The Most Common Cause Of Male Infertility Is – Male infertility is diagnosed when a man shows problems after both partners are tested during the reproductive process.
The reproductive process is usually simple and natural for most couples. However, some couples have a difficult time conceiving for various reasons.
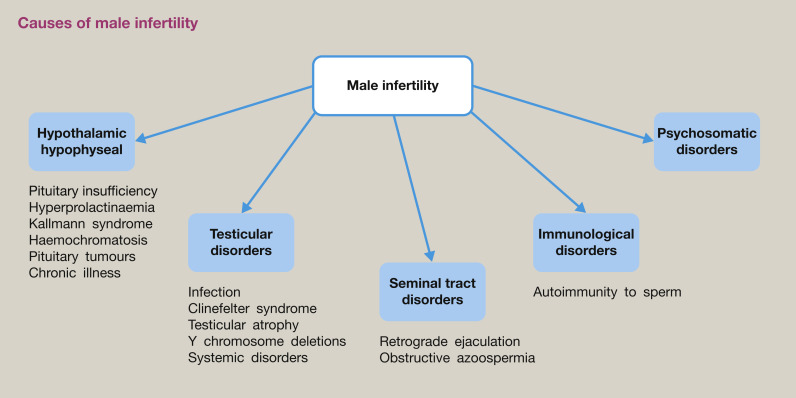
The Most Common Cause Of Male Infertility Is

In general, the quantity and quality of a man’s sperm determine fertility. If a man ejaculates a low sperm count or low sperm quality, it will be challenging and, in some cases, impossible to achieve pregnancy.
Ask The Doc
Infertility is a problem that affects many couples. About one in five infertile couples can blame their infertile male partner alone.
One in twenty men have problems with fertility due to low sperm count in ejaculation. However, about one in every 100 men have no sperm in their ejaculate.
Problems with sperm production or sperm transport most often cause male infertility. Doctors can find the cause of the problem if they do medical tests.
Infertile people have difficulty making sperm in the testicles in about two-thirds of cases. Not enough sperm is produced, or the sperm produced does not function properly.
Male Infertility. What Is Male Infertility?
One in five infertile men have sperm transport problems, including those who have had a vasectomy but now want to have another child. A complete lack of sperm in the ejaculated semen can cause obstructions (also called blockages) in the tube that directs the sperm from the testes to the penis.
The following are less common causes of infertility: sexual problems that interfere with a woman’s ability to receive semen for fertilization (one in 100 infertile couples); low levels of hormones produced by the pituitary gland (one in 100 people are infertile); and sperm defects (one in 100 couples are infertile).
There are 16 infertile men for every one who has antibodies. Most men are not affected by sperm antibodies, but some men will have a reduced chance of conceiving because of these antibodies.Lithium Biodistribution and Nephrotoxicity Studies in a Mouse Model of Cutaneous Melanoma: First Steps to Implementing Neutron Capture Lithium Therapy

Open Access Policy Institutional Open Access Program Guidelines Special Issues Editorial Process Research Ethics and Publication Article Processing Fee Testimonial Awards
Male Infertility: An Overview Of The Causes And Treatments
All published articles are immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by, including figures and tables. For articles published under the open access Creative Common CC BY license, parts of the article may be reused without permission if the original article is clearly cited. For more information, see https:///openaccess.
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper must be a substantial original article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides insight into future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted by invitation or individual recommendations by scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations from scientific editors of journals from around the world. The editors select a number of recently published articles in journals that they believe will be of interest to their readers, or important in their research area. It aims to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in various research areas in the journal.
Male Infertility: Main Genetic Causes
Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, College of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine, Qassim University, Buraydah 51452, Saudi Arabia
Submission received: January 7, 2023 / Revised: January 30, 2023 / Received: February 2, 2023 / Published: February 14, 2023
Male infertility is a major health problem with economic, psychological, and medical attributions. In addition, it is characterized by the inability to produce a sufficient number of sperm for fertilization of the oocyte. Dietary nutrition (DN) has a major impact on male reproductive potential. Observations have shown that increasing DN can protect or treat male infertility. The scope of this critique is to examine DN, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, minerals and other phytochemicals, to improve semen attributes, sperm bioenergetics and sperm function in male infertility. It appears that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids affects sperm quality and maintains the stability of sperm membranes and mitochondria. Administration of phytochemicals leads to improvement of sperm mitochondrial function and reduction of oxidative damage. Furthermore, various natural dietary phytochemicals differently affect (negatively or positively) sperm motility, semen quality, and mitochondrial function, depending on the level. Vitamins and trace elements are also nutritional modulators to reduce oxidative stress, thereby improving sperm quality, which is accurately linked to sperm mitochondrial function. Also, we describe different types of DN as mitochondrial enhancers for sperm function and health. We believe that understanding DN supports sperm mitochondria and epigenetic modulators that may be responsible for sperm quality and health, and will lead to more embattled and efficient therapies for male infertility.

Globally, infertility affects 10-15% of couples, with the male aspect accounting for 20-30% of cases [1]. Male infertility is a syndrome of male reproductive function, characterized by the inability to produce a sufficient number of sperm to fertilize an oocyte. Male infertility has been neglected and understudied because conception was previously observed as a female substance [1]. In addition, male infertility is a multifaceted phenomenon, and many problems include lifestyle, diet, and chronic diseases on the side with industrial exposure to certain chemicals, and sperm variables.
Azoospermia (zero Sperm Count): Causes & Treatment
In addition, male infertility is often triggered by complications in semen ejection, sperm production, absence or inferior sperm, sperm kinetics and sperm abnormalities. Usually, based on the ASRM report, 2014, the term “Infertility disorder” should be defined as “inability to conceive after one year of unprotected intercourse or six months for women aged 35 years or older”. Clinically, infertility is clearly defined as the failure of a couple to conceive one year after unprotected sexual intercourse without conception [2].
Every year, scientists observe a decline in fertility worldwide [3]. The World Health Organization (WHO) states that there are 45-80 million infertile couples internationally [4]. In the UK, it is estimated that one in seven couples experience pregnancy complications, with male infertility accounting for approximately 40-50% of all infertility cases [5]. As referenced by many authors, human male fertility is prejudiced by many problems, such as low sperm production, reduced sperm motility, higher sperm abnormalities, medical influences (cancer and pelvic inflammatory disease), irreversible influences (for example, age, gender , and genetics), and significantly controllable lifestyle issues, for example, alcohol, nutrition, stress, excess weight, physical activity, smoking, and long-term use of preventive medications. Figure 1 shows the potential effects of previous factors associated with male infertility.
In addition, inferior sperm count is the most common cause of infertility, responsible for about 15% of all cases of male infertility [6]. Environmental toxins, hormonal disorders, and genetics can also play an important role in male infertility [7]. Recently, the association between various biological processes has gained more attention in living organisms, especially those influenced by nutrition [8]. Better fertility consequences are found in people with a healthy diet, which includes supplements with high amounts of phytochemicals, fatty acids, antioxidants and micronutrients [8]. In addition, it can be accepted that an adequate or balanced diet can be important to change the consequences related to fertility in both genders. As we know, food is important for everyone to get energy and to carry out all important development, such as reproduction [8]. Providing plenty of active nutrients is essential for all periods of development in humans, including growth, puberty, maturity, and reproduction [9]. Following nutritious / well-proportioned food and being physically active two centers of a healthy lifestyle.; they can support a healthy profile and reduce the risk of chronic diseases [10].
In addition, De Rose et al. [11] showed that an unbalanced diet can increase the incidence of infertility in humans by 27%. In men with low quality semen, dietary supplements with micronutrients and antioxidants can improve sperm superiority, motility, and morphology by reducing OS-induced sperm disturbance and improving hormone synthesis. Future clinical investigations should take into account the relationship of many antioxidants to benefit from synergistic mechanisms of action. Dietary supplementation with antioxidant mediators has been reported to reduce male infertility [12]. As previously documented, a high amount of oxidative stress caused by several factors can cause male infertility. Thus, dietary fortification with antioxidants has shown a constructive influence on fertility competence. Randomized controlled studies are more desirable to validate the efficiency and safety of micronutrients and antioxidant supplements to reduce male infertility, as well as find the optimal dose of each antioxidant and micronutrient to improve fertility competence [9, 13]. The results are of great public interest because dietary fluctuations during the last period may be part of the clarification of the occurrence of abnormal human sperm counts. For example, reducing saturated fat intake may be beneficial for overall reproductive well-being and health. This review aims to reflect the latest information on dietary nutritional supplements and their relationship to reproductive function.
Potential Causes Of Male And Female Infertility In Qatar
Most common cause of male infertility, cause of male infertility, what cause male infertility, most common cause of infertility in females, what is the cause of male infertility, most common cause of infertility, cause of infertility in male, common cause of male infertility, what is the most common cause of male infertility, male infertility cause, what is the most common cause of infertility, common cause of infertility