukopenia include autoimmune disorders such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, which cause the body to attack its own white blood cells. Some medications can also destroy white blood cells. Vitamin deficiencies, excessive alcohol consumption, and a general poor diet can also reduce the number of white blood cells.
Neutropenic Fever: What Is It, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risk Assessment, Treatment, Prevention, And More
An abnormally low white blood cell count can put you at a higher risk of any type of infection. A low white blood cell count does not cause any symptoms by itself, but a patient whose immune system is weakened by severe leukopenia and subsequently develops an infection may experience symptoms associated with this infection, such as fever, local pain, fatigue, muscle pain, loss of appetite, and general malaise.
The main risk of having an abnormally low white blood cell count is how vulnerable a person can be to infection. Without an adequate white blood cell response to fight infection, the body is at greater risk that any infection (including those normally considered minor) could lead to serious illness or death.
The risk of infection is even more worrying for a patient whose immunity is already weakened for some reason. One example is a low neutrophil count (neutrophils are a type of white blood cell involved in fighting bacterial infection) caused by the effects of cancer chemotherapy on the bone marrow. In this case, treatment may need to be rescheduled to restore the white blood cell count, and drugs that stimulate the growth of neutrophils may be given to help maintain appropriate levels.

Because leukopenia itself is asymptomatic, and chronic infection may go unrecognized due to failure to elicit a symptomatic response, immunocompromised patients will usually have periodic blood work to monitor white blood cell counts and other regular health checks.
Low White Blood Cell Count: Causes, Diagnosis, And Treatment
Disclaimer: The content of this knowledge post is intended to provide general information related to topics relevant to blood diagnostics and may not be used with Sight OLO. For detailed information on Sight OLO diagnostic parameters and specifications, please refer to the official operator’s manual. Blood cell disorders are conditions that affect any of your blood cells, including red and white blood cells and even platelets. All of these cells are made in your bone marrow. Although some disorders disrupt the function of one of these cells, they can also affect many blood cells and their specific functions. .
Below are some common benign blood disorders that affect blood cells and platelets. To help our patients better understand each condition, we’ve included symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic tools, and treatment options for each of these benign blood conditions.
What is Anemia? Anemia is a blood cell disorder that affects the function of your red blood cells. If you have anemia, your body lacks the healthy blood cells needed to carry oxygen to the rest of your body. Anemia is also sometimes called low hemoglobin. .
The signs and symptoms associated with anemia depend on the severity and type of anemia you have been diagnosed with. In addition, anemia can sometimes occur without any symptoms. However, some symptoms that may indicate anemia include:
White Blood Cell Count Profiles In Multiple Sclerosis During Attacks Before The Initiation Of Acute And Chronic Treatments
Anemia is often associated with specific vitamin and mineral deficiencies, chronic diseases, and intestinal disorders. Additionally, other risk factors for anemia include pregnancy, menstruation, age, and a family history of anemia.
To diagnose anemia, our hematologists may recommend a complete blood count (FBC), which will tell us about the amount of red blood cells in the blood.
If this is due to a nutritional deficiency, supplementing with the missing nutrients (folate, iron or vitamin B12) may be sufficient. If there are other causes, treatment should be directed accordingly.

Iron deficiency anemia is a common form of anemia where the body does not have enough iron to make hemoglobin.
Low White Blood Cell Count In Dogs
Some common symptoms of iron deficiency anemia include general fatigue, unusual weakness, pale skin, tingling sensation in the legs, swelling and pain of the tongue, brittle nails and frequent headaches.
Iron-deficiency anemia usually results from low dietary intake, blood loss, increased iron requirements during pregnancy, and decreased iron absorption from the diet. Risk factors for iron deficiency include age, genetic conditions, and lifestyle choices.
Our hematologists may recommend several tests to diagnose iron deficiency anemia. These tests may include a complete blood count (CBC), an iron profile, and may require additional diagnostic tests such as colonoscopy and endoscopy to rule out any bowel causes.
Treatment options for iron deficiency anemia may include oral iron supplements, intravenous iron infusion, and red blood cell transfusions.
My White Blood Cells Are Elevated: Should I Be Worried?
More information about iron deficiency anemia, its symptoms, risk factors and treatment options can be found here.
Aplastic anemia is a rare and serious condition in which the body does not produce enough blood cells. This makes the body feel tired and can increase the risk of uncontrolled bleeding and infections.
Some risk factors for aplastic anemia include exposure to toxic chemicals, radiation or chemotherapy for cancer, certain prescription medications, pregnancy, and autoimmune disorders.

Treatment for aplastic anemia depends on the patient’s age and the severity of the condition. Treatment is aimed at restoring the production of blood cells. If the condition is mild, it may go away on its own without treatment, although this is not very common. Patients may require blood and platelet transfusions to prevent and control infection.
Leukocytes In Urine
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that affects the production of red blood cells. Abnormal blood production means that affected individuals do not produce adequate amounts of functional red blood cells.
There are several types of thalassemia, and the most common forms are alpha and beta thalassemia. Clinically, patients with thalassemia may present with thalassemia minor or thalassemia major.
Symptoms of thalassemia can vary, with some people having no symptoms and others having symptoms later in adolescence. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Our hematologists may recommend a full blood count (FBC) to diagnose thalassemia. More specific blood tests, such as hemoglobin electrophoresis and erythrocyte genotyping, are needed to clarify the diagnosis of thalassemia and determine the thalassemia subgroup.
Low White Blood Cell Count
Treatment options may vary depending on the type of thalassemia you have been diagnosed with – some forms of thalassemia do not require treatment. However, if you need treatment, our hematologists may recommend iron chelation, a blood transfusion, or a bone marrow or blood stem cell transplant.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood condition in which a blood clot (thrombus) forms deep in a blood vessel in the body, usually in the leg or arm. As a result, blood flow through the vein is partially or completely blocked, causing the affected limb to become painful, red, and swollen.
Various risk factors increase the likelihood of developing deep vein thrombosis. These include prolonged bed rest or prolonged sitting, age, being overweight, smoking, cancer, heart failure, genetics, birth control pills, and pregnancy.
![]()
Ultrasound is commonly used to diagnose deep vein thrombosis. This allows our haematologists to check that your blood is flowing normally through your veins.
Understanding Hairy Cell Leukemia — Hairy Cell Leukemia Foundation
The recommended treatment is anticoagulants, drugs that will thin the blood and prevent the clot from getting bigger, breaking off and causing a pulmonary embolism. Over time, the blood clot will naturally dissolve in your body.
Pulmonary embolism refers to a condition where a blood clot (thrombus) enters a blood vessel in the lungs. PE usually begins as a clot in the deep veins (also known as deep vein thrombosis, or DVT).
Dangerously low blood count, what is a dangerously low cd4 count, what is a dangerously low white blood cell count, what is a dangerously high white blood cell count, what is a dangerously low white cell count, what is dangerously high white blood cell count, what is a dangerously low platelet count, what is dangerously low platelet count, what is low white blood cell count, dangerously low red blood count, dangerously low white blood cell count, dangerously low red blood cell count