Light Energy Is Stored As Atp And Nadph – After the sun’s energy is converted into chemical energy and temporarily stored in ATP and NADPH molecules, the cell has the fuel it needs to build carbohydrate molecules for long-term energy storage. The products of light-dependent reactions, ATP and NADPH, have lifetimes in the range of millionths of a second, while the products of light-independent reactions (carbohydrates and other forms of reduced carbon) can persist almost indefinitely. Carbohydrate molecules made will have a backbone of carbon atoms. But where does carbon come from? It comes from carbon dioxide—a gas that is a waste product of the respiration of microbes, fungi, plants, and animals.
) enters the leaves through the stomata, where it diffuses short distances through the intercellular spaces until it reaches the mesophyll cells. Once in the mesophyll cells, CO
Light Energy Is Stored As Atp And Nadph

Diffuses into the chloroplast stroma – the site of light-independent photosynthesis reactions. These reactions actually have several names associated with them. Another term, the Calvin cycle, is named after the man who discovered it and because these reactions work as a cycle. Others call it the Calvin-Benson cycle to include the name of another scientist involved in its discovery. The most obsolete name is the “dark reaction”, because light is not directly required ((Figure)). However, the term dark reaction can be misleading because it incorrectly implies that the reaction occurs only at night or that it is independent of light, which is why most scientists and instructors no longer use it.
General Picture Of Photosynthesis Including Light Reactions And The…
Figure 1. Light reactions use energy from the sun to produce chemical bonds, ATP and NADPH. These energy-carrying molecules are produced in the stroma where carbon fixation takes place.
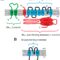
, two other components are present to initiate light-independent reactions: an enzyme called ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) and three molecules of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), as shown in (Figure). RuBP has five carbon atoms, surrounded by two phosphates.
Figure 2. The Calvin cycle has three stages. In step 1, the enzyme RuBisCO incorporates carbon dioxide into an organic molecule, 3-PGA. In phase 2, the organic molecule is reduced using electrons supplied by NADPH. In phase 3, RuBP, the molecule that initiates the cycle, is regenerated so that the cycle can continue. Only one carbon dioxide molecule is incorporated at a time, so the cycle must be completed three times to produce one three-carbon molecule of GA3P and six times to produce a six-carbon molecule of glucose.
Molecule that reacts with one RuBP, two molecules of another compound 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA) are formed. PGA has three carbons and one phosphate. Each round of the cycle involves only one RuBP and one carbon dioxide and forms two molecules of 3-PGA. The number of carbon atoms remains the same, as atoms move to form new bonds during reactions (3 C atoms from 3CO
Light Dependent Reaction
+ 15 C atoms from 3RuBP = 18 C atoms in 6 molecules of 3-PGA). This process is called carbon fixation, because CO
ATP and NADPH are used to convert six molecules of 3-PGA into six molecules of a chemical called glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). It is a reduction reaction because it involves the gain of electrons by 3-PGA. (Recall that reduction is the gaining of electrons from an atom or molecule.) Six molecules of both ATP and NADPH are used. For ATP, energy is released by the loss of the terminal phosphate atom, converting it to ADP; for NADPH, both energy and a hydrogen atom are lost, converting it to NADP
It is interesting that at this moment only one of the G3P molecules leaves the Calvin cycle and is sent to the cytoplasm to contribute to the creation of other compounds needed by the plant. Since G3P exported from the chloroplast has three carbon atoms, it takes three “turns” of the Calvin cycle to fix enough net carbon to export one G3P. But each turn makes two G3Ps, so three turns make six G3Ps. One is exported while the remaining five G3P molecules remain in the cycle and are used to regenerate RuBP, allowing the system to prepare for more CO
This link leads to an animation of the Calvin cycle. Click on Phase 1, Phase 2, and then Phase 3 to see how G3P and ATP are regenerated into RuBP.
Calvin Cycle (dark Reaction) — Equation & Steps
During the evolution of photosynthesis, there was a major shift from the bacterial type of photosynthesis involving only one photosystem and which is typically anoxygenic (does not generate oxygen) to modern oxygenic photosynthesis (generates oxygen), using two photosystems. This modern oxygenic photosynthesis is used by many organisms—from the giant tropical leaves in the rainforest to the tiny cells of cyanobacteria—and the process and components of this photosynthesis remain largely the same. Photosystems absorb light and use electron transport chains to convert the energy into the chemical energy of ATP and NADH. Subsequent light-independent reactions then assemble carbohydrate molecules with this energy.
In a dry desert, plants must conserve every drop of water that must be used to survive. Because the stomata must open to allow CO intake
, water leaves the leaf during active photosynthesis. Desert plants have developed processes to conserve water and cope with harsh conditions. CO capture and storage mechanisms
Allows plants to adapt to life with less water. Some plants such as cacti ((Figure)) can prepare material for photosynthesis during the night by a temporary process of carbon fixation/storage, as stomatal opening at this time conserves water due to lower temperatures. During the day, cacti use the captured CO
Introduction To Bioenergetics
Figure 3. The harsh conditions of the desert led plants like these cacti to evolve light-independent variations of photosynthetic reactions. These variations increase the efficiency of water use, helping to conserve water and energy. (credit: Piotr Wojtkowski)
Whether the organism is a bacterium, plant, or animal, all living things access energy by breaking down carbohydrates and other carbon-rich organic molecules. But if plants make carbohydrate molecules, why would they need to break them down, especially when it has been shown that gases are released by organisms as a “waste product” (CO
) acts as a substrate for the formation of more food in photosynthesis? Remember, living things need energy to perform life functions. Additionally, an organism can either make its own food or eat another organism – either way, the food still needs to be broken down. Finally, in the process of breaking down food, called cellular respiration, heterotrophs release the necessary energy and produce “waste” in the form of CO.

However, there is no such thing as “waste” in nature. Every single atom of matter and energy is stored, recycled over and over ad infinitum. Substances change form or change from one type of molecule to another, but their constituent atoms never disappear ((Figure)).
Photosynthesis: Ap® Biology Crash Course
It is no more a form of waste than oxygen is wasteful for photosynthesis. Both are byproducts of reactions that go on to other reactions. Photosynthesis absorbs light energy to build carbohydrates
In chloroplasts, and aerobic cellular respiration releases energy by using oxygen to metabolize carbohydrates in the cytoplasm and mitochondria. Both processes use electron transport chains to capture the energy necessary to drive other reactions. These two driving processes, photosynthesis and cellular respiration, work in biological, cyclical harmony to allow organisms to access the life energy that originates millions of miles away in the burning star that humans call the Sun.
Figure 4. Photosynthesis consumes carbon dioxide and produces oxygen. Aerobic respiration consumes oxygen and produces carbon dioxide. These two processes play an important role in the carbon cycle. (credit: mod by Stuart Basile)
Using the energy carriers formed in the first steps of photosynthesis, light-independent reactions, or the Calvin cycle, take CO
Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration
And another organic compound, RuBP. After three cycles, the three-carbon G3P molecule leaves the cycle and becomes part of a carbohydrate molecule. The remaining G3P molecules remain in the cycle to be regenerated into RuBP, which is then ready to react with more CO
. Photosynthesis forms an energy cycle with the process of cellular respiration. Because plants contain both chloroplasts and mitochondria, they rely on both photosynthesis and respiration to function in both light and darkness, and to be able to interconvert essential metabolites.
If four molecules of carbon dioxide enter the Calvin cycle (four “turns” of the cycle), how many G3P molecules are produced and how many are exported?

What fraction of light-independent reactions would be affected if the cell could not produce the RuBisCO enzyme?
Light Dependent Reaction: Definition, Diagrams, And Products
Neither cycle could occur, as RuBisCO is required for carbon dioxide fixation. Specifically, RuBisCO catalyzes the reaction between carbon dioxide and RuBP at the beginning of the cycle.
Why does it take three turns of the Calvin cycle to produce G3P, the initial product of photosynthesis?
Because G3P has three carbon atoms, and each round of the cycle takes one carbon atom in the form of carbon dioxide.
Imagine an indoor terrarium containing a plant and a bug. How does each organism provide resources for the other? Could every organism survive if it were the only living thing in a terrarium? Why or why not?
Photosynthesis 6co2 + 6h2o + Energy C6h12o6 + 6o2
Compare the flow of energy with the flow of nutrients in a closed, sunny ecosystem that consists
Energy stored in atp, atp and nadph, atp as an energy source, where is atp stored, what is the role of the atp and nadph molecules, where is atp energy stored, where are atp and nadph made, atp as energy currency, what is atp and nadph, how is energy stored in atp, the energy in petroleum and coal is stored as, energy in petroleum and coal is stored as