The Role Of Enzymes In Chemical Reactions – An enzyme is a type of protein located within a cell, which catalyzes chemical reactions within the body that help sustain life. The function of enzymes is to perform critical tasks. This includes growing muscles, removing toxins, and breaking down food molecules throughout digestion. Temperature, disease, or extreme chemical conditions can damage enzymes and change their form. When this happens, an enzyme no longer works, thus affecting various physiological functions. Enzymes are naturally formed in the body. The efficient functioning of the digestive system involves enzymes.
Metabolic enzymes facilitate and control any biochemical reaction within the human body, making them essential for cellular function and optimal survival. Digestive enzymes convert the food we eat into energy that the body can use for various biochemical purposes. In general, our bodies produce digestive and metabolic enzymes, when needed.
The Role Of Enzymes In Chemical Reactions

Diagnostics also use the calculation of specific enzymes in body fluids to assess the location and degree of tissue damage. In addition to the diagnostic function, enzyme activity can also provide prognostic knowledge (usually measured from the development of enzyme levels over time).
Enzymes Active Site Stock Illustrations
Amylase is produced in the salivary glands, pancreas, and small intestine. A form of amylase, called ptyalin, is produced by the salivary glands and starts working on carbohydrates when food is in the mouth. And after you swallow, it stays alive. Pancreatic amylase is produced in the pancreas and transported to the small intestine. Their starch granules begin to break down into carbohydrates, which are gradually metabolized into glucose by other enzymes. It is then drained through the membrane of the small intestine into the body’s circulatory system.
Protein comes from the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine. Most of the biochemical reactions take place in the small intestine and the stomach. Pepsin is the main type of enzyme that breaks down proteins in the intestine. As the protein particles enter the small intestine, the digestive function of the enzyme begins.
Lipase is produced in the pancreas and the small intestine. Within breast milk, a form of lipase is also used to help the baby absorb fat more easily while breastfeeding. Lipids play many roles such as long-term energy storage and cellular safety services.
The functions of enzymes in the body are to consume and absorb nutrients from food and preserve all the core processes of the system such as cell regeneration, anti-carcinogenic detoxification, digestion, immunity enhancement, supply of energy, and blood flow. For example, the faster the chewing time when the rice is chewed in the mouth, the more noticeable the sweet taste. The carbohydrate in rice is oxidized to maltose by mouth-secreted salivary amylase action. More chewing of food will also combine the food with saliva to the maximum, which is important for digestion. In addition, the human body produces many hydrolytic proteins, such as pepsin and trypsin.
Enzymes: The Proteins In Our Body That Get The Chemical Reactions Necessary Of Life Done Common Enzyme Found In Nearly All Living Organisms Which Are Exposed.
Normally, DNA polymerase enzymes work in a rational way; Each enzyme regenerates one of its two strands – the leading strand and lagging strand – which make up the dual cell. Both are identified by the closest match they repeat.
Repeated strands are formed as models, using leading and lagging strands. After that, the two new double-stranded DNA compounds formed consist of one strand from the first helix and one new strand. This method is called semi-conservative duplication, which is important because it enables the transfer of genetic material from one generation to the next.
The compounds on which the enzyme functions are called substrates. Substrates bind to an area of the enzyme called the active site. Two models describe the relationship between the enzyme and the substrates. In the lock-and-key paradigm, the enzyme’s active site is uniquely shaped to accommodate specific substrates. The active site and substratum of the induced fit model do not match perfectly; instead, each changes their binding form.

Regardless of the situation, the reactions that occur are much higher – more than a million times – once the substrates bind to the active site of the enzyme. Natural processes result in a new substance or molecule that differs from the enzyme afterwards. Enzymes direct and manage the metabolism of a cell, and are carefully controlled. The mechanism of enzyme action involves regulating molecules that either enhance (activators) or inhibit (inhibitors) an enzyme’s function. An enzyme inhibitor is a compound that binds to an enzyme and prevents it from binding to the substrate, thereby reducing its activity. When an enzyme creates a large amount of material in an individual, the material begins to act as a barrier for the enzyme as a presence of low stabilization, speeding up the chemical reaction.
Worksheet On Enzymes
Enzymes also have important uses in manufacturing. Since ancient times, fermentation of wine, raising of bread, curdling of cheese, and brewing of beer have been practiced. However, such processes were not known until the 19th century as a result of the catalytic operation of enzymes. Enzymes have since gained increasing significance in processes involving organic biological processes in manufacturing environments.
The functions of enzymes used in medicine include destroying microorganisms that cause disease, stimulating the healing process, and diagnosing certain diseases. The enzyme thrombin is involved in the healing process. Many enzymes are used to treat other diseases, stimulate the transformation of certain types of leukemia, and prevent adverse reactions in patients with penicillin allergies. The enzyme lysozyme is used to destroy germs that destroy cell membranes. The ability of enzymes to prevent tooth decay and act as anticoagulants in the diagnosis of thrombosis, a condition that results in the development of a clot or plugin in a blood artery, has been studied. Enzymes can also be used to control enzyme deficiencies and disease-induced disorders.
The production and processing of enzymes has become an exciting research topic due to the wide range of applications of enzymes. Enzymes from species such as bromelain can be extracted from pineapple skin. However, due to the low enzyme content in the body, bacterial fermentation creates more enzymes in the field. In general, the necessary strains are selected under appropriate conditions and allowed to spread to obtain a large portion of the enzyme preparations. In addition, people have investigated the synthesis of synthetic enzymes.
As we can see, enzymes play a major role in the daily activities of the human immune system. It is important for the smooth functioning of the digestive system, nervous system, muscles, etc. by connecting and changing substances.
Solution: Composition Structure And Properties Of Enzyme Presentation
What is Soil Stabilization? Description: Have you ever wondered how builders manage to build strong foundations for structures, even on unstable grounds? That’s where soil stabilization becomes critical. At its core, soil stabilization refers to the process of…
In today’s world, where sustainable practices and holistic well-being have become prominent, the eco enzyme has emerged as a unique solution with many benefits for agriculture and general well-being. This powerful organic concoction offers a host of…If you’ve been following us for a while, you probably already know that we work primarily with enzymes, designing and optimizing them through computer simulations. Enzymes are applied everywhere: from food products, cosmetics, in the synthesis of pharmaceutical products, and -as they are natural biomolecules- even inside your own body.
But despite the vital importance of these molecules in our daily lives, not many people know what they do! So in this post we want to break down some of the main points about enzymes, their industrial uses and why they are the key to a greener, more sustainable chemical industry. .

Enzymes are proteins that occur naturally in living organisms. They work as biocatalysts, which means they help “catalyze” or speed up chemical processes. Instead of waiting hours or even days for a reaction to complete, enzymes have the power to speed it up and produce multiple reactions in less than a second!
Concentration (enzyme Reaction Rates) — Effects & Role
Take the lactase enzyme for example. When we drink milk, there is protein whose sole purpose is to break down the lactose so that we can digest it better. However, people who are lactose intolerant don’t have the enzyme, or simply don’t have enough of it, so they have a harder time digesting it (and suffer the consequences).
There are about 20 different types of amino acids in Nature, and they are important in determining the characteristics of an enzyme. An enzyme is made up of a sequence of amino acids, which vary greatly in number. Some may have 50 amino acids, others have more than 200.
Here, the variability is great: proteins can have different lengths, and can be formed with only some of the 20 available amino acids. So In Nature, there are millions of different proteins, each with a specific amino acid sequence.
However, the most important thing to know is that the amino acid sequence of an enzyme determines its shape. And its form determines its function.
Question Video: Identifying The Correct Term For A Biological Catalyst
As we have mentioned before, the function of enzymes is to catalyze chemical reactions. A catalyst is a molecule that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without stopping the reaction.
Enzymes catalyze all reactions that occur in living organisms, and these reactions can be of different types, such as synthesis or degradation of products, etc.
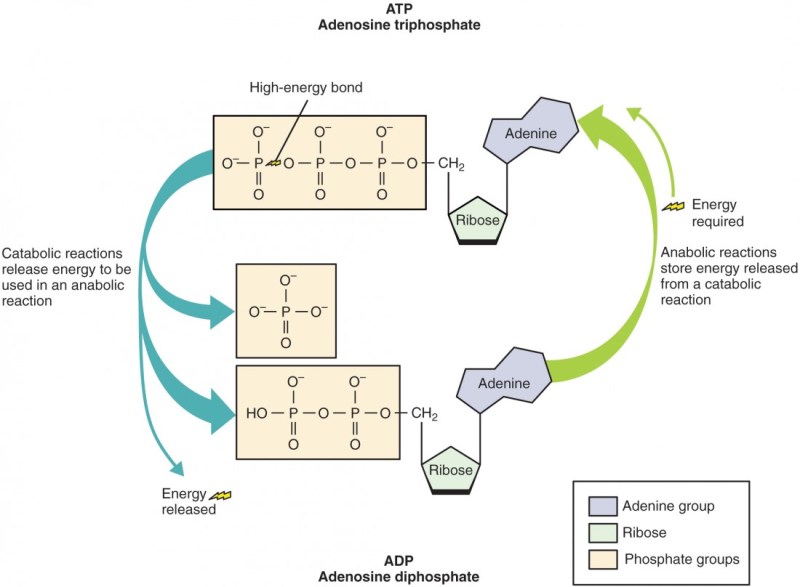
To better understand the process, see the following image, which represents

Chemical reactions in the home, how do enzymes affect chemical reactions, explain how enzymes speed up chemical reactions, chemical reactions of enzymes, analyze the role of catalysts in chemical reactions, the role of energy in chemical reactions, the role of enzymes in digestion, what is the role of enzymes in chemical reactions, enzymes role in chemical reactions, reactions of enzymes, enzymes speed chemical reactions by, the role of enzymes in the body