Function Of Calcium Ions In The Body – Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca. In the human body, calcium is the most abundant metal and the fifth-most abundant element. Calcium is an essential mineral that plays important roles in the skeletal, cardiovascular, endocrine, and nervous systems. This mineral contributes greatly to the formation of bones and teeth and is essential for normal movement by keeping tissues rigid, strong and flexible. Unlike teeth, bones undergo continuous remodeling, with resorption and deposition of calcium in new bone. About 99% of the total calcium in the body is in the bones, which act as calcium reservoirs. The remaining fraction participates in metabolic processes, including vascular and muscle contraction, nervous system signal transmission, blood coagulation, transmembrane transport, enzymatic activation, signal transduction, and hormonal function. Men and women have a constant level of calcium in their bodies, but during menopause calcium levels begin to decrease in women due to increased bone remodeling due to decreased estrogen production. Rich natural sources of calcium include milk, yogurt and cheese. Nondairy sources include canned salmon and sardines with bones, as well as broccoli, kale, and Chinese cabbage (bok choy). The recommended intake of calcium for adults ages 19 to 50 is 1,000 milligrams per day. This amount can be increased for teenagers, pregnant and lactating women and women over 50 years of age.
Calcium deficiency (also known as hypocalcemia) is usually caused by vitamin D or magnesium deficiency, poor diet, impaired parathyroid hormone function, impaired calcium resorption by bone, underlying conditions, or the use of certain medications. Furthermore, certain subgroups of the population are at risk of calcium deficiency, including adolescents, menopausal women, women with amenorrhea, women involved in high-intensity sports, and individuals with lactose intolerance or cow’s milk allergy. Age can also affect dietary calcium absorption. Calcium absorption is as high as 60% in infants and young children, who need adequate amounts for bone formation, but it drops to about 25% in adults and continues to decline with age.
Function Of Calcium Ions In The Body

Dietary calcium deficiency is thought to be widespread worldwide. According to published estimates, about half of the world’s population has inadequate access to dietary calcium. Because low serum calcium levels can affect many organs, symptoms can vary widely. Numbness around the face, tingling in the hands and feet, and neuropathic irritation with muscle spasms are usually the most pronounced symptoms. In severe cases, individuals may develop renal calcification or injury, brain calcification, neurologic symptoms (eg, depression and bipolar disorder), cataracts, cancer, congestive heart failure, seizures, and even coma. Insufficient calcium can cause bone weakness and osteoporosis, a condition that leads to brittle bones and an increased risk of falls. Calcium deficiency can cause other bone problems such as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Vitamin D levels are closely related to calcium to prevent rickets and osteomalacia, meaning that the lower the vitamin D level, the more calcium is needed. Inadequate calcium intake is also associated with other health outcomes such as pregnancy complications, tooth decay, dermatitis, brittle nails, as well as fractures and osteopenia in older adults. Low calcium levels have also been linked to severe premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
The Calcium–cancer Signalling Nexus
Some people need calcium supplements to meet their calcium requirements. However, the use of calcium supplements may cause gastrointestinal side effects in individuals, including constipation, gas, bloating, or a combination of these symptoms. Also, some food compounds can form specific salts with calcium ions in the intestine and reduce its solubility and absorption. Calcium supplements may also interact with various prescription medications, including blood pressure medications, synthetic thyroid hormones, and antibiotics, resulting in reduced intestinal calcium absorption and bioavailability. Additionally, some calcium supplements need to be taken with meals because they require stomach acid for bioavailability and absorption. To solve these problems, liposomal delivery systems have been developed. Liposomal calcium does not cause any side effects because it prevents the interaction of calcium with the intestinal mucosa. In addition, liposomes can protect calcium ions from interacting with food compounds and prevent them from becoming digestible calcium salts. Most importantly, liposomes have a different way of absorption than other drugs. This prevents liposomal calcium from interacting with other drugs. Also, liposomal calcium can be absorbed equally well with or without food so it is suitable for people with low stomach acid. Therefore, liposomes can increase calcium bioavailability without side effects. Nanoliposomes are smaller in size than liposomes and may be more effective in regulating calcium release and absorption. These nanocarrier systems can provide high stability, cell uptake, bioavailability and sustained release. Consequently, nanoliposomal calcium supplements are the best calcium supplements.
SUPREME PHARMATECH CO., LTD. SUPREME PHARMATECH CO., LTD. 399/90-95 Moo 13 Kingkaew Rd. Soi 25/1, T. Rachateva, A. Bangplee, Samutprakan 10540, Thailand E-mail: [email protected] ID Line: Hotline: 0888 700-007 Tel. +66-2-1307888 Fax +66-2-1307889Calcium voltage-gated calcium channels are used in many nerves, which are slightly slower than voltage-gated potassium channels. It is most notably used to treat cardiac action
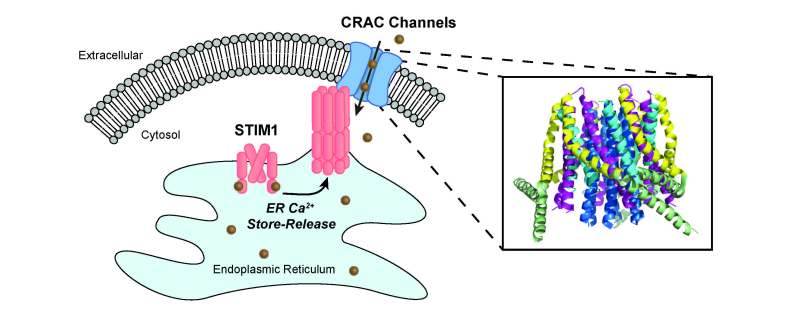
) contribute to the physiology and biochemistry of living cells. They play an important role in signal transduction pathways,
Where they act as second messengers, in the release of neurotransmitters from neurons, in the contraction and relaxation of all muscle cells. Many zymes require calcium ions as cofactors, including several coagulation factors. Extracellular calcium stimulation is important for proper bone formation as well as maintaining putative differentiation across cell membranes.
Pdf) Regulated Natural Solution Containing Calcium Ions
, under controlled conditions is released from the blood stream. Calcium is transported through the bloodstream as dissolved ions or bound to proteins such as serum albumin. Parathyroid hormone secreted by the parathyroid gland regulates the resorption of Ca.
From the bone, reabsorption in the kidney returns to the circulation and vitamin D3 increases in calcitriol activation. Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D
, promotes calcium absorption from intestines and bones. Calcitonin, secreted from the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland, also affects calcium levels by opposing parathyroid hormone; However, its physiological significance in humans is questionable.

Characteristic concentrations of calcium in model organisms are: e. coli 3mM (bound), 100nM (free), 2mM (bound) in budding yeast, 10-100nM (free) in mammalian cells and 2mM in blood plasma.
Macromolecular Recognition Directs Calcium Ions To Coccolith Mineralization Sites
In 2020, calcium was the 204th most prescribed drug in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.
The US Institute of Medicine (IOM) established Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for calcium in 1997 and updated those values in 2011.
Look at the table. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) uses the term Population Reference Intakes (PRIs) instead of RDAs and sets slightly different numbers: ages 4–10 800 mg, ages 11–17 1150 mg, ages 18–24 1000 mg, and > 5 years 950 mg.
Because of concerns about long-term adverse side effects such as calcification of arteries and kidney stones, both the IOM and EFSA set Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (ULs) for a combination of dietary and supplemental calcium. From the IOM, individuals ages 9-18 should not exceed 3,000 mg/day; not more than 2,500 mg/day for ages 19–50; For those 51 years of age and older, not more than 2,000 mg/day.
Binding Energy And Free Energy Of Calcium Ion To Calmodulin Ef Hands With The Drude Polarizable Force Field
EFSA set the UL for adults at 2,500 mg/day but decided that data for children and adolescents were insufficient to set a UL.
Serving amounts are expressed as Daily Value (%DV) for US food and dietary supplement labeling purposes. 1000 mg was 100% of the daily value for calcium labeling purposes, but as of May 27, 2016, this was revised to 1300 mg to bring it into agreement with the RDA.
Although, as a general rule, dietary supplement labeling and marketing are not permitted to make disease prevention or treatment claims, the FDA has reviewed the science for certain foods and dietary supplements, concluded that there is significant scientific agreement, and has issued specifically approved health claims. . An initial ruling allowing a health claim for calcium dietary supplements and osteoporosis was later amended to include calcium and vitamin D supplements, effective January 1, 2010. Examples of permitted words are shown below To qualify for a calcium health claim, a dietary supplement must contain at least 20% of the Reference Dietary Intake, meaning at least 260 mg/serving of calcium.

In 2005 the FDA approved a qualified health claim for calcium and high blood pressure, with the proposed wording “Some scientific evidence suggests that calcium supplements may reduce the risk of high blood pressure. However, the FDA has determined that the evidence is inconsistent and inconclusive.” Evidence for pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia was considered inconclusive.
Calcium In Biology
The same year the FDA approved a QHC for calcium and colon cancer, with the proposed wording “Some evidence suggests that calcium supplements may reduce the risk of colon/rectal cancer, however, the FDA has determined that this evidence is limited and not conclusive.” Evidence for breast cancer and prostate cancer was considered inconclusive.
QHC’s proposals for calcium as protective against kidney stones were rejected.
EFSA rejected a claim that a cause and effect relationship exists between dietary intake of calcium and potassium and maintaining normal acid-base balance.
EFSA
Question Video: Describing The Series Of Events At A Neuromuscular Junction
The function of calcium, negative ions in the body, calcium ions in the body, calcium ions in blood clotting, what are the function of calcium, function of calcium carbonate, ions of calcium, calcium ions in muscle contraction, function of calcium in heart, ions in the body, function of calcium, function of calcium ions