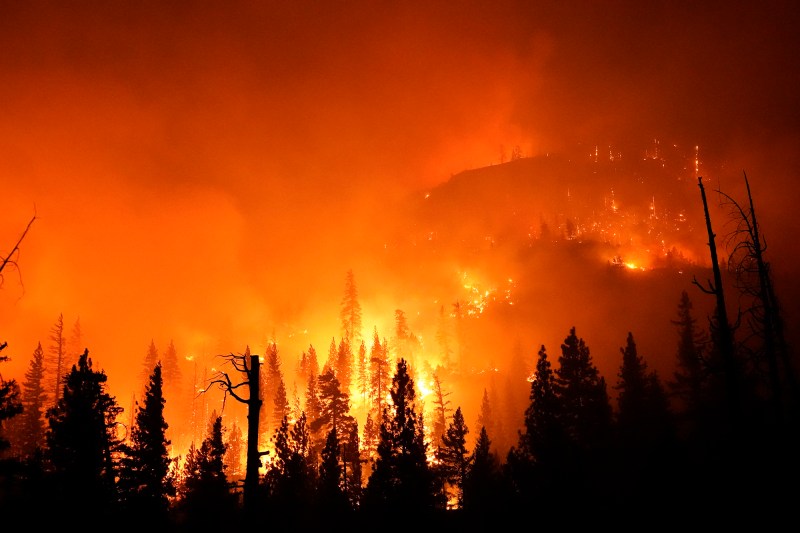
Negative Effects Of Wildfires On The Environment – With just 10 years left to reach the Sustainable Development Goals, in September 2019 world leaders called for accelerated action over the next decade to achieve the scale and speed needed. However, climate change and global warming are increasing the likelihood and intensity of wildfires, which could increasingly affect the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
For example, in 2019-2020 Australia’s 2018 bushfire season came at the end of the second-hottest year on record, with Australia seeing a number of record high temperatures at the start of its bushfire season. This has created much more flammable conditions than usual, leading to several mega-fires, with a total burnt area of more than 18 million hectares (186,000 square kilometres, larger than England and Wales).
Negative Effects Of Wildfires On The Environment

In addition to the well-reported impact of immediate loss of life, homes and animals in developed parts of the world, the increasing scale of forest fires around the world can also seriously affect several sustainable development goals.
Ten Impacts Of The Australian Bushfires
Global warming often hits the poor the hardest. They are the least adaptable; they also tend to be more dependent on natural resources such as firewood, forage and herbs. Forests provide food and medicine for indigenous people and many others. Many people, especially in developing countries, depend on intact forest resources for their livelihoods, and an unusually large fire can be devastating.
Smoke from wildfires causes air pollution and harms your health, no matter where you live. Wildfires release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, including particulate matter and toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and organic compounds other than methane. Wildfires can cause displacement, stress and suffering for people who have to flee them, not just those who suffer direct impacts.
The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) reported on 23 September 2019 that wildfires in forests and peatlands in Kalimantan and Sumatra, Indonesia, have put nearly 10 million children at risk of air pollution. In many countries, escape and protection from air pollution is a privilege that not everyone can afford or have equal access to. Air purifiers and good quality pollution masks can be expensive. Those who can’t afford to take time off from work may not be able to avoid places covered in smoke, for example.
Women and girls, especially in developing countries, are generally at greater risk during disasters such as fires. According to the United Nations Development Programme, the poor are more likely to live in conditions that make them less likely to survive and recover from a disaster. Studies have shown that the death toll in disasters is much higher for women than for men, which is largely due to gender differences in the ability to cope with such events and insufficient access to information and early warnings.
Biophysical Feedback Of Global Forest Fires On Surface Temperature
Particulate matter and black carbon from wildfires are carried into the air and into waterways. Researchers have quantified and characterized the black carbon flowing into the Amazon. “In aquatic ecosystems, the effects of acidity, nitrogen and mercury on organisms and biogeochemical processes are well documented. Air pollution causes or contributes to lake acidification, eutrophication of estuaries and coastal waters, and mercury bioaccumulation in aquatic food webs,” says the study, titled Effects of Air Pollution on Ecosystems and Biodiversity in the Eastern United States.
When fires spread in urban or semi-urban areas, they can damage infrastructure such as power lines, cell phone towers, and homes. Remodeling can be expensive or time-consuming.
Extravagant lifestyles and unsustainable consumption of natural resources in many countries, as well as the associated pollution, contribute to global warming, which in turn increases the likelihood of fires.

) and other greenhouse gases enter the atmosphere and contribute to global warming when the size of the fire exceeds CO
Explainer] The Good, The Bad, And The Ugly Side Of Forest Fires
Regrowth reabsorption potential. Particles and gases produced by burning biomass can be transported over long distances, affecting air quality in remote regions. Particles can also fall on snow and ice, causing the ice to absorb sunlight it would otherwise reflect, thereby accelerating global warming. Wildfires in highly flammable peatlands are particularly important for the climate because they release much more CO
Than normal forest or bush fires. These phenomena are known as climate feedback loops and add to the burden of emissions that must be reduced to limit global temperature increases.
Although humans have used fire to manage landscapes for thousands of years, current wildfires, exacerbated by global warming and drought, are becoming more widespread and impactful, destroying homes, infrastructure and wildlife, affecting biodiversity. They can lead to an economic downturn, at least in the short term.
“We have 10 years to drastically reduce emissions to maintain the 1.5°C target,” says Niklas Hagelberg, a climate change expert at the United Nations Environment Programme. “Failure to achieve this goal will seriously undermine efforts to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals.” Wildfires are natural events that have shaped our natural environment. In the past, fire regimes occurred every 5-30 years, creating a mosaic of vegetated land. This cycle is actually so ancient that some plants evolved the means to use it to their advantage. Some species, such as oak, have bark that resists fire damage, while some species have cones that only open after a fire.
Studies Connect Wildfire Smoke Side Effects To Covid 19 Risk
But eventually the human population grew and we moved closer to forests, scrubland and other wild areas where wildfires occur naturally. Even now, people choose to live in the wild-urban interface where such disorders are common. As a result, wildfires cause damage to our properties and people die.
In general, post-fire ash becomes an important source of soil nutrients. Studies show that after a fire, ash deposits usually contain calcium, magnesium, potassium and phosphorus
. The exact proportion of each element, of course, depends on the fuel composition and combustion temperature.

If ash is not washed away by rainfall, it can form a reservoir of nutrients for plants. This is especially important for species that require fire to germinate, such as eucalyptus. Thus, the ash provides a source of nutrients for their growth.
Wildfires In Yellowstone: Lasting Environmental Impacts And Changes To Wildfire Management Policy
At the same time, forest fires destroy soil microorganisms. They often compete with seedlings for nutrients and can cause disease.
Wildfires also often leave thick layers of ash and carbon on the forest floor. These eventually break down to form peat in bogs and bogs.
Peat is basically a mixture of organic matter that accumulates in the soil. It develops mainly in places where the soil has high water content but low oxygen content. Peatlands are common in Canada, Russia and Indonesia.
Since wildfires have occurred since the evolution of trees, many species actually adapted to this phenomenon. Today, there are many plant species that depend on fire episodes for reproduction. In fact, if we remove fire from their natural environment, they may die out.
Pdf) Environmental Impact Of Fire
Some seeds germinate only in the presence of combustion products such as ash and smoke. Examples include alder (
In addition, a thick resin covers the seeds of some tree species, which can only be melted by fire. An example is aspen. Here, the fire releases an enzyme in the seeds that causes them to grow. Aspen can actually produce about one million seedlings per acre after a fire. At the same time, these sprouts provide food for elk and moose.
For example, prairies regrow beautifully after a fire. This is because 90% of the biomass of meadows, which dominate the prairie ecosystem, is deep in the soil. So fires do not affect them. The Native Americans understood very well the importance of wildfires on the prairies.

As a result, new plants can grow with more nutrients and sunlight. There is less competition for nutrients, sunlight, water and space, allowing fire-dependent species to thrive.
Wildfires In The United States 101: Context And Consequences
Eventually, as these shoots grow, they provide food for animals such as elk, deer, and bison. Research in the boreal forests of Quebec, Canada, shows an increase in the number of black bears after wildfires. This is because berries become abundant, an important part of the diet of black bears
Research also shows that after a forest fire, several animals also colonize the burned area. In fact, many insects benefit from fires, which kill predators, expose soil, and provide nutrients.
Some fire-loving (pyrophilic) species have special adaptations to burnt habitats. This can be in the form of a fire or smoke detector.
Several species of birds also find homes in burnt forests. This includes ground-nesting birds such as the hermit thrush, flycatchers and the American robin.
How Wildfire Smoke Raises Infectious Disease Risk
The number of cavity-dwelling birds, such as woodpeckers, also increases after a forest fire. In fact, the black-backed woodpecker (
) is an important cavity-forming species in burnt wood. They can be inhabited by other birds that cannot create cavities but need them for breeding.
Black-backed woodpeckers are important bird species that colonize burned forests and create cavities for other birds; Image by Kurayba via Flickr
Unfortunately, wildfires also affect soil properties. In a very hot fire, burnt materials can infiltrate the soil and form a waxy layer on the soil particles. As a result, water cannot penetrate the ground during rain.
Climate Change Worsening Canadian Fires; Smoke Hits Chicago Again
Because plant roots are burned, they are no longer able to hold soil particles in place. This results in erosion. In addition, erosion will be greater on steep slopes. These
Negative effects of deforestation on the environment, negative effects of veganism on the environment, negative effects of plastic on the environment, negative effects of pesticides on the environment, negative effects of agriculture on the environment, negative effects of mining on the environment, negative effects of gmos on the environment, negative effects of cars on the environment, negative effects of wildfires, negative effects on the environment, effects of wildfires on the environment, negative effects of fracking on the environment