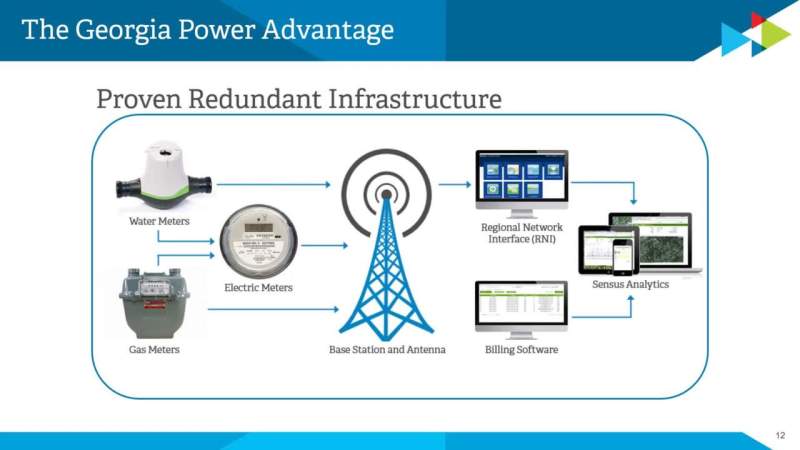
- The Role Of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (ami) In Energy Management
- Energy Management System. Nsoft Is A Utility Revenue Maximization…
- Smart Meter Deployments Result In A Cyber Attack Surface Of “unprecedented Scale”
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (ami): A Key To Achieving Efficiency In Water And Gas Utility
- Ami Meter Program
The Role Of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (ami) In Energy Management – Advanced measurement infrastructure (AMI) is typically designed as a clustered network consisting of several major components. Figure 1 provides an overview of all components and most networks. It consists of the meter, the collector and the server system of the distribution system (DSO) or on the side of the metering company.
An end-to-end system (HES), also known as a meter control system, is located within a company’s network. Most of the meter company is responsible for DSO. HES communicates directly with meters. Therefore, HES is located in some demilitarized zone (DMZ) as the services and functionality will be provided abroad.
The Role Of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (ami) In Energy Management
Many infrastructures exist on the DSO or measurement company side. The collected data will be managed by the measurement data management (MDM) system which also processes the data for the relevant customer. Depending on the level of automation, the measurement data will influence the actions of the DSO to balance the network.
Smart Meter Roll Out And Advanced Metering Infrastructure: Expert Exchange In Switzerland
Introducing HES to customers enables significant DSO risks. For example, an adversary with a HES can read all customer data. Moreover, one can control the meter or manipulate the usage data or generate alerts to disrupt the DSO’s operations or at least trigger the computer incident response team (CIRT) which may force the DSO to delay some of the one of the business continuity plan (BCP) being analyzed. and HES recovery.
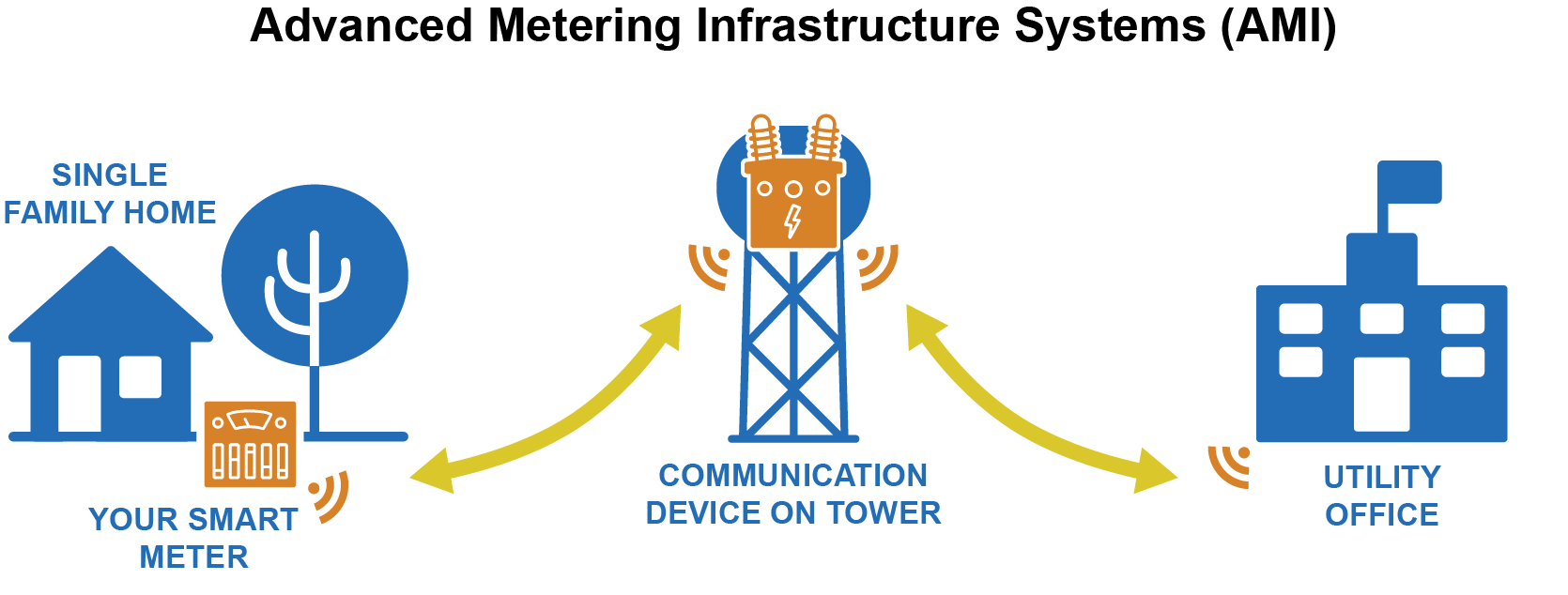
The collector, also known as the concentrator or gateway serves as the communication hub of the HES. Depending on the infrastructure the fundraiser can be a meter itself. Its primary function is to connect the HES with other meters and/or collectors in its neighborhood – the neighborhood area network (NAN).
Not only the head-end but also the compiler presents threats. The collector is physically exposed to the enemy. Moreover, it has the credibility of HES and NAN and therefore has the privilege of communicating with both parties. Adversaries may use this fact to attack HES. In addition, on the NAN side, adversaries can impersonate the collector to set a neutral state or to invoke arbitrary commands on the meter.
The meter is installed at the customer’s premises. In addition to the collector, it is directly connected to the HES. A meter is connected to the collector or can serve as a relay to route packets between the nearest meter and the collector. Some meters offer a hardware interface. For retail customers, that network is called a home area network (HAN). The meters also provide internal diagnostic ports for manual reading, installation and maintenance operations as shown in figure 2.
Energy Management System. Nsoft Is A Utility Revenue Maximization…
From an offensive perspective the meter is the entry point to building automation, DER and usage data. But the meter is also a part of the smart grid and under no circumstances should its manipulation be allowed to have a significant effect or impact on the availability of the network or its components.
Their infrastructure consists of several networks that may all rely on different media and multiple protocols. In total, three networks are commonly described when referring to AMI. WAN, NAN and HAN.
The WAN connects to the HES meter or collector. A WAN is sometimes also called a backbone network. WAN communication is mostly based on Internet Protocol (IP) and often relies on conventional information technology (IT) media and technology packages such as fiber optic cables (FOC), digital subscriber line (DSL), service general radio (GPRS) Multi-protocol label switching (MPLS), power lines (PLC) or some type of private network. A brief overview of PLC communication over the WAN is given in [1].

The CEN/CENELEC/ETSI Smart Meter Co-Coordination Group (SMCG) does not specify a specific protocol but suggests relying on “secure and non-proprietary protocols and communication platforms” for meters.
State Of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (ami) And Data Analytics Adoption
NAN connects the meter and the collectors. Typical NAN devices are electricity, gas, water or heat meters. Organizations sometimes refer to NAN as a local meter network (LMS) [3], a field area network (FAN) [4] or a LAN meter [5].
Although standards such as IEEE 802.15.4 [6], [7] based on ZigBee profiles are gaining momentum, industry and regulators are struggling to come up with a common standard. The services of the European Union nations seem to prefer the meter bus standard for NAN communication [3] although ENISA does not list [4] the meter bus for the NAN protocol.
Depending on the type of transaction HAN can also be called a building area network (BAN) or an industrial area network (IAN). Regardless of the name, the purpose of HAN is to integrate additional gas, water or heat meters. The HAN can enable intelligent building equipment and also allow the integration of DERs with smart grids.
To improve usage during peak hours a utility may for example decide not to shut down completely but instead turn off heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) equipment to balance the grid. For this purpose, customers will be required to allow the utility or third party supplier access to their equipment. However, intelligent control does not necessarily require the intervention of an external entity. So, an intelligent HVAC may decide to turn it on automatically based on the real-time price data provided by the utility.
Smart Meter Deployments Result In A Cyber Attack Surface Of “unprecedented Scale”
Meters in the US mainly focus on ZigBee for HAN communication [8]. The profile of home automation and smart energy is described in [9], [10]. The European-based Open Measurement System (OMS) is pushing an M-Bus-based specification in which the wireless M-Bus package is compatible with the KNX specification [11]. KNX is very popular for home automation.
A typical interface for diagnostic purposes is provided as a two- or three-wire series, current loop or interface interface [12], [13].
[1] M. Rafiei and S. M. Eftekhari, Smart metering using a combination of power line communication (PLC) and WiFi protocol, Proceedings of the 17th Conference on Electric Power Distribution Network (EPDC), 2012, pp. 1-5, May 2012

[2] Smart Meter Coordination Group. Obligations of CEN, CENELEC and ETSI standards in the field of measurement equipment for the development of an open architecture for energy meters involving communication protocols enabling interoperability M/441: Final report v0.7. Dec. 2009
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (ami): A Key To Achieving Efficiency In Water And Gas Utility
[3] Federal Office for Information Security (BSI) Germany. Technische Richtlinie BSI-TR-03109-1: Erdensungen an die Interoperabilität der Kommunikationseinheit eines intelligenten Messsystems, v0.5. 2012
[6] IEEE Std 802.15.4:2011. IEEE Standard for Local and Urban Area Networks – Section 15.4: Low-Range Wireless Personal Area Networks (LR-WPANs)
[7] C. Bennett and D. Highfill. Connecting to AMI Smart Meters. Energy Activities 2030 Conference, 2008. ENERGY 2008. IEEE. Page 1-8. November 2008 (DOI 10.1109/ENERGY.2008.4781067)
[8] V. Aravinthan, V. Namboodiri, S. Sunku and W. Jewell. Wireless AMI Application and Security for Controlled Home Area Networks. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Flow Society General Conference, 2011 IEEE. Page 1-8. Jul. 2011 (DOI 10.1109/PES.2011.6038996)
Ami Meter Program
[11] EN50090-4-1:2004. Home and Building Electronic Systems (HBES) Part 4-1: Independent media – application layer for HBES Class 1
TS EN 62056-21 Electricity measurement – Data exchange for meter reading, tariff and load control – Part 21: Direct local data exchange Here, I am an energy professional with knowledge and experience in the electrical system. I want to know more about myself professionally. Take a moment to check out my LinkedIn profile. Cheers 🙂
The integration of technology is changing the dynamics of every business and changing the way we work and create value for customers. The same is the case with electricity services. Electricity is now looking towards smart grid(s) (SGs), grids capable of two-way communication. SGs are a complex combination of technologies to achieve maximum reliability and efficiency in a power system. An ideal SG design should be able to address advanced challenges such as integration of distributed energy sources, load management and demand adjustment, restoration and self-healing of lines and quality of power delivered to consumers. In addition, market empowerment, flexible pricing and cost and asset optimization are also a few of the targets that should be achieved by suitable SGs.

SG is an integrated system. All the layers are very interconnected. The solid foundation and functionality of each layer is instrumental to SG’s performance. The following matrix shows the relationship between the layers with the role summarized for each layer.
Maximizing The Roi For Ami Investments
The most basic layer is AMI and it is also a combination of number of technologies. This infrastructure includes smart meters, communication networks & meter data management system (MDMS). Smart meters collect time-stamped data and this data is communicated to AMI host systems aka (Head-End Systems (HES)) through communication channels. This data is then sent to the MDMS which manages, validates and cleans the data before it is available for use by the energy service provider. AMI enables two-way communication between system layers and makes the system more controllable and flexible in many aspects.
An end-user energy meter is a sophisticated electronic device with software capable of time-stamped measurements and data collection at desired time intervals. These devices have established system communication and are capable of transmitting data at required times set by system administrators. Unlike Automatic Meter Reading (AMR), two-way communication
Advanced metering infrastructure pdf, advanced metering infrastructure jobs, ami automated metering infrastructure, ami metering infrastructure, advanced metering infrastructure companies, advanced metering infrastructure market, advanced metering infrastructure presentation, ami advanced metering, advanced metering infrastructure, ami advanced metering infrastructure, advanced metering infrastructure water, advanced meter infrastructure ami