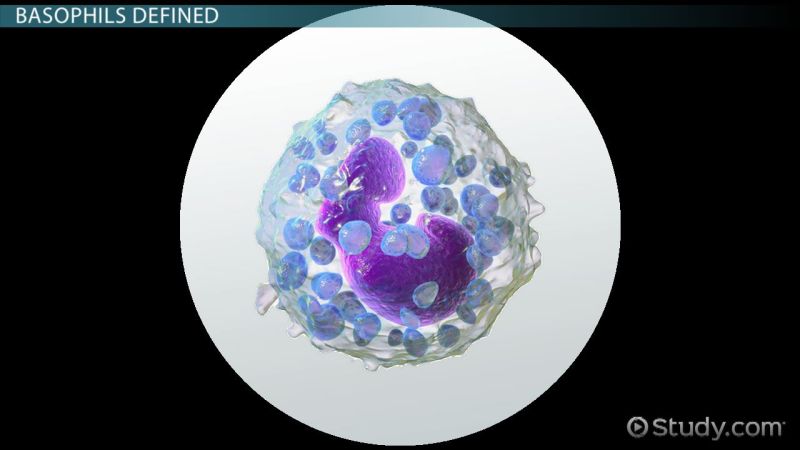
Structure And Function Of White Blood Cells – Basophils are a type of white blood cell that work together with your immune system to protect your body from allergens, viruses and bacteria. Basophils release enzymes to improve blood flow and prevent blood clots.
Basophils are a type of white blood cell. There are three types of white cells, each with its own role in boosting the immune system, including granulocytes, monocytes and lymphocytes. Basophils are one of the three granulocytes, along with neutrophils and eosinophils. They are the smallest in number of granulocytes and the largest in cell size. Basophils play an important role in helping your body respond to an allergic reaction.
Structure And Function Of White Blood Cells
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical institution. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse products or services outside of Cleveland Clinic. Law
Solution: Hemoglobin Structure
Basophil cells are unique in that they do not recognize pathogens that have been exposed to them. Instead, they attack any animal they see that doesn’t know your body. Basophils destroy foreign objects from the environment and absorb them (phagocytosis).
Histamine dilates your blood vessels to increase blood flow and heal the affected area. Histamine paves the way for other cells in your immune system to quickly target and react to the allergen. You can tell when your basophil cells are releasing histamines because you will experience physical symptoms of an allergic reaction such as itchy skin, runny nose and watery eyes.
Basophils secrete both histamine and heparin. When foreign substances enter your body, your basophils are activated and release these enzymes to help the immune system’s response to destroy the organism.
Basophils develop in the soft tissue of your bones (bone marrow). After the cells mature, they travel through your bloodstream and migrate to damaged tissue to help heal the area after an injury.
Blood: Composition, Properties And Functions
Basophils are microscopic round cells. To view these cells under a microscope, a lab technician adds a stain or dye to a sample of cells, causing the cells to turn a shade of purple. black color. Basophil cells have two lobed cells (which look like two raindrops connected by a thin thread) that appear as black granules and small purple ones, which float on the purple liquid (cytoplasm ).
Basophils are a type of white blood cell. White blood cells make up about 1% of all the cells in your body. Basophils are the smallest in number and make up less than 1% of all white blood cells.
There are two types of conditions that affect your basophils depending on how many basophils are in your body:

If you have basopenia, your basophil cells may be overactive to fight infection or an allergic reaction or your thyroid gland may be overactive (hyperthyroidism). Your healthcare provider will perform follow-up blood tests to determine and treat the cause to bring your basophil count back to normal levels.
Blood Structure And Its 3 Main Circulatory Functions In The Body
Having a high basophil count (basophilia) can be an indication of an underlying medical condition. Your healthcare provider will do a blood test to count your cells, followed by other tests to confirm the diagnosis. Conditions that manifest basophilia include:
If your basophils are negative, there are no symptoms related to your count itself. Any symptoms you experience are symptoms of an underlying medical condition.
Your health care provider will check your cells with a complete blood count, where they will take a sample of your blood from your vein to diagnose and test for many diseases, conditions and diseases by checking and counting your blood cells.
Since basophils are a type of white blood cell, your healthcare provider will order a complete blood count, which counts the five types of white blood cells in your blood to determine whether Your cell count is high, normal or too. down.
Why Is The Cell Called A Structural And Functional Unit Of Life?
Often, your basophil count is suggestive of the condition, but other tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis.
A normal basophil count is .5% to 1% of your white blood count. This ranges from zero to 300 basophils per microliter of blood in healthy adults. If your basophil count is outside of those ranges, you are at risk for a basophil-related condition.
Basopenia can be a result of your basophils working overtime to attack an allergen or healing an illness that takes longer than it should. It can also be the result of the thyroid gland producing too much thyroid hormone.

Mast cells and basophil cells are types of white blood cells that target allergic reactions. Mast cells are oblong in shape and basophil cells are round. Both cells have a nucleus and granulocytes. The difference between mast cells and basophil cells is that mast cells have about 90% more granulocytes than basophil cells (granulocytes appear as small polka dots inside the cell). Mast cells also live in tissues in your body and basophil cells spend their entire lives traveling through your circulatory system.
Lakhmir Singh Science Class 8 Solutions For Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Its Functions
When the allergy season starts, your runny nose and tears show that your basophil cells are doing their job. Your healthcare provider will recommend a complete basophil count to check for cell abnormalities, which can be the first step in diagnosing an underlying medical condition or providing treatment options for allergies or chronic diseases. Home Games & Quizzes History & Society Science & Tech Biographies Animals & Geography Geography & Arts Travel & Finance Videos
While every effort has been made to follow the reference style rules, there may be misunderstandings. Please refer to the appropriate model manual or other sources if you have any questions.
Encyclopaedia Encyclopaedia editors are responsible for their subject area with a great deal of knowledge, either through years of experience gained from working on the content or from studying for a higher degree. They write new content and review and edit content received from sponsors.
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes or white corpuscles, are cells of the blood that do not have hemoglobin, have a hole, can move the body, and protect the body from disease and illness. White blood cells perform their protective function by attacking foreign substances and debris in the cell, by destroying infectious agents and cancer cells, or by producing drugs. prevention of disease. Although white blood cells are found in circulation, many occur outside of circulation, within the body, where they fight disease; few of the blood is transferred from one site to another. White blood cells are highly differentiated for their special function, and they do not undergo cell division (mitosis) in the blood; However, some retain the ability of mitosis.
Complete Blood Count, Red Blood Cell Morphology
Based on their appearance under the light microscope, white blood cells are grouped into three main classes—lymphocytes, granulocytes, and monocytes—each of which performs a slightly different function. Lymphocytes, which are further divided into B cells and T cells, are responsible for the identification of foreign agents and their subsequent removal from the host. Granulocytes, the most white cells, clear the body of large pathogens such as protozoans or helminths and are the main mediators of allergies and other types of inflammation. Monocytes, which make up between 4 and 8 percent of the total number of white blood cells in the blood, travel from the blood to the site of infection, where they further divide into macrophages.
A healthy adult has between 4,500 and 11,000 white blood cells per cubic millimeter of blood. Changes in white blood cell count occur during the day; Low values are achieved during rest and high values during exercise. An abnormal increase in the number of white blood cells is known as leukocytosis, while an abnormal decrease in the number is known as leukopenia. The number of white blood cells can increase in response to severe stress, anxiety, severe emotional reactions, pain, pregnancy, pregnancy, and certain medical conditions, such as illness and alcohol abuse. The number can decrease in response to certain types of diseases or drugs or in conjunction with certain conditions, such as chronic anemia, malnutrition, or anaphylaxis. In general, newborns have a high white blood cell count that gradually declines to adult levels during childhood.
White blood, also called leukocyte or white corpuscle, the cell part of the blood that does not contain hemoglobin, has a nucleus, can move the body, and protects the body from disease and illness by incorporating foreign substances into cellular debris, by destroying infectious agents. and cancer cells, or by developing antibodies.

In adults, the bone marrow produces 60 to 70 percent of white blood cells (ie, granulocytes). Lymphatic tissues, especially thethymus, thespleen, and thelymph nodes, produce lymphocytes (which comprise 20 to 30 percent of white blood cells). The reticuloendothelial tissue of the spleen, liver, lymph nodes, and other organs produce monocytes (4 to 8 percent of white blood cells). A healthy adult has between 4,500 and 11,000 white blood cells per cubic millimeter of blood. Changes in white blood cell count occur during the day; Low values are achieved during rest and high values during exercise.
Shapes Of Cells
The survival of white blood cells, like living cells, depends on their continuous energy production. Chemical methods are used
Structure and function of plant cells, structure and function of red blood cells, structure and function of cells, structure and function of human cells, structure and function of cells worksheet, cells structure and function quiz, cells structure and function powerpoint, blood cells function and structure, cells structure and function class 8, structure and function of animal cells, structure and function of nerve cells, function of red and white blood cells