Role Of Calcium In The Human Body – Calcium is used in many nerves in a voltage-gated calcium channel, which works slightly more slowly than a voltage-gated potassium channel. It is most commonly used in the cardiovascular system
) contribute to the physiology and biochemistry of the cells of organisms. They play an important role in signal transmission pathways,
Role Of Calcium In The Human Body

Where they act as second messengers in the release of neurotransmitters from neurons, in the contraction of all types of muscle cells, and in fertilization. Many enzymes require calcium ions as a cofactor, including several blood coagulation factors. Extracellular calcium is also important for maintaining the potential difference in excitable cell membranes, as well as for proper bone formation.
Are Calcium Supplements Bad For The Heart?
, are released from the bones into the blood under controlled conditions. Calcium is transported in the blood as dissolved ions or bound to proteins such as serum albumin. Parathyroid hormone secreted by the parathyroid gland regulates Ca resorption
From bone, renal reabsorption back into circulation, and increased activation of vitamin D3 to calcitriol. Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D
, promotes absorption of calcium from the intestines and bones. Calcitonin, secreted from the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland, also affects calcium levels by counteracting parathyroid hormone; however, its physiological significance for humans is doubtful.
Typical concentrations of calcium in model organisms: in E. coli 3 mM (bound), 100 nM (free), in budding yeast 2 mM (bound), in mammalian cells 10-100 nM (free) and in blood plasma 2 mm.
Essential Nutrients Your Body Needs For Building Bone
In 2020, calcium was the 204th most popular drug in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.
The US Institute of Medicine (IOM) established Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for calcium in 1997 and updated these values in 2011.
See the table. The European Food Safety Agency (EFSA) uses the term Population Intake (PRI) instead of the RDA and sets slightly different numbers: age 4–10 800 mg, age 11–17 1150 mg, age 18–24 1000 mg, and >25 years 950 mg.

Due to concerns about long-term adverse side effects such as arterial calcification and kidney stones, the IOM and EFSA have established acceptable upper intake levels (UELs) for a combination of dietary and supplemental calcium. According to the IOM, people aged 9–18 should not exceed 3,000 mg/day; for the 19–50 age group, not to exceed 2,500 mg/day; for ages 51 and older should not exceed 2,000 mg/day.
Biology 2e, Animal Structure And Function, The Endocrine System, Regulation Of Body Processes
EFSA set the UL at 2500 mg/day for adults, but decided that there was insufficient information for children and adolescents to determine a UL.
For US food and dietary supplement labeling purposes, the amount per serving is expressed as a percentage of the Daily Value (%DV). For calcium labeling purposes, 100% of the daily value was 1000 mg, but as of May 27, 2016, this was revised to 1300 mg to align with the RDA.
Although as a general rule, the labeling and marketing of dietary supplements prohibits disease prevention or treatment claims, the FDA has reviewed the science on certain foods and dietary supplements, concluded that there is substantial scientific agreement, and issued specifically worded permitted health claims. . The original ruling, which allowed health claims for calcium dietary supplements and osteoporosis, was later amended to include calcium and vitamin D supplements, effective January 1, 2010. Examples of permitted wording are provided below. In order to meet the health claims for calcium, a dietary supplement must contain at least 20% of the RDI, which for calcium means at least 260 mg/serving.
In 2005, the FDA approved a qualified medical statement regarding calcium and hypertension with the proposed wording: “Some scientific evidence suggests that calcium supplements may reduce the risk of hypertension. However, the FDA has determined that the evidence is inconsistent and inconclusive.” The evidence for pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia was considered inconclusive.
Pdf) Human Uptake Of Eggshell Powder As An Alternate Source Of Calcium
That same year, the FDA approved QHC for calcium and colon cancer with the proposed wording: “Some evidence suggests that calcium supplements may reduce the risk of colon/rectal cancer, but the FDA has determined that this evidence is limited and inconclusive.” The evidence for breast cancer and prostate cancer was considered inconclusive.
Proposals for a QHC for calcium to protect against kidney stones or against menstrual disorders or pain were rejected.
EFSA rejected the claim that there is a causal relationship between dietary calcium and potassium intake and the maintenance of normal acid-base balance.

EFSA also rejected claims for calcium and nails, hair, blood lipids, pre-estrous syndrome and body weight maintenance.
What Is The Role Of Calcium In Our Body
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) website has a very comprehensive table of calcium content (in milligrams) in foods, searchable by standard figures such as per 100 grams or per standard serving.
The amount of calcium in the blood (more precisely, in the blood plasma) can be measured as total calcium, which includes both protein-bound and free calcium. In contrast, ionized calcium is a measure of free calcium. An abnormally high plasma calcium level is called hypercalcemia, and an abnormally low plasma calcium level is called hypocalcemia, with “abnormal” usually referring to levels outside the reference range.
Perst in tissue can be measured by atomic absorption spectroscopy, in which the tissue is vaporized and burned. To measure Ca
Concentration or spatial distribution in the cell cytoplasm in vivo or in vitro, a number of fluorescent reporters can be used. These include cell-permeable calcium-binding fluorescent dyes such as Fura-2 or a genetically engineered variant of gre fluoresct protein (GFP) called Cameleon.
What Is The Function Of The Kidneys In The Human Body?
Since access to ionized calcium is not always available, adjusted calcium can be used instead. To calculate the adjusted calcium level in mmol/L, the total calcium in mmol/L is taken and added to ((40 minus the serum albumin in g/L) multiplied by 0.02).
However, there is controversy regarding the usefulness of adjusted calcium, as it may not be superior to total calcium.
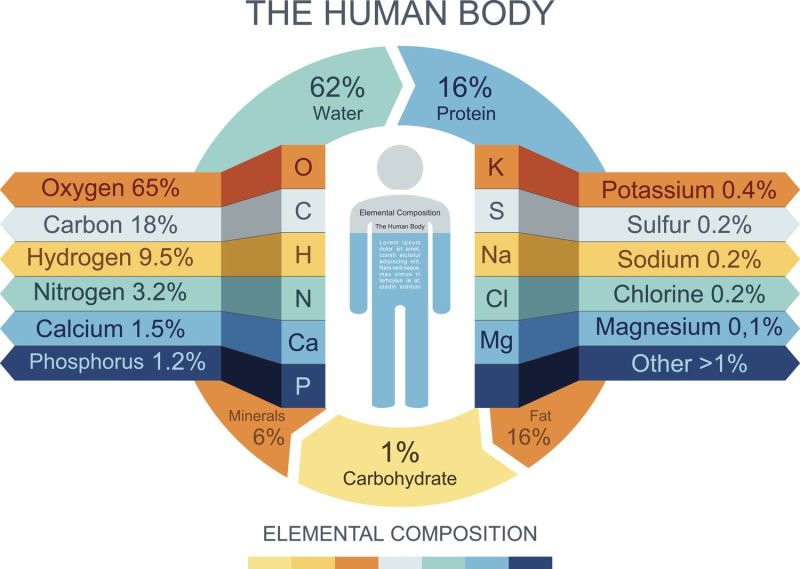
In vertebrates, calcium ions, like many other ions, are so vitally important for many physiological processes that their concentration is maintained within certain limits to ensure adequate homeostasis. This is confirmed by the calcium content in human blood plasma, which is one of the most regulated physiological variables in the human body. Normal plasma levels range from 1 to 2% at any given time. About half of all ionized calcium circulates in unbound form, while the other half is complexed to plasma proteins such as albumin and to anions including bicarbonate, citrate, phosphate, and sulfate.

(mainly calcium phosphate and some calcium sulfate) is the most important (and specific) element of bone and calcified cartilage. In humans, the total calcium content in the body is stored mainly in the form of bone mineral (approximately 99%). In this state, it is largely unavailable for exchange/bioavailability. The way to overcome this is in the process of bone resorption, during which calcium is released into the blood under the action of bone osteoclasts. The rest of calcium is stored in extracellular and intracellular fluids.
Phosphorus Binders: The New And The Old, And How To Choose
In a typical cell, the intracellular concentration of ionized calcium is approximately 100 nM, but undergoes a 10- to 100-fold increase during various cellular functions. Intracellular calcium levels are kept relatively low relative to the extracellular fluid, approximately 12,000 times. This gradient is supported by various plasma membrane calcium pumps that use ATP for energy, as well as significant accumulation in intracellular compartments. In electrically excitable cells such as skeletal and cardiac muscle and neurons, membrane depolarization leads to Ca
. It has been estimated that the concentration of free calcium in the mitochondrial matrix increases to ts micromolar levels in situ during neuronal activity.
The effect of calcium on human cells is specific, that is, different types of cells react differently. However, under certain circumstances, its effect can be more general. approx
Ions are among the most common second messengers used in signal transduction. They enter the cytoplasm in trance or from outside the cell across the cell membrane via calcium channels (such as calcium-binding proteins or voltage-gated calcium channels), or from some internal calcium stores such as the preplasmic reticulum.
How Much Major Minerals Are Used?
And mitochondria. Intracellular calcium levels are regulated by transport proteins that remove it from the cell. For example, the sodium-calcium exchanger uses energy from the electrochemical sodium gradient, coupling the influx of sodium into the cell (and down the concentration gradient) with the transport of calcium out of the cell. In addition, plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA) obtains energy to pump calcium out of the cell by hydrolyzing adoxin triphosphate (ATP). In neurons, voltage-gated calcium-selective ion channels are important for synaptic transmission through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft by synaptic vesicle fusion.
The function of calcium in muscle contraction was discovered by Ringer back in 1882. Further research revealed its role as a messenger about a century later. Since its action is interconnected with cAMP, they are called synergistic messengers. Calcium can bind to several different calcium-modulated proteins, such as troponin-C (the first to be identified) and calmodulin, proteins required to promote muscle contraction.
Activated pathways include stimulation of OS to produce nitric oxide as well as stimulation of K

And cause hyperpolarization of the cell membrane. Both nitric oxide and hyperpolarization cause smooth muscle to relax to regulate
Solution: Calcium Homeostasis Converted
What is the role of calcium in the body, calcium in the human body, what is the role of calcium in the human body, role of water in the human body, role of calcium in human body ppt, functions of calcium in the human body, role of proteins in the human body, role of iron in the human body, role of calcium in the heart, role of calcium in plants, what is the role of triglycerides in the human body, role of calcium in the body