The Source Of Oxygen During Photosynthesis Is – Composite image showing the global distribution of photosynthesis, including oceanic phytoplankton and terrestrial plants. Dark red and blue-gray indicate areas of high photosynthetic activity in the ocean and on land, respectively.
It is a biological process used by many cellular organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy, which is stored in organic compounds that can later be metabolized through cellular respiration to fuel the organism’s activities. The term usually refers to the process of oxygenic photosynthesis, where oxygen is produced as a byproduct and some of the chemical energy produced is stored in carbohydrate molecules such as sugars, starch, glycogen and cellulose, which are made from the reaction of carbon dioxide with water. Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; These organisms are called photosynthetic organisms. The process of photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of Earth’s atmosphere, and it also provides most of the biological energy needed for complex life on Earth.
The Source Of Oxygen During Photosynthesis Is

Some bacteria also perform anoxygenic photosynthesis, in which bacterial chlorophyll is used to split hydrogen sulfide as a reductant instead of water, and sulfur is produced as a byproduct instead of oxygen. Archaea such as Halobacterium also perform a type of anoxygenic, non-carbon-fixing photosynthesis, where the simpler photosynthetic retinal and its microbial rhodopsin derivative are used to absorb gray light and pump proton energy to directly synthesize adosine triphosphate (ATP). This archaeal photosynthesis may be the oldest form of photosynthesis to have evolved on Earth, dating back to the Paleolithic, and predating cyanobacteria (see Purple Earth hypothesis).
Photosynthesis: What Is It And How Does It Work?
Although photosynthesis occurs differently in different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction units that contain photosynthetic pigments or chromophores. In plants, these proteins are chlorophyll (a porphyrin derivative that absorbs the red and blue spectrum of light, and thus reflects gray) located within organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-deep reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable materials, such as water, to produce oxygen gas. The hydrogen liberated by the dissociation of water is used to form two additional compounds that act as a short-term store of energy, allowing it to be transferred to catalyze other reactions: These are nicotinamide dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) reductases and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the “energy energy” of cells.
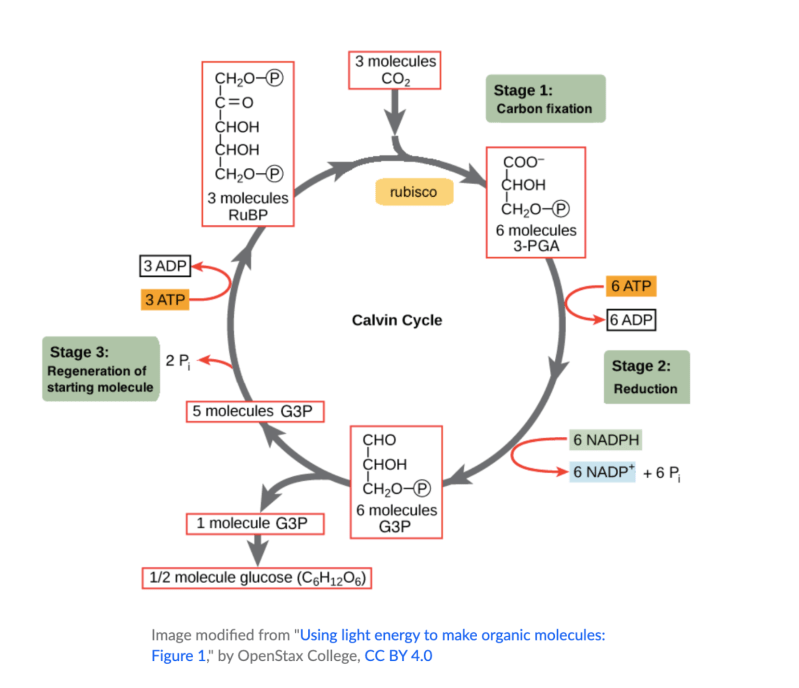
In plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, sugars are synthesized through a subsequent series of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).
Using the ATP and NADPH produced by light-digesting reactions, the resulting compounds are reduced and removed to form more carbohydrates, such as glucose. In other types of bacteria, different mechanisms such as the reverse Krebs cycle are used to achieve the same result.
The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life, and most likely used reducing elements such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, rather than water, as sources of electrons.
The Effect Of Water Deficits On Oxygen Production In Sunflower Plants
Which made the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is about 130 terawatts.
Photosynthetic organisms also convert about 100-115 billion tons (91-104 petagrams, or billion metric tons) of carbon into biomass annually.
The fact that plants receive some energy from light – as well as air, soil and water – was first discovered in 1779 by Jan Ingusz.

Photosynthesis is vital to climate processes, because it captures carbon dioxide from the air and binds carbon in plants as well as in soil and harvested produce. It is estimated that grains alone are associated with 3,825 teragrams (teragrams) or 3,825 picograms (peg) of carbon dioxide each year, or 3.825 billion metric tons.
Unbelievable Facts About Photosynthesis
Most photosynthetic organisms are photoautotrophs, meaning they are able to manufacture food directly from carbon dioxide and water using energy from light. However, not all organisms use carbon dioxide as a source of carbon atoms for photosynthesis; Phototrophs use organic compounds, rather than carbon dioxide, as a carbon source.
In plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, photosynthesis releases oxygen. Oxygenous photosynthesis is the most common type of photosynthesis used by living organisms. Some shade-loving plants (sciophytes) produce such low levels of oxygen during photosynthesis that they use it all themselves rather than releasing it into the atmosphere.
Although there are some differences between anoxic photosynthesis in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, the overall process is quite similar in these organisms. There are also many types of anoxygenic photosynthesis, mostly used by bacteria that consume carbon dioxide but do not release oxygen.
Carbon dioxide is converted into sugars in a process called carbon fixation; Photosynthesis captures energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrates. Carbon fixation is a thermal redox reaction. In general terms, photosynthesis is the opposite of cellular respiration: while photosynthesis is the process of reducing carbon dioxide to carbohydrates, cellular respiration is the oxidation of carbohydrates or other nutrients to carbon dioxide. Nutrients used in cellular respiration include carbohydrates, amino acids, and fatty acids. These nutrients are oxidized to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing chemical energy to drive the body’s metabolism.
Question Video: Linking Photosynthesis, Respiration, And Glucose In Plants
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two different processes, occurring through different sequences of chemical reactions and in different cellular compartments.
CO2 + 2H2A electron donor + light energy photons ← [CH2O] carbohydrate + 2A oxidized electron donor + water H2O
CO2 carbon dioxide + 2H2O water + light energy photons → [CH2O] carbohydrates + O2 oxygen + H2O water

This equation confirms that water is a reactant in the light intensity reaction and the product of the light intensity reaction, but canceling out n water molecules on each side gives the net equation:
Overview Of The Global Oxygen Cycle With Major Sources And Sinks….
Other processes replace water with other compounds (such as arcite) in the electron supply role; For example, some microbes use sunlight to oxidize arcite to arcite:
Carbon dioxide CO2 + (AsO3− 3 ) arcite + energy of photons → (AsO3 − 4 ) arcite + carbon monoxide CO (used to build other compounds in subsequent reactions)
The process of photosynthesis takes place in two stages. In the first stage, light reactions, or light reactions, capture the energy of light and use it to form the hydrogen carrier NADPH and the energy storage molecule ATP. During the second stage, light-dependent reactions use these products to capture and reduce carbon dioxide.
Most organisms using oxygenic photosynthesis use visible light for light-based reactions, although at least three use shortwave infrared, or more specifically, far-red radiation.
How To Analyze Photosynthesis In Plants: Methods And Tools
Some organisms use more radical forms of photosynthesis. Some archaea use a simpler method that uses a pigment similar to that used for vision in animals. Bacteriodopsin changes its conformation in response to sunlight and acts as a proton pump. This results in a more direct proton gradient, which is converted into chemical energy. This process does not involve fixation of carbon dioxide or release of oxygen, and appears to have evolved separately from the more common types of photosynthesis.
In photosynthetic bacteria, proteins that collect light for photosynthesis are embedded in cell membranes. In its simplest form, this includes the membrane surrounding the cell itself.
These structures can fill most of the interior of the cell, giving the membrane a very large surface area and thus increasing the amount of light that the bacteria can absorb.

In plants and algae, photosynthesis takes place in organelles called chloroplasts. A typical plant cell contains about 10 to 100 chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are closed by a membrane. This membrane consists of a phospholipid inner membrane, a phospholipid outer membrane, and an intermembrane space. The membrane is closed by a watery fluid called the stroma. There are stacks of thylakoids (grana) within the stroma, which is the site of photosynthesis. Thylakoids appear as flat disks. The thylakoid itself is enclosed by the thylakoid membrane, and within the enclosed volume there is a void or thylakoid space. In the thylakoid membrane there are integral and peripheral membrane protein complexes of the photosynthesis system.
What Is The Source Of Oxygen Released During Photosynthesis ?
Plants absorb light mainly using the pigment chlorophyll. The gray part of the light spectrum is not absorbed but reflected, which is why most plants have a gray color. Besides chlorophyll, plants also use pigments such as carrot and xanthophyll.
Algae also use chlorophyll, but many other pigments are used as crystals, such as phycocyanin, carotene, and xanthophyll in gray algae, phycoerythrin in red algae (rhodophytes) and fucoxanthin in brown algae and diatoms, resulting in a wide range of colors.
These pigments are incorporated in plants and algae into complexes called antennae proteins. In such proteins, the chromosomes are arranged to work together. This combination of proteins is also called the light-harvesting complex.
Although all cells in the green parts of the plant contain chloroplasts, the majority of these cells are found in specially adapted structures called leaves. Some species adapted to conditions of strong sunlight and drought, such as many species of Euphorbia and cacti, have their main photosynthetic organs in their stems. Cells in a leaf’s inner tissue, called mesophyll, can contain between 450,000 and 800,000 chloroplasts per square.
Why Photosynthesis Is Important
The oxygen released during photosynthesis comes from, source of oxygen during photosynthesis, what is the source of oxygen produced during photosynthesis, the source of oxygen produced during photosynthesis is, photosynthesis source of energy, the energy source in photosynthesis is, source of oxygen, evolution of oxygen during photosynthesis, oxygen is released during photosynthesis, oxygen is produced during photosynthesis in the presence of light, what is the energy source of photosynthesis, oxygen released during photosynthesis