What Are Three Chemical Properties Of Cfcs – Poly halogens can be divided into subgroups. Because of their widespread use, important polyhalogens include Freon, DDT, and carbon tetrachloride. Carbon tetrachloride is a colorless, flammable liquid with no odor. Prior to the 1970s, commercial and household use of carbon dioxide as a cleaning agent was popular.
Users are at risk if these refrigerants are released into the air. This calls for the development of innovative, safe and non-toxic refrigerants. DDT (dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane) was developed in the 1940s and was the first of the modern synthetic pesticides. It was first employed to treat military and civilian populations for insect-borne diseases, including malaria and typhus.
What Are Three Chemical Properties Of Cfcs

Polyhalogen compounds are those that contain several halogen atoms (group 17 elements of the modern periodic table). In both manufacturing and cultivation, poly-halogen compounds are a common staple. They have several applications and are widely used as insecticides, solvents and anesthetics.
Pdf) Determination And Analysis Of Time Series Of Cfc 11 (ccl 3 F) From Ftir Solar Spectra, In Situ Observations, And Model Data In The Past 20 Years Above Jungfraujoch (46°n), Lauder (45°s),
There are several important poly-halogen compounds, but some of the best known are methylene chloride, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, iodoform, DDT, and benzene hexachloride.
Freon, or chlorofluorocarbon, is a popular refrigerant. Fluorine and chlorine atoms replace hydrogen atoms in methane ((C)) to form it. The properties of CFCs can be changed by incorporating different numbers of chlorine and fluorine atoms. The rule of 90 is used as the naming convention for chlorofluorocarbons. CFC is usually called CFC-n, where n is any number listed below. Following that pattern, we can find n by subtracting 90 from the total number of fluorine, hydrogen, and carbon atoms given. If, for example, a CFC has the formula (CCF), then that CFC is designated as CFC-11.
Molten sodium and hot, concentrated mineral acids have no effect on Freon. Therefore, as the ratio of fluorine to carbon atoms in Freon gas increases, the length of the solid C-F bond decreases. C-F bond lengths range from 1.29 to 1.358 for molecules such as (CF), (C) etc.
To produce chlorofluorocarbons, chlorinated methane and ethane are usually subjected to a halogen exchange reaction. The process for converting chloroform to chlorodifluoromethane is described below.
Fighting For A Climate Change Treaty
The chemical formula for DDT, or dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, is (}C). This chemical compound is a crystalline solid that is odorless, tasteless and colorless under normal pressure and temperature conditions.
In 1939, Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Müller developed the insecticidal properties of DDT. In the years ending World War II, DDT protected civilian and military personnel from insect-borne diseases, including malaria and typhus.
DDT is composed of 2 phenyl groups with five carbons as substituents. The chemical formula of DDT is (}C). DDT and its IUPAC name is 1, 1, 1-trichloro-2, 2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane.

To make DDT, a mixture of chloral and chlorobenzene (in a 1:2 ratio) is cooked in strong sulfuric acid.
Pdf) Catalytic Hydrolysis Of Chlorofluorocarbon (cfc12) Over Wo3/zro2
In addition to xylene or petroleum distillate solutions, DDT is available as emulsifiable concentrates, water-wettable powders, granules, aerosols, smoke candles, vaporizers, and lotion charges. DDT was used extensively in agriculture between the 1950s and 1980s. Fifteen different organizations from around the United States worked together to create it. DDT was also used inside the structure as an insecticide. Malaria, typhus, body lice, and bubonic plague were some of the diseases it was used to combat.
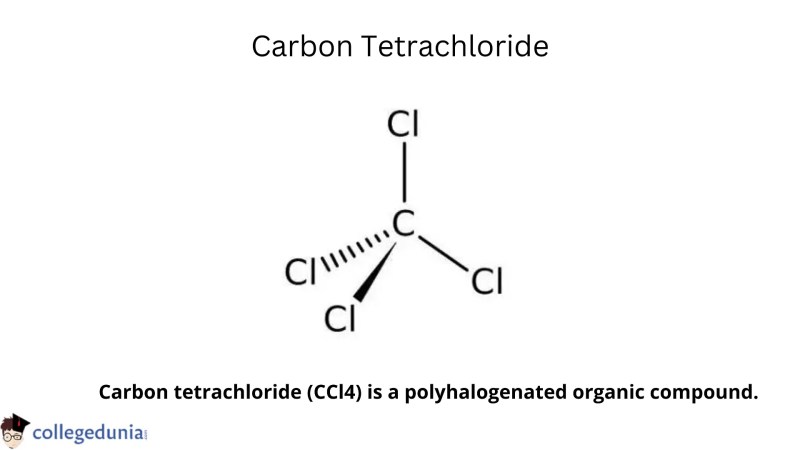
The chemical tetra chlorocarbon was created in a lab; It doesn’t happen naturally. It is a clear liquid with a faintly aromatic fragrance. Some of its alternative names are benziform, perchloromethane, methane tetrachloride, carbon chloride and methane tetrachloride. Carbon tetrachloride is a colorless gas that regularly floats in the air.
The Lewis structure of carbon tetrachloride consists of a single carbon atom in the center, surrounded by four chlorine atoms. Molecular (CC). and its electron geometry is tetrahedral in both forms. A bond angle (CC) of 109.5 degrees is obtained.
Carbon compounds with multiple halogen atoms are referred to as polyhalogens. Polyhalogen compounds include Freon, DDT, and carbon tetrachloride. These polyhalogens can be used in a variety of contexts. Freons are used to produce refrigerants and aerosols, DDT and carbon tetrachloride are used in agriculture as effective pesticides.
Conclusions And Recommendations
While Freon actually contains chlorine atoms, the chlorine that is removed from Freon by UV light forms a chemical bond with ozone.
Because of this, ozone cannot quickly return to its normal state, which leads to ozone depletion and creates ozone holes in space.
DDT is toxic because it causes severe disease in humans and animals when ingested. It can cause growth defects and reproductive problems, is carcinogenic and can cause neurological disorders.

Carbon tetrachloride was a chemical used for dry cleaning and as a fire extinguisher before it was outlawed worldwide under the Montreal Protocol in 1987. It damages the ozone layer and contributes to the ozone hole that has formed over Antarctica.
Energetic Properties, Spectroscopy, And Reactivity Of Nf3o
Established with the social objective of making quality video-based learning material available to all Indian students. Technology, connectivity and social media are rapidly changing the world of education and we want to lead the transformation of the tuition industry in India.
A perfect complement to the current tuition model. Creates a wonderful opportunity for children and parents to bond while engaging in a valuable learning activity. It also provides the entire curriculum at your fingertips for those moments when you need some help at short notice. We believe this approach to teaching can be transformative, adding hours to a child’s day by providing complete control over the learning process.
Each course is taught by the best teachers from top schools in India and conducted in an engaging manner to keep students engaged. The e-learning process consists of video-based instruction, computer-graded assignments, and a dashboard that allows students and parents to track progress. Atmospheric chemistry is a fascinating field that explores the complex interactions between the various chemical compounds present in the Earth’s atmosphere. . It plays an important role in understanding the structure, behavior and changes taking place in our atmosphere. By studying atmospheric chemistry, scientists can gain insight into the factors influencing climate change, air pollution, and ozone layer depletion. In this section, we will explore the basics of atmospheric chemistry, highlight its importance, and provide a glimpse of the complex processes at play.
1. Composition of the atmosphere: Earth’s atmosphere is made up of various gases with trace amounts of other gases such as nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O) and methane (CH4). ) and ozone (O3). These gases interact with each other and with external factors such as sunlight to create a dynamic system.
Quantitative Correlation Of Physical And Chemical Properties With Chemical Structure: Utility For Prediction
2. Natural versus anthropogenic sources: Atmospheric chemistry studies both natural and man-made sources of chemical compounds in the atmosphere. Natural sources include volcanic eruptions, forest fires, and biological processes, while anthropogenic sources include emissions from industry, transportation, and agricultural activities. Understanding these sources is crucial for assessing their impact on atmospheric composition.
3. Chemical Reactions: Chemical reactions occurring in the atmosphere are essential for the conversion of one compound into another. For example, nitrogen oxides (NOx) emitted from vehicles can react with volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the presence of sunlight to form ground-level ozone, a harmful pollutant. These reactions are often complex and involve multiple steps, making them challenging to study.
4. Depletion of ozone layer: A significant aspect of atmospheric chemistry is the study of ozone depletion in the stratosphere. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), once widely used in refrigerants and aerosol propellants, have been found to be responsible for depleting the ozone layer. The release of CFCs into the atmosphere produces chlorine radicals, which catalytically destroy ozone molecules. This discovery spurred international efforts to phase out CFCs and protect the ozone layer.

5. Climate Change: Atmospheric chemistry also plays an important role in understanding climate change. Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming. Studying the interaction between these gases, aerosols and solar radiation helps scientists model and predict climate patterns.
Properties Of Halogens
Understanding the composition of Earth’s atmosphere is crucial to unraveling the complexities of atmospheric chemistry. The atmosphere is a dynamic mixture of gases, particles and other matter that surrounds our planet. It plays an important role in supporting life on Earth by providing oxygen, regulating temperature and protecting us from harmful radiation. However, human activities have significantly altered the composition of the atmosphere, leading to various environmental problems such as climate change and ozone depletion.
1. Principal Gases: Earth’s atmosphere consists primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). These two gases are essential to sustain life as we know it. Nitrogen is relatively inert and does not react easily with other substances, while oxygen supports combustion and is essential for respiration. Other significant gases include argon (0.93%), carbon dioxide (0.04%), and trace amounts of neon, helium, methane, and ozone.
2. Greenhouse Gases: Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor are known as greenhouse gases because of their ability to trap heat in the atmosphere. Although these gases occur naturally, human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation have significantly increased their concentrations. This advanced greenhouse
What are chemical properties of matter, properties of cfcs, three examples of chemical properties, what are the chemical properties of lipids, what are some chemical properties of helium, what are chemical properties of water, three chemical properties, what are chemical properties of helium, what are chemical properties of gold, what are some examples of chemical properties, what are three chemical properties, what are the chemical properties of copper