The Central Nervous System Structure And Function – The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It acts as the body’s control center, processing sensory information and directing responses. The CNS coordinates voluntary activities, such as movement, and involuntary ones, such as breathing and heartbeat.
However, the brain cannot do this on its own because it needs to receive information from the body’s sensory receptors, which it achieves through communication with the spinal cord.
The Central Nervous System Structure And Function

The CNS is called ‘central’ because apart from occupying the central position of the body, the CNS is also the most important part of the nervous system for maintaining and producing behaviour.
Autonomic Nervous System: Anatomy, Divisions, Function
The central nervous system has three main components which are the brain, spinal cord and nerve cells: the brain
The brain is responsible for functions such as thought, forming memories, movement and awareness. The human brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
The brain stem is located at the base of the brain and is one of the most primitive regions of the brain; and is made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
The cerebellum is situated just above the brain stem, which monitors and regulates motor behavior, especially automatic movements and balance.
Solved Worksheet Central Nervous System (cns) 1. Brain
The cerebrum is the most recently developed in the human brain and is the largest part of the brain (which makes up about 85% of the total mass). The cerebrum is divided into two cerebral hemispheres that work together to produce various functions such as voluntary behaviors, speech, cognitive thinking, and awareness.
The left hemisphere is responsible for controlling the movements on the right side of the body, while the right hemisphere is responsible for controlling the movements on the left side of the body.
The surface of the cerebrum is covered by the cerebral cortex, often referred to as gray matter. Gray matter consists of a thin layer of tissue, approximately 3 mm thick, containing billions of neurons. The gray matter is the structure through which memories are stored, perceptions take place and information is processed.

The neurons in the gray matter are connected to other parts of the brain through a layer of nerve fibers called white matter, so called because of the shiny white appearance of the substance that insulates it.
Cells Of The Nervous System
Gray matter is distinctively wrinkled in appearance – it is full of bulges separated by grooves. A bulge in the brain is called a gyrus, or gyri, when plural. The grooves in the brain are called fissures. The fissures and gyri expand the surface area in the cerebral cortex, and ultimately increasing the number of neurons it can contain.
Animals with the largest and highest functioning brains, such as humans and some primates, have the most wrinkled brains and, thus, the largest cerebral cortices.
The spinal cord is a long, thin collection of neurons attached to the base of the brain (brain stem), running the length of the spinal column.
The spinal cord contains circuits of neurons that can control some of our simple reflexes, such as moving a hand away from a hot surface without the involvement of the brain.
Structure And Functions Of Cells Of The Nervous System
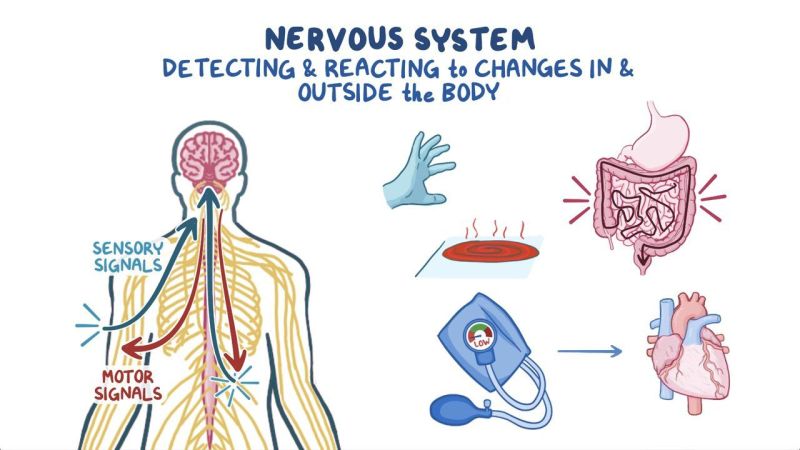
The CNS communicates with the rest of the body through the nerves, which are bundles of fibers that transmit signals to and from the CNS. The nerves that are attached to the spinal cord make up the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The nerve roots exit the spinal cord and travel to both sides of the body, carrying messages back and forth between the brain and the peripheral nerves.
The middle structure of the spinal cord is made of gray matter, and the external tissues are made of white matter. In the spinal cord, there are 30 segments, each belonging to one of four sections:

For messages to be transmitted throughout the CNS and the body, there are billions of cells that aid in the functioning of the brain and spinal cord.
Autonomic Nervous System
Neurons, or nerve cells, connect with each other in order to send and receive messages in the brain and spinal cord. Neurons work together to transmit sensory information to the brain and are responsible for making decisions, emotions and muscle activity.
There are approximately 86 billion neurons in the CNS, with thousands of different subtypes identified that serve different functions. Each neuron is made up of a cell body (soma), axons and dendrites.
Glial cells are non-neuronal cells in the CNS that do not carry messages themselves but protect and support the neurons. Glia cells account for around 90% of the overall cells in the CNS. There are three types of glial cells in the CNS: astrocytes, microglial, and oligodendrocytes.
Astrocytes are the main supporting cells of the CNS, which make and secrete proteins called neurotrophic factors (which support the growth and survival of neurons). These types of cells also help remove harmful proteins and chemicals that could damage neurons.
Central Nervous System
Microglia cells are responsible for removing damaged neurons and infections and are important for maintaining the health of the CNS. They also produce molecules called cytokines that regulate the cell’s immunity in response to injury.
Oligodendrocytes are responsible for producing a fatty substance called myelin, which is used as insulation that wraps around the axons of neurons. Myelin is essential for neurons to conduct electrical messages at a much faster speed than neurons that are not insulated by myelin.
As the central nervous system is vital for a variety of functions as well as survival, it is exceptionally well protected. A skull encloses the brain, and the spinal cord runs through the middle of a column of hollow bones known as vertebrae.

As well as this, the brain and the spinal cord are also protected by a three-layered set of membranes called the meninges (the layers specifically called pia mater, arachnoid and dura mater).
Central Nervous System (cns): Structure & Main Functions
To ensure that the brain and spinal cord do not come into direct contact with any bones of the skull or vertebrae, they float in a clear liquid called cerebrospinal fluid.
The cerebrospinal fluid fills the space between two of the meninges, as well as circulates within the ventricles of the CNS, providing a surrounding cushion to the brain and spinal cord, protecting them from damage.
Noback, C. R., Ruggiero, D. A., Strominger, N. L., & Demarest, R. J. (Eds.). (2005). The human nervous system: structure and function (No. 744). Springer Science & Business Media.
Saul McLeod, Ph.D., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years’ experience working in further and higher education. He has published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Autonomic Nervous System: Parts, Organization And Functions
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She previously worked in the healthcare and educational sectors. Illuminate the complex pathways of the nervous system with our definitive guide. Nursing students, unlock the secrets of the intricate web that dictates our every thought, action and feeling.
The nervous system does not work alone to regulate and maintain body homeostasis; The endocrine system is a second important regulatory system.
We have only one nervous system, but, because of its complexity, it is difficult to consider all of its parts at the same time; So, to simplify its study, we divide it in terms of its structures (structural classification) or in terms of its activities (functional classification).

The structural classification, which includes all the nervous system organs, has two subdivisions – the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
Somatic Nervous System
Even though it is complex, nervous tissue is made up of only two main types of cells – supporting cells and neurons.
Neurons, also called nerve cells, are highly specialized to transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another.
During embryonic development, the CNS first appears as a simple tube, the neural tube, which extends down the dorsal median plane of the developing embryo body.
Because the brain is the largest and most complex mass of nervous tissue in the body, it is commonly discussed in terms of its four main regions – cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem and cerebellum.
Nervous System Basic Structure And Function
The pair of cerebral hemispheres, collectively called the cerebrum, are the uppermost part of the brain, and together are much larger than the other three brain regions combined.
Nervous tissue is very soft and delicate, and the irreplaceable neurons are injured by even the slightest pressure, so nature has tried to protect the brain and the spinal cord by enclosing them in the bone (the skull and vertebral column), membranes (the meninges). ), and a watery cushion (cerebrospinal fluid).
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a watery “broth” similar in its makeup to blood plasma, from which it forms.

No other body organ is as completely dependent on a constant internal environment as the brain, and so the blood-brain barrier is there to protect it.
Sympathetic Nervous System: Definition, Function & Examples
The white matter of the spinal cord is composed of myelinated fiber tracts – some running to higher centers, some traveling from the brain to the cord, and some conducting impulses from one side of the spinal cord to the other.
The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves and scattered groups of neuronal cell bodies (ganglia) found outside the CNS.
The 31 pairs of human spinal nerves are formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord.
The sympathetic division mobilizes the body during extreme situations and is also called the
The Spinal Cord
Central and peripheral nervous system function, what is the central nervous system function, the central nervous system function, structure of the central nervous system, structure and function of the nervous system in humans, the nervous system structure and function, nervous tissue structure and function, nervous system structure and function, central nervous system function definition, nervous cell structure and function, structure and function of autonomic nervous system, describe the structure and function of the nervous system