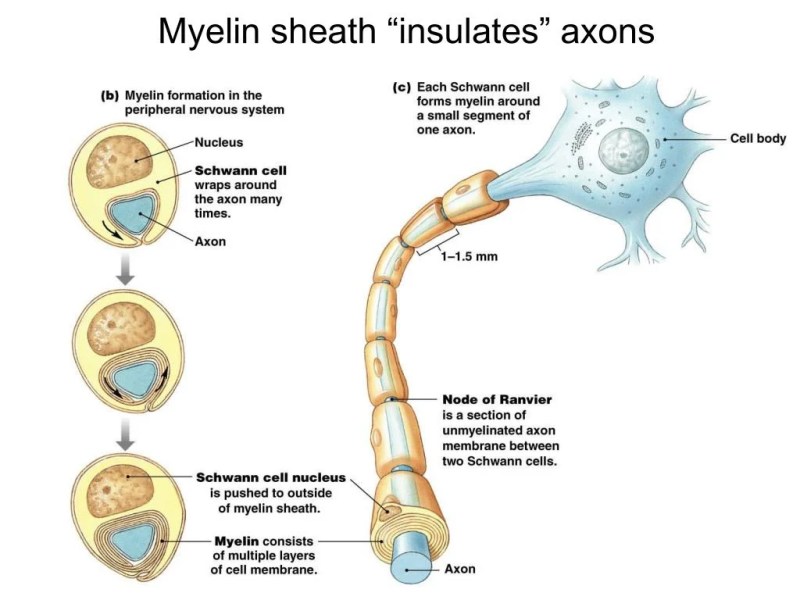
In The Central Nervous System Myelin Is Formed By – Oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system (in contrast to Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system) form sections of the myelin sheaths of numerous neurons simultaneously.
Myelin is a substance that forms the myelin sheath associated with nerve cells. This coat is a layer of phospholipids that increases the conductivity of electrical messages sent by the cell. Diseases like Multiple Sclerosis are caused by a lack of this myelin sheath, resulting in the conduction of signals being very slow and the effectiveness of the nervous system being reduced in sufferers.
In The Central Nervous System Myelin Is Formed By

In total, there are 43 main nerves that branch from the central nervous system (CNS) to the peripheral nervous system. (The peripheral nervous system is the nervous system outside the CNS.) These are afferent neurons that carry signals from the CNS to the peripheral system.
Myelin In The Central Nervous System: Structure, Function, And Pathology.
. Somatic fibers are responsible for the voluntary movement of our body, i.e., our conscious thought.
The autonomic nervous system includes all impulses that are carried out involuntarily and are usually associated with essential functions such as breathing, heartbeat, etc. However, this type of system can be further broken down into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems that complement each other. Check for negative feedback such as insulin and glucagon release in blood sugar control.
These pulses of information carried out in our nervous system allow us to perform our daily tasks. This information is processed in the CNS, the brain, a highly developed mass of nerve cells. The inner workings of the brain are examined in the next tutorial, Types and Causes of Brain Damage.
This tutorial deals with the abiotic factors in the freshwater environment that determine what type of life a needle will have.
N Wasp Regulates Oligodendrocyte Myelination
DNA is a double helix structure consisting of nucleotides. A nucleotide, in turn, is composed of a phosphate molecule, deoxy.
Learn how genes control and determine every aspect of the body. This chapter uses the lac operon as an example. ..
This tutorial describes the different types and causes of brain damage. Learn about genetics, physical trauma, lack of…

A balanced diet is essential for a healthy body. Inadequacy or too much of a particular element or compound, such as .. Open Access Policy Institutional Open Access Program Special Issues Guidelines Editorial Procedures Research and Publication Ethics Article Processing Fees Awards Acknowledgments
Glial Cells: Types And Functions
All articles published by are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse the published article in whole or in part, including figures and tables. For articles published under the Open Access Creative Commons CC By License, any part of the article may be reused without permission, provided the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https:///openaccess.
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A feature paper should be a truly original article that covers multiple techniques or approaches, provides perspectives for future research directions, and describes potential research applications.
Feature papers are submitted at the personal invitation or recommendation of scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations from scientific editors of journals around the world. The editors select a few articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be of particular interest to readers or in relevant research areas. It aims to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the journal’s various research areas.
A Little Myelin Goes A Long Way To Restore Nervous System Function
Received: 30 April 2023 / Revised: 31 May 2023 / Accepted: 3 June 2023 / Published: 5 June 2023
The myelin sheath is an insulating layer around the brain and spinal cord that allows for fast and efficient nerve conduction. Myelin is composed of proteins and lipids and provides protection for the transmission of electrical impulses. The myelin sheath is formed by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS) and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The myelin sheath presents a highly organized structure and extends both radially and longitudinally, but in different ways and with different structures. Changes in myelin determine the onset of many neuropathies, as the electrical signal can be slowed or stopped. Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) and ras (rat sarcoma)-related binding proteins (rabs) have been shown to contribute to several aspects of myelin formation or dysmyelination. Here, I will describe the role of these proteins in regulating membrane trafficking and nerve conduction, myelin biogenesis and maintenance.
The brain is an important organ that is fundamental to the regulation of many biological and physiological functions. It is divided into several areas that can change during development, maturation, normal aging, neurological disorders and trauma. Along with the spinal cord, it forms the central nervous system. It is composed of neurons, which store information and transmit impulses, and glial cells, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, which support, insulate, and protect neurons. Neurons are very sensitive cells, with a high demand for oxygen, glucose and other molecules. To function properly, neuron activity is based on the generation of action potentials and generation of ion gradients. Neurons use electrical impulses and chemical signals to send information between different parts of the brain and between the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Glial cells typically outnumber neurons, and in the adult central nervous system (CNS) they include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglial cells. In the peripheral nervous system (PNS) they are named Schwann cells, enteric glial cells and satellite cells [1]. Interestingly, it has been demonstrated that astrocytes, microglia and oligodendrocytes contribute to the modulation of neuronal synaptic structure and function. In fact, astrocytes play a role in neuronal activity by exhibiting excitability, due to changes in intracellular calcium levels. They regulate neurotransmitter release, the extracellular environment, and contribute to synapse elimination by phagocytosis or trogocytosis (synapse engulfment). Microglia can affect synapses by removing redundant neuronal dendritic spines and secreting microvesicles and specific molecules such as cytokines and transmitters, while cells of the oligodendrocyte lineage can form functional synaptic contacts and regulate synapses in a unidirectional or bidirectional growth manner. 3].

Signal transmission depends on the myelin sheath, which determines the speed of information and affects capacitance/resistance and current flow. Myelin consists of several layers of specialized cell membranes that surround axons larger than 1 µm in diameter. Myelin sheath covers axons with the exception of nodes of Ranvier (~1 µm small area and <1% of myelinated axon area), which are small gaps between two adjacent myelin sheaths, small axons (<0.2– 0.8 µm diameter), some large axons in white matter, Most axons in the gray matter [4, 5], C-fibers in the PNS [6] and synapses [7].
Brain Cell Insight Could Lead To New Treatments For Neurological Based Diseases
Each myelin segment has an internode, which is usually 0.2–1 mm long. In the PNS, the length of the myelin sheath along the axon is about 1 mm. In the CNS, and particularly in the anterior medullary velum of the adult rat, the internodal length is 50–750 µm [ 8 ]. However, myelin sheaths are critical for the formation, health, and function of the CNS, and its length is highly variable and fundamental to axonal conduction velocity and functional plasticity of neural circuits [9].
Small-diameter axons have a large number of internodes (up to 80), 20 to 200 μm long, whereas oligodendrocytes that myelinate large-diameter axons have fewer processes but longer internodes and thicker myelin sheaths. A single oligodendrocyte may have a surface area of 20 × 10 myelin
The membrane of the myelin sheath opposes and forms the intraperiodic line (IPL), a thin space that separates the membrane and which is attached to the extracellular space. On the other hand, the major dense line (MDL) is a 3 nm compartment between the two cytoplasmic sheets of the stacked myelin membrane, where myelin basic protein (MBP) is abundant.
The myelin sheath prevents signal loss and is slightly different in the CNS than in the PNS. Although structurally similar, specific cell types (oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells) are responsible for myelin formation in the CNS and PNS, respectively. Oligodendrocytes are responsible for the formation of 80 different layers of myelin membrane around the axon. The synthesis and maturation of these sheaths is a fast and efficient nerve conduction, while the maintenance and remodeling of myelin is linked to the interaction between oligodendrocytes and glial and neuronal cells and its role in providing neurons, ion and metabolic support. water homeostasis, and adaptation to activity-dependent neuronal signals [10].
Remodeling Myelination: Implications For Mechanisms Of Neural Plasticity
Interestingly, gap junctions and cytoplasmic diffusion pathways in myelin have been shown to be linked to myelin sheath functions. The main types of voltage-gated channels are K
Channels and P2X ligand-gated ion channels.
Lymphoma in the central nervous system, drugs affect the central nervous system by, what is in the central nervous system, cancer in the central nervous system, nervous system myelin sheath, diseases in the central nervous system, myelin central nervous system, the myelin sheath is formed by, how is myelin formed, the central nervous system is, the central nervous system, myelin is formed by