Functions Of Blood In The Human Body – The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) pumps blood from the heart to the lungs to get oxygen. The heart then sends oxygenated blood through the arteries to the rest of the body. Veins return oxygen-poor blood to the heart to begin the circulatory process. Your circulatory system is critical to healthy organs, muscles, and tissues.
Heart and blood vessels make up the circulatory system. The main function of the circulatory system is to deliver oxygen, nutrients and hormones to the muscles, tissues and organs of your body. Another part of the circulatory system is to remove waste from cells and organs that your body can get rid of.
Functions Of Blood In The Human Body

Your heart pumps blood around the body through a network of arteries and veins (blood vessels). Your circulatory system can also be described as the cardiovascular system. Cardio means heart, and artery refers to blood vessels.
Functions Of Blood: Regulation
Cleveland Clinic is a not-for-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The function of the circulatory system is to move blood throughout the body. This circulation keeps organs, muscles and tissues healthy and works to keep you alive.
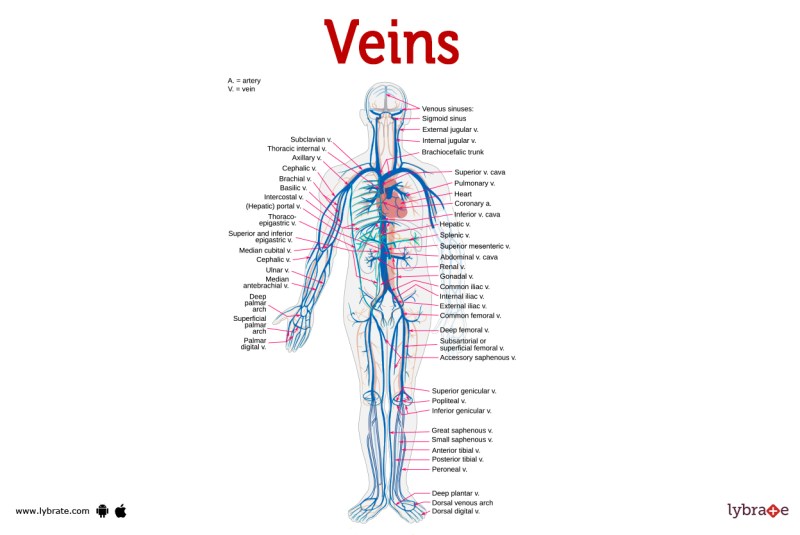
Your circulatory system consists of arteries, veins, and capillaries with the help of blood vessels. These blood vessels work with your heart and lungs to keep blood circulating throughout your body. Here’s how:
Your circulatory system has three circuits. Blood circulates through your heart and through these circuits in a series pattern:
Right & Left Atrium
Your heart is the only part of the circulatory system. Blood goes from the heart to the lungs to get oxygen. Lungs are part of the respiratory system. Your heart then pumps the oxygenated blood through the arteries to the rest of the body.
Your body has over 60,000 miles of blood vessels that circulate about 1.5 gallons of blood each day.
All blood is red. The iron-rich hemoglobin in red blood cells combines with oxygen to give blood its red color. Blood rich in oxygen is known as red blood.

Your veins carry oxygen-poor blood. This is sometimes called blue blood because the veins can appear blue under the skin. The blood is actually red, but the low oxygen level gives the blood vessels a blue color.
Viktor Schauberger Quote: “actually, The Mysteries Of Water Are Similar To Those Of The Blood In The Human Body. In Nature, Normal Functions Are Fu…”
Mostly, yes. The special ones are the pulmonary arteries and veins. The pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs. The pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the heart.
Your circulatory system plays a vital role in keeping you alive. Blood vessels carry blood to the lungs for oxygen. Your heart then pumps oxygen-rich blood through the arteries to the rest of the body. Blood vessels help your body get rid of waste. Conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis can affect the health of your circulatory system. If you have one of these conditions, talk to your healthcare provider about steps you can take to maintain cardiovascular health. Blood is a special body fluid that constantly flows through your body. It does many things to keep your body functioning, such as carrying oxygen around your body. Blood cancers and blood disorders can prevent blood from doing its necessary work. Health care providers have many ways to treat blood cancers and blood disorders.
Blood is mostly liquid but contains cells and proteins. Blood has four components: red blood cells (bottom right), white blood cells, platelets (middle right), and plasma (top right).
Blood is a vital life force, constantly flowing and keeping your body functioning. Blood is mostly a liquid but contains cells and proteins that make it literally thicker than water.
Functions Of Potassium In Human Body With Sources In Food Outline Diagram Stock Vector
Blood has four components: red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma. Each cell has specific and important functions, from transporting oxygen to processing waste products.
Your blood acts as a kind of health barometer. Abnormal blood test results can be the first sign of changes that may indicate a serious illness. This article focuses on how blood works and the conditions that affect blood health.
Cleveland Clinic is a not-for-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy

Blood has four parts. Red blood cells and plasma make up most of your blood. White blood cells and platelets, sometimes referred to as buffy coats, make up less than 1% of your blood.
Human Circulatory System
Red blood cells (erythrocytes) make up 45 percent of your blood. They carry oxygen in your body. They also help to cleanse the waste from your body. These cells are:
Your white blood cells (leukocytes) make up less than 1% of your blood and are part of your immune system. When invaders such as viruses or cancer cells attack, your white blood cells move quickly to find and destroy them. White blood cells can enter your tissues from hairs. There are five types of white blood cells:
When your blood vessels are injured and bleeding, your platelets (thrombocytes) are the first to go. Platelets control blood flow by forming blood clots that block damaged blood vessels so they don’t lose too much blood. Platelets:
Your blood cells and platelets float in plasma. Plasma is the yellowish fluid that makes up 55 percent of your blood. Plasma is your blood’s utility player, which covers a lot of bases when it comes to keeping your body functioning. Some functions of plasma include:
Great Vessels Of The Heart: Anatomy & Function
There are four types of blood. Blood is of different types depending on which antigens it contains. Antigens are substances that cause the body’s immune system to respond.
Blood flows through your body. It starts in your bone marrow, which contains stem cells. Stem cells give rise to trillions of cells, including blood cells. Before blood cells enter your blood vessels, they develop and multiply in your bone marrow. Blood represents 8% of body weight.
Blood cancer, blood disease and common cardiovascular diseases affect the blood. Blood cancers affect how your body produces blood cells. Blood diseases make your blood stop working. Atherosclerosis is a disease of the heart and blood vessels that affects blood circulation. In general, blood cancers and blood disorders have a more general impact on blood health than atherosclerosis.

Blood cancer occurs when something disrupts how your body makes blood cells. If you have blood cancer, the abnormal blood cells overpower the normal blood cells. There are three types of blood cancer:
Question Video: Stating The Primary Function Of Blood Plasma In The Body
Blood disorders are non-cancerous conditions that prevent the parts of your blood from doing their job. Anemia includes anemia, coagulation disorders, and bleeding disorders.
Some blood disorders may not cause symptoms or require treatment. Others are chronic (lifelong) illnesses that require treatment but do not affect how long you live. There are also serious and life-threatening blood disorders.
Anemia is the most common non-cancerous blood disorder. It happens when you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells. Sometimes people inherit anemia, but they can catch it or develop it. There are many types of anemia. Some common anemias include:
Blood clotting disorders affect your platelets or clotting factors (blood clotting factors). Clotting factors are proteins in your blood that help the platelets in your blood to control bleeding. You may inherit an acquired blood clotting disorder or a genetic mutation that causes abnormal blood clotting.
Function Of Bone Marrow: What Is It And What Does It Do?
Prothrombin gene mutations and factor V Leiden syndrome are examples of inherited clotting disorders. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) are examples of coagulation disorders.
A bleeding disorder occurs when your blood is abnormal, causing it to bleed more than usual. Von Willebrand disease is the most common bleeding disorder in the U.S. Hemophilia, an inherited rare condition, is another example of a bleeding disorder.
Your blood is a precious resource, it constantly nourishes your body, so it works as it should. Your blood brings oxygen to your cells to make energy. Your immune system helps protect your body from enemies. It controls how much blood bleeds when injured. Although you can take care of your blood, you cannot avoid diseases that affect it. Fortunately, health care providers can treat more serious blood conditions, including blood cancers and blood disorders. It helps maintain the internal state of the body when external conditions change outside the body or when other factors affect the body such as illness or exercise.
It plays a role in temperature control. It distributes heat in the body, from the core up and vice versa.
Normal Heart Function
By changing the flow to the skin, the body can control heat exchange at the surface with the environment.
By widening the vessels, increasing the amount and speed of blood flow to the skin and inside (vasodilation) causes more heat to be lost, thus reducing the body temperature. Narrowing of the vessels (vasoconstriction) means that less heat is lost in this way, thus maintaining the body’s core temperature.
Have you ever noticed the veins in your arms and legs on a hot day? They look bigger and more clear. Your body realizes that it needs to heat up and cool down more than usual. The vessels are spread out so more flows near you and on your own floor
Functions of cells in the human body, functions of the liver in human body, functions of water in the human body, functions of potassium in the human body, functions of iodine in the human body, functions of proteins in the human body, functions of the human body, functions of organs in the human body, functions of magnesium in the human body, functions of oxygen in the human body, functions of bones in the human body, functions of calcium in the human body