- How Many Blood Cells Are In The Human Body
- Under The Microscope: Blood
- Red Blood Cells: Function And Structure
- Cell Of The Human Body Poster Illustration Stock Vector Image & Art
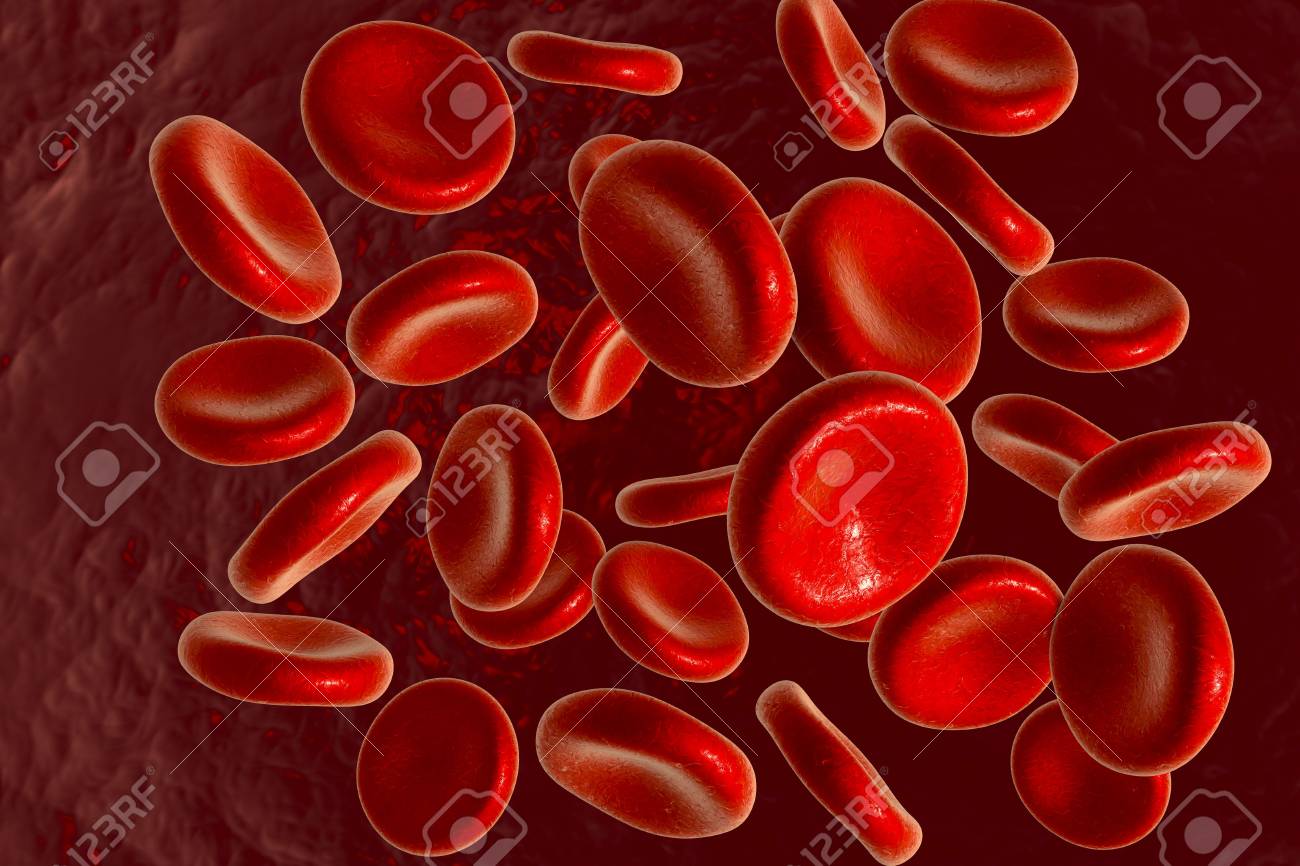
- Human Blood Cells Enlarged 2,000 Times
- Mapping The Human Body One Cell At A Time: New Study Reveals The Intricate Relationship Between Cell Size And Count
How Many Blood Cells Are In The Human Body – No matter where you go, I’m sure there are a few facts about your body that you don’t know!
1. In the human body, DNA extends from the Sun to Pluto and back – up to 17 times!
How Many Blood Cells Are In The Human Body

There are about 37 trillion cells in the human body, all of which contain about 5 cm of DNA (put together). DNA is made up of many different nucleotide pairs that can determine some of our characteristics, such as eye and hair color.
Axis Scientific Human Blood Cells
But bacteria are much smaller, so don’t take up that much space. Many of these bacterial cells are important, such as the gut bacteria that help keep our immune systems healthy.
We all smell like we each have our individual fingerprints. It is determined by your genes and can be used by other animals to identify individuals.
An average heart pumps about 70 ml of blood with each beat, and a healthy heart beats 70 times per minute.
5. When you go to bed at night, you will be 1 cm shorter than when you wake up in the morning.
Under The Microscope: Blood
A nerve impulse is an electrical signal sent to the brain when a nerve is stimulated. It’s important that they travel quickly, so if you burn your finger, for example, it’s important that your brain gets the message to quickly stop touching it.
Humans are not the naked monkeys we were made to be. We have a lot of hair, but for most of us it is not obvious because most of the hair is too fine or too light to be seen.
To put it into perspective, the distance around the earth is about 25,000 miles, so your blood vessels can circle the earth more than twice as far.
Your eye color depends on the genes you get from your parents, but most babies have blue eyes at birth. The reason for this is the pigment melanin. Melanin in a newborn’s eyes often accumulates completely after birth or darkens with exposure to ultraviolet light, revealing the child’s true eye color later.
Type Of Human Blood Cells On White Background Vector Image
Your body not only needs energy to keep your organs functioning, but it also needs energy to constantly repair and build new cells to create your body’s building blocks. Blood group (or blood group) is determined in part by ABO blood group. Antibodies are produced in red blood cells.
Blood type (also known as blood type) is a classification of blood based on the presence and absence of antibodies and inherited antigens on the surface of erythrocytes (erythrocytes). These antibodies may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells in various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens may come from the same allele (or alternative version of a gene) and together form the blood group system.
A total of 44 human blood group systems are recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT).
The two most important blood group systems are ABO and Rh; they determine whether someone’s blood type (A, B, AB and O, with a + or – marginal RhD status) is suitable for a transfusion.
Investigators May Unlock Mystery Of How Staph Cells Dodge Immune System, Allowing Infections Again
A complete blood group describes each of the 44 blood groups, and a person’s blood group is one of the possible combinations of blood group antigens.
A person almost always has the same blood type throughout life, but very rarely a person’s blood type changes due to the addition or suppression of antibodies during infection, malignancy, or autoimmune disease.
Another common reason for a blood type change is a bone marrow transplant. Bone marrow transplants are performed for many leukemias and lymphomas, among other diseases. If a person receives bone marrow from someone with a different ABO type (for example, a person with type O receives bone marrow from type A), the patient’s hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are destroyed, so the person’s blood type must eventually change to the donor’s. , either by bone marrow ablation or donor T cells. After all of the patient’s original red blood cells die, they are completely replaced by new cells derived from donor HSCs. If the donor has an ABO type, the surface antigens of the new cells differ from those on the surface of the original erythrocytes of the patient.

Some blood types are associated with the inheritance of other diseases; for example, Kell antigen is sometimes associated with McLeod syndrome.
Red Blood Cells: Function And Structure
Certain blood groups may be resistant to infections, such as resistance to a certain type of malaria in people without Duffy antibodies.
Duffy antigen is less common in population groups from malaria-endemic areas, probably as a result of natural selection.
The ABO blood group system includes two antigens and two antibodies found in human blood. Two are antig A and antig B. Two antibodies are antibody A and antibody B. The antibody is in the red blood cells and the antibody in the serum. All people can be classified into four groups according to their blood antigen properties: those with antigen A (group A), those with antigen B (group B), those with both A and B antibodies (group AB), and those without either. antig (group O). Antibodies are found along with antigens as follows:
There is an agglutination reaction between similar antigens and antibodies (for example, antigen A agglutinates antibody A, and antibody B agglutinates antibody B). Thus, a transfusion can be considered safe if the recipient’s serum does not contain antibodies to the donor’s blood cells.
First Human Patients Receive Transfusions Of Lab Grown Blood Cells
The ABO system is the most important blood group system in human blood transfusion. Associated anti-A and anti-B antibodies are usually immunoglobulin M, abbreviated IgM, antibodies. It is hypothesized that ABO IgM antibodies are produced during the first years of life by sensitization to viral substances such as food, bacteria, and viruses, but as a practice, blood group compatibility rules apply to newborns and infants.
The original terminology used for classification by Karl Landsteiner in 1901 was A/B/C; “C” became “O” in later editions.
The Rh system (Rh stands for Rhesus) is the second most important blood group with 50 antigens in human blood transfusions. The most important Rh antigen is the D antibody because it can trigger an immune system response of the five major Rh antigens. It is common for D-negative individuals to have no anti-D IgG or IgM antibodies because anti-D antibodies are not normally produced by sensitization to viral substances. However, D-negative people can produce IgG anti-D antibodies after ssitizing: possible fetal blood transfusion during pregnancy or sometimes blood transfusion with D positive erythrocytes.

Rh negative blood types are less common in Asian populations (0.3%) than in European populations (15%).
Cell Of The Human Body Poster Illustration Stock Vector Image & Art
The presence or absence of the Rh(D) antigen is marked with a + or − sign, so, for example, group A− is ABO type A and does not have the Rh(D) antigen.
As with many other genetic traits, the distribution of ABO and Rh blood groups varies significantly between populations.
, the International Society of Blood Transfusion has identified 42 blood group systems in addition to the ABO and Rh systems.
Thus, in addition to ABO antibodies and Rh antibodies, many other antibodies are expressed on the RBC surface membrane. For example, an individual can be AB, D positive and at the same time M and N positive (MNS system), K positive (Kell system), Le.
Human Blood Cells Enlarged 2,000 Times
Negative (Lewis system) and others, each blood group system is positive or negative for antig. Many blood group systems were originally named after the antibodies to which the corresponding antibodies were directed. Blood group systems other than ABO and Rhesus pose a greater but relatively minor risk of complications when mixing blood from different individuals.
Transfusion medicine is a specialized branch of hematology that deals with the study of blood groups in addition to blood banking to provide transfusion services for blood and other blood products. All over the world, blood products must be prescribed by a doctor (licensed physician or surgeon) just like drugs.
Much of the day-to-day work of a blood bank involves testing blood from both donors and recipients to make sure that each recipient’s blood is compatible and as safe as possible. If a unit of mismatched blood is transfused between the donor and the recipient, a severe acute hemolytic reaction with hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells), renal failure, and shock may occur and may be fatal.

Antibodies can be highly reactive and bind components of the complement system to attack red blood cells and cause massive hemolysis of the transfused blood.
Mapping The Human Body One Cell At A Time: New Study Reveals The Intricate Relationship Between Cell Size And Count
Patients should ideally receive their own blood or specific blood
How many nerve cells are in the human body, how many different cells are in the human body, how many white blood cells are in the human body, how many cells are there in the human body, how many muscle cells are in the human body, how many blood cells in human body, how many stem cells are in the human body, how many cells are in the adult human body, approximately how many cells are in the human body, how many cells are in the human body at birth, about how many cells are in the human body, how many cells are in human body